Laser cutting is the earliest and most commonly used technology in the field of laser processing, accounting for over 70% of the entire field. It is widely used in industries such as machinery, automobiles, aerospace, light textiles, food, and medical treatment.
Traditional laser cutting was mainly limited to planar cutting. With the development of laser cutting technology, processing of free-form three-dimensional workpieces has gradually become possible.
Since the world’s first five-axis CO2 laser cutting machine was developed by Prima in 1979, 3D laser cutting machines have been favored for their strong flexibility, high accuracy, minimal tooling equipment requirements, and short production preparation time.
At present, they are widely used for processing 3D workpieces in industries such as automobiles, mechanical manufacturing, and aerospace.

1. Types of 3D Laser Cutting Machines
To guarantee processing quality and efficiently utilize laser beam energy in 3D laser cutting, the cutting head must move along a predetermined spatial trajectory while its laser beam axis remains perpendicular to the surface of the workpiece being cut.
Therefore, 3D laser cutting machines typically require at least 5 axes, including three linear motion axes (X, Y, Z) and two rotary axes (two of A/B/C axes). Currently, there are two basic structures of 3D laser cutting machines, gantry type and robotic style, available in the commercial market.
The former usually has a bed or worktable that provides linear motion along the X, Y, and Z axes, while the cutting head provides the remaining two rotary (or swing) motion axes.
The latter utilizes fiber transmission (or articulated arm with internal reflecting mirrors) to integrate with robots and perform 3D laser cutting.
The performance comparison of the two is shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Performance comparison of Gantry and Robotic Cutting Machines.
| Performance | Gantry Style | Robotic Style |
| Working space | Large | Small |
| Processing speed | High | Small |
| Processing accuracy | Low | Low |
| Ability to approach processing area | Poor | Good |
| Floor space | Large | Small |
High-power laser is a critical component of laser cutting equipment. According to the type of laser used, 3D laser cutting machines are usually divided into three categories: fiber laser cutting machines, CO2 laser cutting machines, and YAG laser cutting machines.
The main performance comparison of the three types of laser cutting machines is shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Performance comparison of fiber, CO2, and YAG laser cutting machines.
| Performance | Fiber Laser Cutting Machine | CO2 Laser Cutting Machine | YAG Laser Cutting Machine |
| Processing material types | Metal | Metal, Non-Metal | Metal |
| Cutting speed | High | Relatively high | Low |
| Cutting accuracy | High | High | Relatively high |
| Photoelectric conversion efficiency | Around 30% | Around 10% | Around 3% |
| Equipment cost | Medium | High | Low |
| Harm to human body | High | Low | Medium |
| Market positioning | High precision processing of thin plates with a thickness of ≤12 mm | Processing of thin plates with a thickness of ≤8mm of high reflection materials. | Processing of metals and multiple non-metallic sheets with thicknesses of 6-25mm. |
Currently, in the commercial market, fiber laser cutting machines and CO2 laser cutting machines are the main types of 3D laser cutting machines.
2. Research Status at Home and Abroad
2.1 Three-dimensional fiber laser cutting machine
Compared with CO2 laser cutting and YAG laser cutting, fiber laser cutting has certain advantages in cutting efficiency, photoelectric energy conversion efficiency, optical path structure, maintenance cost, cutting accuracy, etc.
In recent years, the development of fiber laser cutting machines has been rapid, gradually replacing traditional CO2 laser cutting machines and becoming the new market mainstream.
Currently, well-known foreign manufacturers producing three-dimensional fiber laser cutting machines include Germany’s Trumpf, Italy’s Prima Power, America’s PREISER, as well as Japan’s Komatsu, NTC, Koike, Mitsubishi, AMADA, and MAZAK.
Among them, Trumpf’s TruLaser Cell 3000, TruLaser Cell 5030, TruLaser Cel 8030, Prima Power’s Rapido, Laserdyne 75G, Komatsu’s TLH-N series, and AMADA’s LCG3015AJ II and other products of three-dimensional fiber laser cutting machines have high visibility.
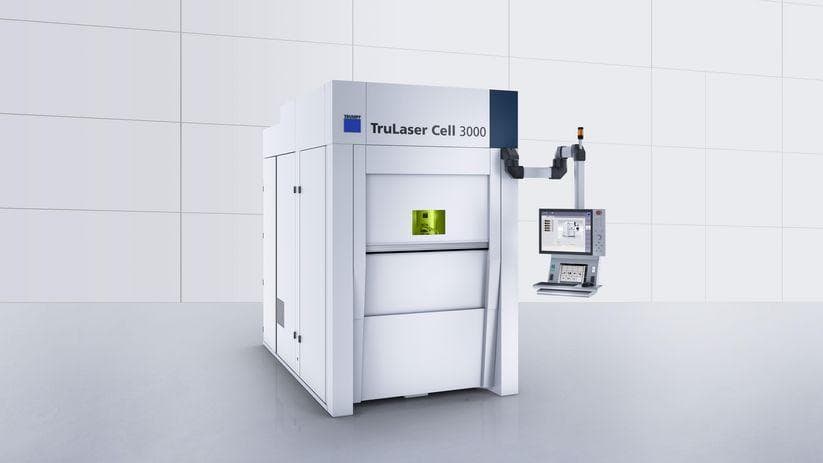
The TruLaser Cell 3000 five-axis laser processing machine tool adopts a modular structure and can use a variety of lasers. It can implement processing such as welding, cutting, and laser cladding by replacing the laser processing head. It is also easy to achieve machine tool automation and can meet the needs of mass production. The positioning accuracy is relatively high, with XNZ axis positioning accuracy of ± 0.015mm and A, C axis positioning accuracy of 0.02°.
The TruLaser Cell 8030 3D laser cutting machine is suitable for fast cutting of large-scale thermoformed vehicle side panels. Its X/Y/Z axis movement range is 3000mm/1300mm/600mm, and the axis acceleration is 4g. It also adopts an optimized rotary processing table, which greatly reduces non-production time and improves efficiency and productivity, as shown in Figure 1.

