With the improvement of people’s living standards, there is a higher demand for the quality of the living space we occupy. For instance, in communication, we expect ultra-high definition, fast response speed, safety, reliability, and confidentiality, which put forth more demanding requirements for communication infrastructure.
To address this need, scientists have overcome the barriers of 4G communication and developed 5G communication, which has been applied to civilians, and technology has driven the progress of 5G.
National confidential communication is particularly significant regarding security. Countries have launched research and development programs, as well as investments, in quantum confidential communication, which positions them at the forefront of the world and takes a crucial step towards national security communication. This has been made possible thanks to the scientific advances in aerospace, satellite, and communication fields.
These technological advancements are not only scientific and technological breakthroughs in single fields but also a series of industrial scientific achievements. Ultra-thin metal materials, including copper foil, aluminum foil, stainless steel foil, nickel alloy foil, and titanium alloy foil, are among the most widely used materials in satellite, aerospace, communications, and 5G fields.
Ultra thin metal
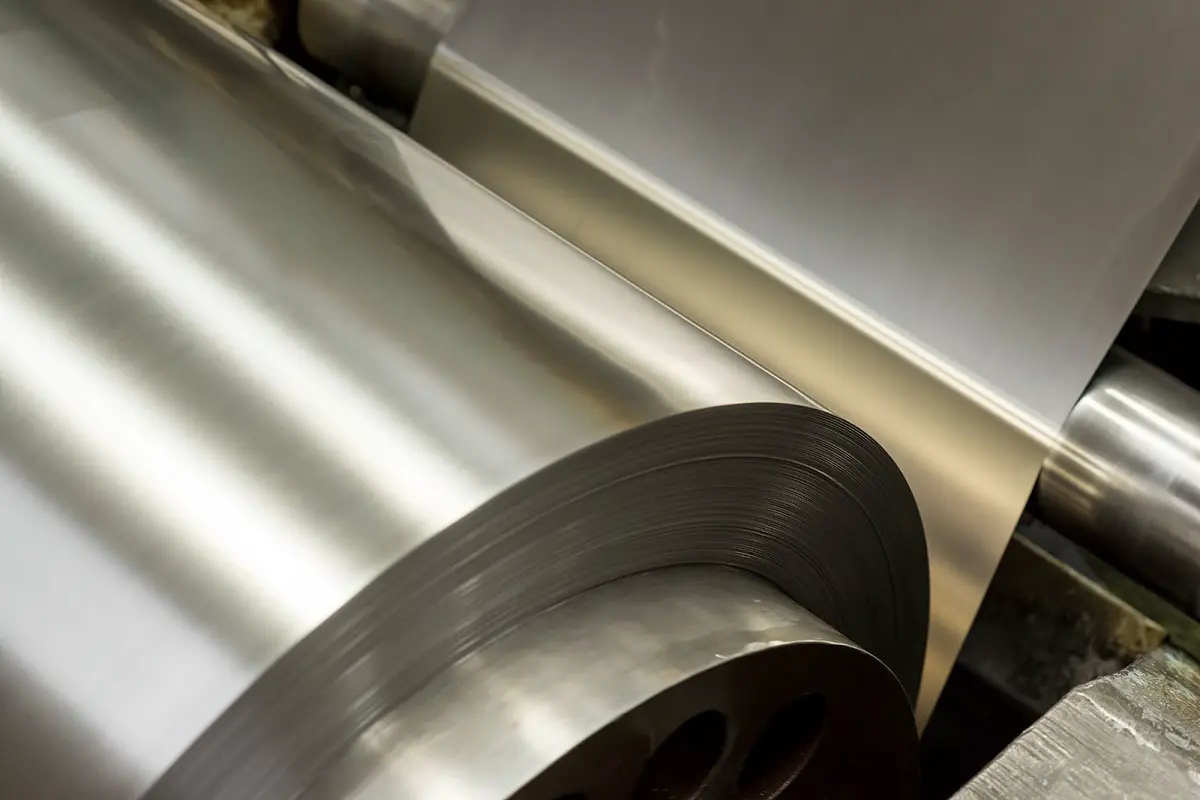

Ultra-thin metals have a wide range of applications in various fields, including aerospace, satellites, communication, 5G, and even in human blood vessels, where they play a crucial role.
In the past, the requirements for ultra-thin metal materials were relatively simple, primarily ensuring conductivity. However, as technology advances, the demand for characteristics such as lightness, conductivity, and high precision has grown, which has resulted in higher standards for ultra-thin metals. They must have no burrs, no deformation, ultra-fine linewidths, ultra-high precision, and be made from ultra-thin materials.
These high standards also require higher demands for processing tools. Copper foil, stainless steel foil, titanium alloy foil, nickel alloy foil, and other materials processing tools are used in the field of ultra-thin metal materials, such as knife die cutting or chemical etching.
However, as demand increases, especially under the high standard requirements in 5G, aerospace, satellite, and other fields, the traditional process mode shows weaknesses. For example, the cutting of knives and dies can produce deformation and burr residue, which can affect product performance.
Chemical etching processing requires screen printing, particularly for the processing of multi-specification materials. This process demands a significant amount of screen printing, which is not conducive to processing various products.
Furthermore, chemical etching has a severe environmental impact. Under the pressure of environmental protection control, many chemical etching processing plants have been evacuated, causing significant trouble for processing enterprises.
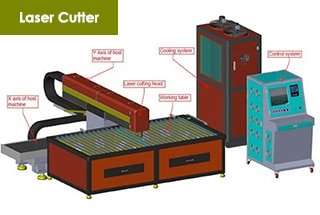
Given this situation, a new process of laser cutting ultra-thin metal foil has emerged in relevant fields, providing new ideas for the industry’s development.
In the laser cutting industry, suitable types for cutting ultra-thin metal foil materials include infrared nanosecond laser cutting, nanosecond ultraviolet laser cutting, and ultrafast laser cutting.
Laser cutting ultra-thin metal foil has the advantage of being unrestricted by graphics. It can import CAD drawings or draw graphics in software at any time, which is convenient, fast, and has a short processing cycle.
However, laser cutting of copper foil, stainless steel foil, nickel alloy foil, and other materials still encounter the problems of traditional technologies, along with new challenges.
Nanosecond infrared laser cutting machine

