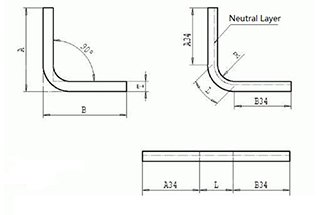
Bending Accuracy
Angle error and straightness error
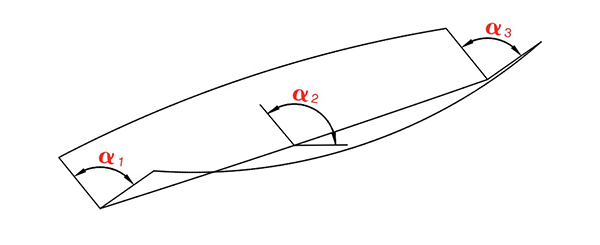
Question: is there angle error and straightness error in the “ideal bending state”?
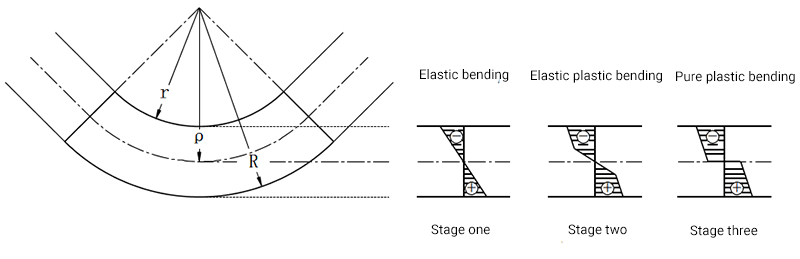
Stress and strain analysis of sheet metal bending process
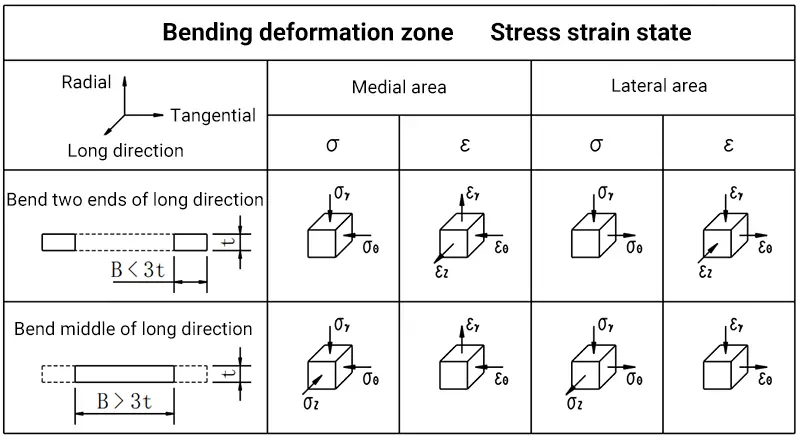
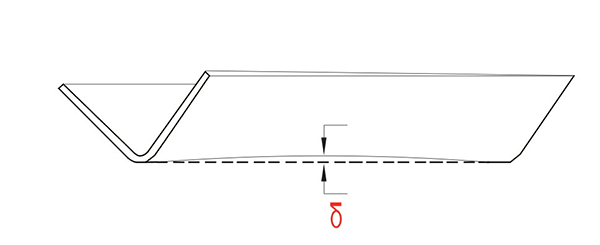
Straightness error analysis
After sheet metal bending, the edge of the bent workpiece will exhibit natural deflection, which is typically measured by its maximum deflection (δ).
According to stress analysis, the stress (σZ) in the deformation zone is tensile on the outside and compressive on the inside. These opposing tensile and compressive stresses create a bending moment, which is required to keep the workpiece straight during bending. However, at the end of the bending process, this moment disappears, causing the workpiece to deflect upward.
The longer the bend plate is, the greater the deflection (δ) will be. Similarly, the wider the bend plate is, the smaller the plate width, the greater the deflection (δ) will be.
However, reducing the bending angle from 150° to 90° will reduce the deflection (δ).
In addition, as the plate thickness increases, the deflection (δ) will increase proportionally.
Applying pressure to the edge of the bending sheet, such as through correction bending or three-point bending, can improve the straightness of the workpiece.
Factors Affecting Bending Accuracy
The main factors that influence bending accuracy in a press brake machine are the stiffness of the press brake, the bending mode, and the bending force.
1. Press brake stiffness
How to determine the stiffness index of press brake machine in design?