The Rapido 3D 5-axis laser cutting machine uses a 2.0-4.0kW fiber laser, which provides flexible processing for various cutting and welding applications. The machine features a collision prevention system, as well as a direct drive that eliminates recoil and wear.
The Laserdyne 795 multi-axis laser processing machine uses high-precision machining surfaces and large-diameter, high-rigidity drive screws, providing high mechanical accuracy and making it suitable for high-speed cutting applications. It is also compatible with different types of laser sources such as fiber, CO2, and YAG, as shown in Image 2.

The TLH-N series ultra-high-speed 3D 5-axis control laser cutting machine features high rigidity, high speed (X/Y/Z axis rapid traverse speed of 100m/min, A/C axis rapid traverse speed of 540°/s), good operability, and single-side open design with high approachability.
The LCG3015AJⅡ high-efficiency fiber laser processing machine has a rapid traverse speed of up to 170m/min and a machining feed rate of 120m/min. It boasts high production efficiency, good scalability, and a new digital improvement solution for sheet metal processing, from process improvement to factory reform, as shown in Image 3.

China’s industrial laser industry started relatively late, and there is a significant gap in the research and development of commercial laser cutting technology compared to developed countries. With the Chinese government listed laser processing technology as a key scientific and technological research project, there has been a surge of interest in the industry, and more and more companies and research institutions have started relevant technology research.
Currently, several Chinese companies have launched 3D fiber laser cutting machine products, including Hans Laser, HG Laser, Chutian Laser, Bystronic Dne, Gweike, and LeMing Laser.
Among them, Hans’ Laser’s HyRobot C20 fiber laser cutting machine, HG Laser’s AUTOBOT car 3D 5-axis laser cutting machine, SF series 3D 5-axis laser cutting machine, Dne Laser’s FC-CBD large enclosed auto exchange table fiber laser cutting machine, Focus Laser’s FK3015S car 3D 5-axis laser cutting machine, Stark’s STK-S-3015 3D 5-axis laser cutting machine, and LeiMing Laser’s LMR 3D multi-axis intelligent laser cutting equipment are well-known products.
At present, the major technical indicators of domestic 3D fiber laser cutting machine products are not much different from those of foreign mainstream products, as shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Major technical indicators of 3D fiber laser cutting machines.
| Name | Technical Parameters | |
| Linear Axes (X/Y/Z Axes) | Positioning speed /mm/min | 50-120 |
| Positioning acceleration /m·s-2 | 0.8-1.0 | |
| Positioning accuracy /mm | ±0.05-0.03 | |
| Repeated positioning accuracy /mm | ±0.05-0.01 | |
| Rotary Axes (C/B/A Axes) | Positioning speed / °·s) | 540-720 |
| Positioning acceleration / (°·s-2) | 3600-6000 | |
| Positioning accuracy /° | 0.02-0.015 | |
| Repeated positioning accuracy /° | 0.01-0.005 |
2.2 Three-Dimensional CO2 Laser Cutting Machine
CO2 laser cutting machines are currently widely used for processing stainless steel with a thickness not exceeding 12mm and non-metallic materials with a thickness not exceeding 25mm. They have been widely used in the cutting and processing of automotive interior and exterior parts and non-metallic parts in other industries.
Currently, the main foreign manufacturers of CO2 laser cutting machines include Germany’s Trumpf, Italy’s Prima Power, and Japan’s Komatsu and NTC, among others. Among them, the Tru Laser Cell 7040 three-dimensional CO2 laser cutting machine from Trumpf, the Optimo 3D 5-axis laser cutting machine from Prima Power, the TLM series 3D 5-axis control laser cutting machine from Komatsu, and the TLM610 3D 5-axis laser cutting machine with a dual exchange work table from NTC are well-known products.
The TruLaser Cell 7040 three-dimensional CO2 laser cutting machine has an XY/Z axis travel of 4000mm × 2000mm × 1000mm, B/C axis travel of ±135° and n × 360°, and a maximum axis acceleration of 4g. It has multiple work areas that can be selected conveniently according to needs, and various lasers can be used. It can perform a variety of processing techniques such as welding, cutting, and laser cladding by replacing the laser processing head, as shown in Image 4.