Low power pulse infrared laser cutting machines or MOPA infrared laser cutting machines can be utilized for cutting ultra-thin metal foil.
The advantage of using these types of laser cutting machines is their speed. However, the drawback is that they can cause material heat deformation, burrs, and carbonization.
Compared to nanosecond ultraviolet or ultrafast laser cutting machines, nanosecond infrared laser cutting machines can process thicker materials. They are generally suitable for cutting metal foil above 0.2mm.
Particularly for customers who prioritize high processing speed and low precision requirements, cutting stainless steel foil, copper foil, nickel alloy foil, etc. with a nanosecond infrared laser is suitable. The equipment has low cost and long service life, making it suitable for cutting metal foil above 0.2mm.
Nanosecond ultraviolet laser cutting machine
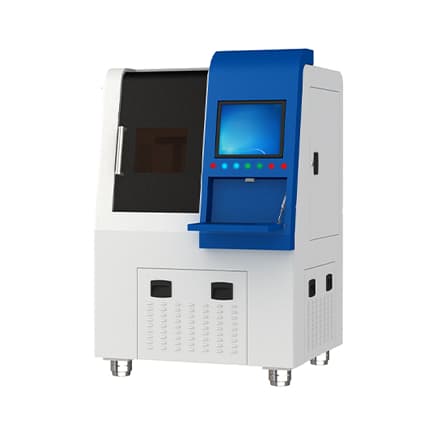

For cutting ultra-thin metal foil, it is recommended to use a nanosecond ultraviolet laser cutting machine with a power of more than 10W.
The advantage of using this type of laser cutting machine is that there is no deformation and burr in the cutting process, but the disadvantage is that carbonization may occur, especially for thicker materials.
The degree of carbonization becomes more obvious as the material thickness increases, and black edges of soot may be visible to the naked eye, which can be removed through ultrasonic cleaning.
Under high-power magnification, there may be burrs.
Compared to the nanosecond infrared laser cutting machine, the single pulse energy of the nanosecond UV laser cutting machine is smaller and the cutting speed is relatively low, making it unsuitable for cutting thick metal foil and more suitable for processing materials below 0.1mm.
The nanosecond UV laser cutting machine is also suitable for multi-layer material processing, such as multi-layer copper foil UV laser cutting or cutting aluminum foil with a layer of PET film, making it a suitable choice for processing with a nanosecond UV laser cutting machine.
Ultrafast laser cutting machine

Ultrafast laser cutting machines are used to cut ultra-thin metal materials using ultrashort pulse laser cutting equipment such as picosecond infrared laser cutting machines, ultraviolet laser cutting machines, and femtosecond infrared laser cutting machines.
Among these, femtosecond infrared laser cutting machines are preferred for cutting materials such as stainless steel foil, copper foil, nickel alloy foil, and titanium alloy foil. These machines have significant advantages over nanosecond laser cutting equipment, as they produce no burrs, deformation, low thermal impact, and low carbonization levels (as low as 2 microns).
Femtosecond laser cutting machines use ultra-fast femtosecond pulse laser technology and can be equipped with 1030nm, 515nm or 315nm band lasers based on the material characteristics. In China, the equipment is mainly equipped with 1030nm and 515nm femtosecond lasers and is used for cutting, etching, punching, micro/nano scribing, and other applications.
Femtosecond laser cutting machines have minimal thermal effects on the material and interact with the material for a very short duration, which is lower than the Brownian motion time between material molecules. Thus, the thermal effect on the material is minimal and does not cause any deformation of ultra-thin metal materials, burrs, particle dust, or other issues.
Wrap it up
The ultra-fast femtosecond laser cutting machine is highly advantageous for micro precision machining of ultra-thin metal foil, owing to its high precision.
On the other hand, the UV laser cutting machine is better suited for precision processing, multi-layer material processing, and material processing with thicknesses less than 0.1mm.
Meanwhile, the infrared laser cutting machine is best for processing thick and ultra-thin materials above 0.2mm with low accuracy requirements.
In addition to cutting ultra-thin metal materials, the femtosecond laser cutting machine is highly flexible and can be used for etching multi-layer materials, processing micro nano guide structures on material surfaces such as silicon scribing, stainless steel grating, ceramic scribing, thin film material scribing, glass scribing, and more.