Deflection deformation of press brake machine
2. Bending mode
1)Air bending
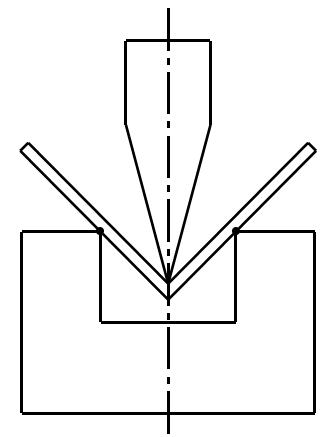
2)Three point bending
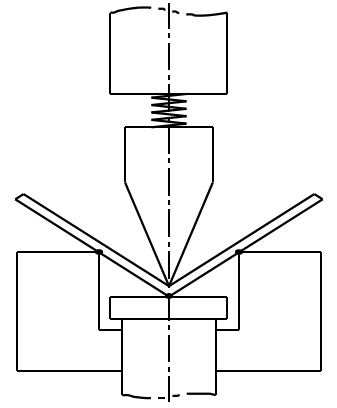
3)Coining
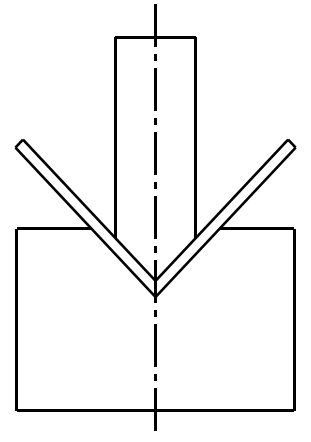
3. Bending force
How does bending force change during bending?
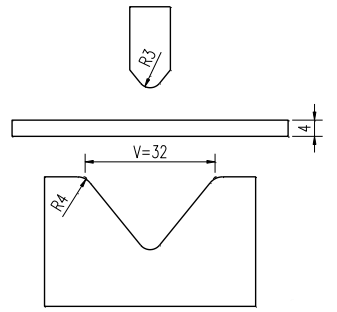
1)Free bending of acute punch
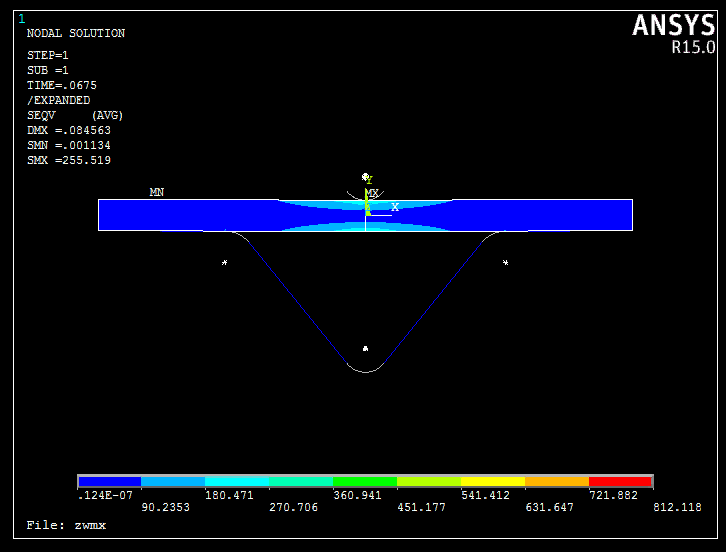
As illustrated in the accompanying figure, in the free bending mode, the sheet material is made of Q235 steel, which is considered to have ideal elastic-plastic behavior with linear hardening. The yield strength of this material is σS = 250 MPa, and its hardening modulus (also known as the tangent modulus) is 1050 MPa.
The results of ANSYS analysis are as follows
Bending force curve:
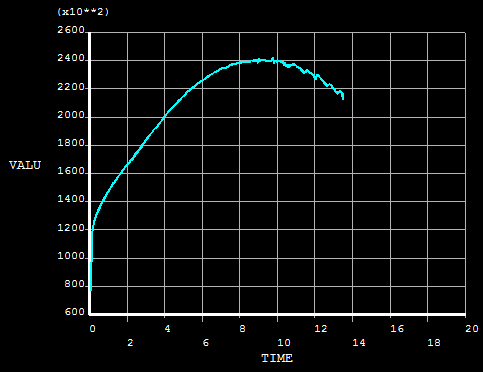
The results of the analytical method are as follows
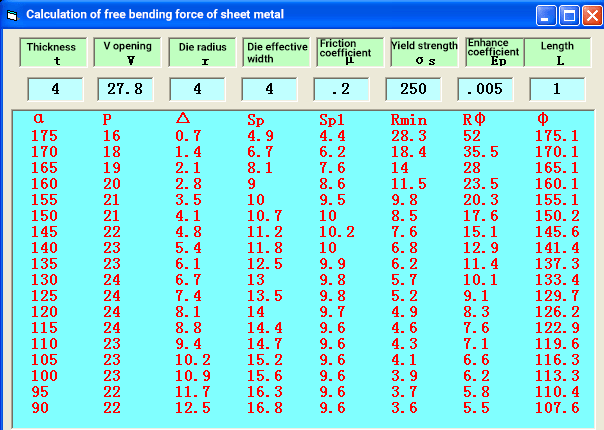
2)Wide knife bending
As depicted in the accompanying figure, the upper die is designed with a wide R180 arc, and the sheet material is set as X80. This material has ideal elastic-plastic behavior with linear hardening, and its yield strength is σs = 552 MPa. The hardening modulus (also known as the tangent modulus) of this material is 840 MPa.
