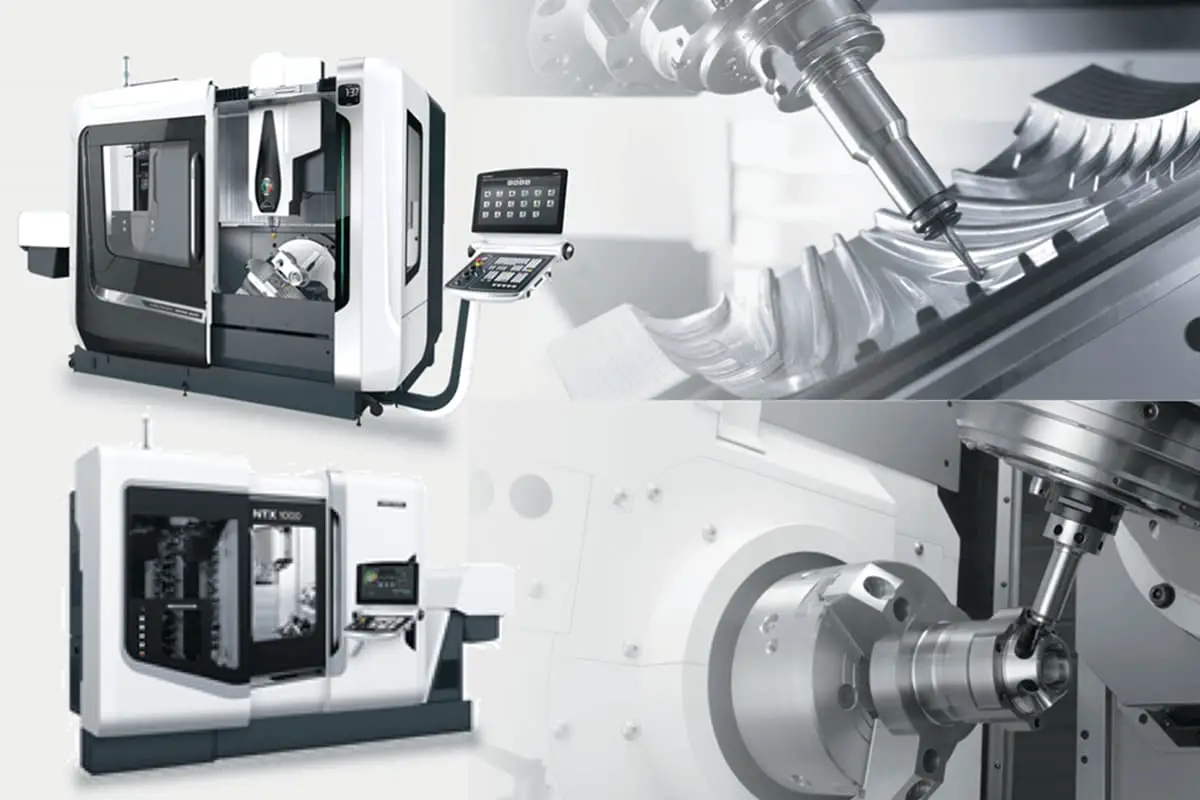
In this article, we’ll explore the world of Japanese machine tool manufacturers, the unsung heroes behind many industrial innovations. Discover their cutting-edge technologies, time-tested expertise, and significant contributions to various sectors. Get ready to gain a newfound appreciation for these engineering marvels and the visionary companies that create them.


Okuma Corporation, based in Japan, stands as one of the largest and most reputable CNC machine tool manufacturers globally. With over a century of experience, Okuma has built a legacy of innovation and quality in the machine tool industry. The company produces a wide range of high-quality machine tools, including:
Okuma’s products are celebrated for several key attributes:
Approximately 50% of Okuma’s machine tools are exported, reflecting the global demand and recognition of their quality. Users worldwide appreciate the reliability and advanced features of Okuma’s products.
Since the 1960s, Okuma has been at the forefront of CNC control technology with its proprietary OSP (Okuma Sampling Path) control system. The OSP system is known for its:
Several of Okuma’s advanced machines support the OSP control system, including:
Okuma has a significant presence in China, with annual sales of CNC machines, grinding machines, and precision machining systems nearing 400 million RMB. This makes Okuma one of the most influential foreign machine tool suppliers in the Chinese market.
Founded in 1884, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) stands as Japan’s largest heavy industry manufacturer. With a portfolio encompassing over 700 types of products, MHI boasts a rich history and a reputation for exceptional product quality. The company is ranked among the top 500 globally and operates 11 business headquarters, divisions, and six research institutes across Japan. MHI’s technology development system is centralized at its technology headquarters, focusing on cutting-edge research for future advancements and technology development closely tied to each production site.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries has a long-standing involvement in the development and production of machine tools, beginning with the MIB Machine No. 1 in 1960. A significant milestone was achieved in 1986 with the introduction of the world’s largest super milling machine, which boasts a width of 13 meters. In recent years, MHI has concentrated on the rapid development of large special-purpose machines, earning recognition as a “leading manufacturer of large machines” by consistently meeting customer needs and producing high-quality, advanced machining machines.