The Optimo 3D 5-axis laser cutting machine is also suitable for cutting and welding large workpieces, with an XNZ axis travel of 4500mm × 2500mm × 1020mm and B/A axis travel of ±135° and 360°. It uses a 2.5-4kW fast axial flow and flat CO2 laser. As shown in Image 5.

The TLM610 3D 5-axis laser cutting machine adopts a gantry-type bed, a movable worktable, a single-point cutting head, and a rocker control box with patented technology, a special cutting nozzle structure, TDLC-04R high-performance CNC system, and provides offline programming.
Currently, domestic CO2 laser cutting is mainly used in 2D cutting machine products, such as the MS-1380 laser cutting machine developed by Mingsheng Laser Technology Co., Ltd., and the ZT-CC1610 laser cutting machine developed by Zongtong Laser Technology Co., Ltd. There are currently no commercial 3D CO2 laser cutting machine products available.
3. Development Trends
(1) High-power
Increasing the power of the laser can improve processing capabilities and efficiency while reducing processing costs. With the decrease in the cost of lasers, the power of mainstream products in 3D cutting machines has increased from 2kW and 3kW several years ago to 4kW and 6kW.
Nowadays, even megawatt-level products have emerged, and it is believed that megawatt-level products will become the market mainstream in the next few years.
(2) High speed and high precision
Improving positioning speed and accuracy helps improve machining efficiency and meet the performance requirements of engineering machinery and other high-value-added products, thereby enhancing product competitiveness.
Currently, the positioning speed of mainstream cutting machine products is 100 m/min, while the highest positioning speed of high-speed cutting machines can reach 280 m/min.
(3) Intelligence
Automation and intelligence in operation are requirements of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing. More and more enterprises pay attention to the intelligence of machine tools, such as open systems, automatic discharge, self-diagnosis of faults, intelligent management of process data, remote control, etc.
(4) Diversification of functions
Expanding the machining range of machine tools can increase the flexibility and adaptability of machine tools, thereby enhancing product competitiveness. Many advanced 3D cutting machine products abroad have a wide range of processes.
For example, Trumpf’s TruLaser Cel3000 and TruLaser CⅡ7040 3D laser cutting machines have 3D cutting and welding metal deposition functions. Prima Power’s Rapido 3D 5-axis laser cutting machine can use multiple lasers to meet the needs of various welding and cutting processes.
4. Conclusion
Against the backdrop of the transformation from traditional processing to high-end manufacturing in China’s industrial sector, the laser cutting industry will continue to maintain a trend of high-speed development.
In the future, 3D laser cutting equipment will develop towards high power, high speed and high precision, intelligence, and diversification of functions.
Currently, compared with developed countries such as Germany, Japan, and Italy, there is still a large gap between China in terms of 3D laser cutting machine products, as well as core components such as laser cutting heads and high-power lasers, and key technical fields such as laser cutting machine research and development and high-performance CNC system research and development.
Therefore, scientific and technological personnel should continue to conduct in-depth research.