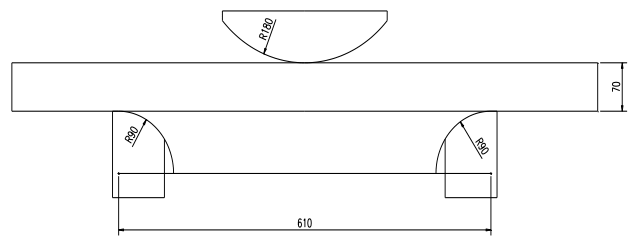
The results of ANSYS analysis are as follows
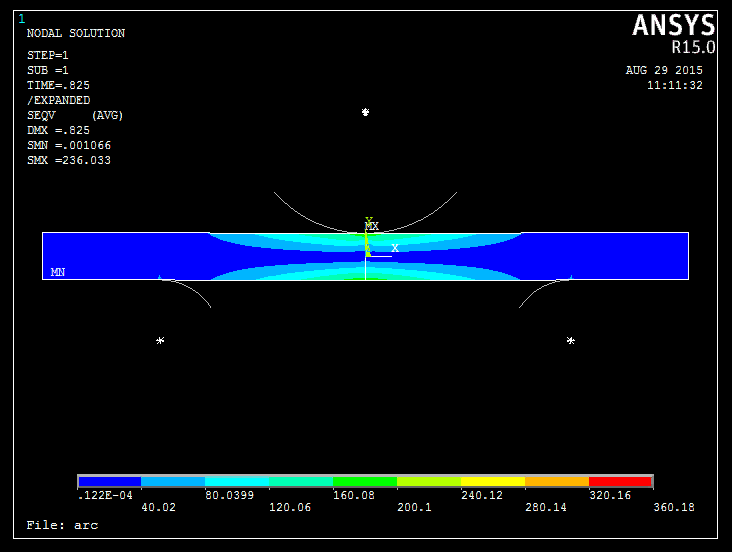
Bending force curve:
There other factors affecting bending accuracy, among which are uneven plate thickness, plate hardness, workbench and ram deformation during bending, die opening selection, depth of upper die into the lower die, die wear, and workbench convexity. These factors can cause errors in the bending angle and straightness of the workpiece after bending.
The die opening and the depth of the upper die into the lower die are controlled by manual programming.
4. Influence of material quality on accuracy
The nominal bend is a free bend of low carbon steel plate with tensile strength σb = 450 N/mm², which bends the sheet into a 90° angle on the V-shaped die with an opening distance V = 8 × S.
When nominal bending is performed with plates of uneven thickness, angle errors may occur.
When the plate’s hardness is not uniform, the workpiece’s springback during bending is not equal.
Therefore, the quality of materials has a significant impact on processing quality.
5. Worktable convex compensation
Under the action of load, the workbench and ram will undergo elastic deformation.
The depth of the upper die into the lower die is uneven along the entire length, which can affect the bending angle and straightness of the workpiece.
To solve this problem, the machine adopts the NC convex of the worktable to compensate for its deformation, maintain the depth of the upper die into the lower die essentially uniform along the entire length, and improve the accuracy of the bending angle and straightness of the workpiece.
6. Eccentric load
Eccentric load refers to load operation on the left or right side of the ram. The machine has a strong ability to resist eccentric load.
Under the action of eccentric load force, tilt will be generated between the workbench and the ram.
The grating detection mechanism at both ends of the ram will detect the deviation and provide feedback to the computer. The computer controls the proportional servo valve to adjust the amount of oil entering the oil cylinder, to keep the position of the two pistons synchronized and maintain a small parallelism error between the workbench and the ram.
When processing special parts, one should consider the above eccentric load. In general, it is necessary to avoid operating under eccentric load.
7. Correction of bending angle error
After the bending part has been formed, and the angle is about α°, the measured angle error value △α° can be corrected by adjusting the position Y of the bottom dead center. The correction value △Y can be approximately calculated according to the following formula: △Y = K × V × △α
Where:
- △ Y – correction value of bottom dead center (mm)
- V – selected die opening (mm)
- △ α – Angle error value (degrees)
- K – Correction factor (degree /mm)
When α ≈ 90°, K ≈ 0.0055; for folded 8-12-sided steel rod, when α ≈ 135°-157.5°, K ≈ 0.004.
If the inspected part angle is greater than the drawing requirements, adjust the bottom dead center position downward according to the correction value △Y; otherwise, adjust upward.
Example 1:
The angles at both ends are equal to the middle angle.
For folding a dodecagon with α= 150°, select the opening V = 200mm, and measure the angle after bending, α= 151.5°. Using the above method, △α is calculated to be 1.5°, and K is 0.004.
△Y = K × V × △α = 0.004 × 200 × 1.5 = 1.2mm.
Input the bottom dead center position Y + △Y into the computer.
Example 2:
The angles at both ends are not equal to the middle angle.
For a workpiece bent at α=90° with opening V = 60mm, the actual measured angles at both ends are α=90°, and the middle angle is α=91° (the convex amount is not enough).
Using the above method: △α = 1°; K=0.0055
△Y = K × V × △α = 0.0055 × 60 × 1 = 0.33mm.
Add △Y to the original convex value and input it into the computer.
If the middle angle is smaller than the angles at both ends (the convex amount is too large), reduce the convex value by △Y from the original basis and input it into the computer.
Example 3:
The angles at the lower ends of the column are not equal. With opening width V = 60mm, a workpiece is bent at α= 90°.
The actual measured angle at the left end is α=90°, and the angle at the right end is α=91° (lower left and higher right).
Using the above method: △α=1, K=0.0055
△Y=K × V × △α=0.0055 × 60 × 1=0.33mm
Input the Y + △Y value at the right end’s zero point upward to change its reference position.
8. Angle Accuracy
Angle accuracy is arguably the most complex and challenging parameter to control in bending operations. There are two common bending methods: bottoming bending and air bending. Various applications of bottoming bending are illustrated as follows.

Bottoming bending is controlled by adjusting the downward force applied during the bending process to shape the metal. Its advantages include high angle accuracy, reaching up to ±15 minutes, with consistent bending angles.
However, the drawbacks are significant: it requires up to five to eight times more force than air bending and has lower flexibility. Different angles or shapes require different tooling.
Air bending, also known as free bending, is more commonly used. It is controlled by regulating the Y-axis descent, meaning the depth to which the upper die penetrates the lower die, thereby controlling the bend angle.
The advantages of air bending include lower required force and high flexibility, as one set of tooling can bend workpieces at various angles. The downside is lower precision in the angle of the bent workpiece and poorer consistency.
Why is the angle accuracy of air-bent workpieces lower? For example, when bending sheet metal with a V10 lower die, a 0.05mm difference in the distance the upper die presses down can result in an angle deviation of 1°, as shown in the table below.
Table: Changes in the depth of descent corresponding to a 1° angle variation for different lower die openings and bending angles
| Bending angle/Lower mold opening | 30° | 45° | 60° | 75° | 90° | 105° | 120° | 135° | 150° | 165° |
| 4 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 6 | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| 8 | 0.36 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| 9 | 0.41 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| 10 | 0.45 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| 12 | 0.54 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| 14 | 0.61 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| 15 | 0.66 | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.06 |
| 16 | 0.71 | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| 18 | 0.81 | 0.32 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| 20 | 0.90 | 0.36 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.08 |
| 22 | 1.00 | 0.40 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| 24 | 1.09 | 0.44 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
Currently, the Y-axis precision of bending machines can generally reach 0.01mm, so the angle deviation should not be too severe. But can the thickness of the metal sheet be guaranteed to be perfectly consistent?
If a 1.5mm thick sheet varies by 10% in thickness, that’s a 0.15mm difference, equivalent to a 0.15mm difference in the distance between the upper and lower dies, resulting in an angle deviation of approximately 3°.
Similarly, a 10% variation in the strain hardening characteristics of the metal sheet can cause about a 1.5° change in the bending angle. The impact of metal sheet thickness and strain hardening on the bending angle during air bending is depicted in Figure 6.

This is where bending machines differ from metal cutting machine tools. With metal cutting machines, regardless of the size differences between raw workpieces, the final accuracy of the machined parts can be guaranteed as long as the machine tool is precise enough.
However, this is not the case with the common practice of air bending on press brakes; it’s not a question of the machine’s inherent precision.