What distinguishes Mitsubishi Heavy Industries from other machine tool manufacturers is its unique advantage as a comprehensive machinery manufacturer. The Mitsubishi Machine Tool Division benefits from its dual role as both a manufacturer and a customer. This unique position allows MHI to collaborate closely with research institutes, leveraging information gathered from Mitsubishi Group products to develop first-class machine tools applicable across various industries.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries is renowned for its state-of-the-art gear grinding machines. Notable models include:
Additionally, MHI offers a series of gear processing machines such as the ZG400, ZG1000, and ZGA1600, catering to high-precision gear manufacturers. The company’s automatic programming system simplifies the creation of NC programs for dressing and grinding by merely inputting various parameters, ensuring high-precision machining for power generation applications.
Mori Seiki Corporation, founded in 1948, is one of Japan’s largest machine tool manufacturers. The company specializes in producing CNC lathes, machining centers, and CNC grinding machines and has the largest market share of CNC lathes and machining centers in Japan. The company is listed on the Tokyo and Osaka stock exchanges and had consolidated operating income of approximately $2 billion in 2011.
Mori Seiki’s vertical, horizontal, and gantry high-speed machining centers have a high reputation both in Japan and abroad and have won the Japanese Machine Tool New Product Award and Manufacturing Award. The company has sales companies in Shanghai and technology centers in cities including Beijing and Tianjin.
Since 1980, over 2,000 Mori Seiki lathes and machining centers have been installed in Chinese factories. The company currently has 9 technical centers in China (for marketing and after-sales service) with plans to establish a 10th center in Xi’an. In 2004, Mori Seiki’s sales of machine tools in China (excluding Taiwan) were RMB 130 million, and over 300 devices were installed.
The company plans to have more than 50 employees in China to provide the best after-sales service, with a goal of reaching 100 employees by 2008. Mori Seiki (Tianjin) Machine Tool Co., Ltd. was established in May 2012 in the Tianjin Development Zone with a total investment of $75 million and mainly produces high-end CNC machine tools. The first phase of the plant is expected to reach full capacity in 2017, with an annual turnover of $157 million.
In addition to complete machine production, the base will also supply important parts and components to Mori Seiki’s factories in Japan and the United States in the future. This development is expected to double Mori Seiki’s domestic market share. The company also holds approximately 20% of Demag, Germany’s largest machine tool maker.
JTEKT Corporation is a prominent entity in the machinery and automotive industry, owning several well-known brands such as JTEKT, KOYO, and TOYODA. The company provides technical support for a wide array of machinery, including cars, Shinkansen trains, aircraft, and robots, all of which play crucial roles in our daily lives.
JTEKT was established through the merger of Koyo Seiko and Toyota Kogyo. This strategic merger has positioned JTEKT as a global leader in the steering system industry, holding the largest market share worldwide. The company has successfully integrated various industries, including bearings, machine tools, and transmissions, to deliver top-tier systems on a global scale.
JTEKT is committed to continuous technological improvement, aiming to enhance safety, security, speed, comfort, resource conservation, and environmental benefits. One notable innovation is the introduction of an advanced gear manufacturing technology. By incorporating the turning process into the standard configuration of its Universal Wedge Plus product, JTEKT has achieved significant cost savings for its customers.
KOYO Seiko, a subsidiary of JTEKT, specializes in the production of bearings. It has established itself as a leading bearing manufacturer both in Japan and globally. In 1988, KOYO Seiko developed the first electric power steering system, marking a significant milestone in automotive technology.
TOYODA, another key brand under JTEKT, is recognized as the world’s leading machine tool manufacturer. TOYODA offers a comprehensive range of products, including industrial machine tools and automotive components, catering to diverse industrial needs.
JTEKT has a substantial presence in China, with a robust infrastructure that includes:
JTEKT (China) Investment Co., Ltd., headquartered in Changning District, Shanghai, oversees sales and business integration functions for JTEKT in China, ensuring seamless operations and strategic growth in the region.
Sodick Corporation, a prominent Japanese company, specializes in the mold industry, encompassing manufacturing firms, sales companies, and research and development entities. Over the past 30 years, the Sodick Group has consistently increased its production capacity and now operates four main factories in Fukui and Kaga, Japan; Bangkok, Thailand; and Suzhou, China.
In 2006, the Sodick Group launched a new global development strategy aimed at continuously expanding its business scale. Xiamen, China, was chosen as the city to implement this strategy due to its favorable geographic location and business environment.
Sodick Group executes various manufacturing projects in line with its philosophy, including:
With world-leading technology, Sodick offers the best production solutions to its customers, ensuring high efficiency and precision in manufacturing processes.
In 1991, Sodick Co., Ltd. established a joint venture with Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Shanghai Mould Technology Research Institute) to develop software for industrial control systems and enterprise information management systems, as well as to sell the developed products. This collaboration has significantly contributed to advancements in industrial technology.
In 1994, Sodick opened a factory in Suzhou New District, China, primarily producing EDM machines and wire-cut EDM machines. The factory features an environment suitable for precision machinery production, including a temperature-controlled production line with heating, cooling, and air conditioning. The newly built plant, completed in August 2004, has a monthly output capacity of 150 units, reflecting Sodick’s commitment to high-quality manufacturing.
On July 16, 2014, Sodick Corporation of Japan announced the development of the “OPM250L” 3D printer that uses metal materials, which it planned to start selling in October 2014. This innovative 3D printer integrates metal additive manufacturing with high-speed milling, offering unparalleled precision and efficiency. Sodick signed a licensing agreement with Panasonic for this processing technology and continues to independently develop related technologies, having filed for five patents.
Mr. Tsunezo Makino founded Makino in 1937, initially specializing in the production of Type 1 vertical milling machines. This marked the beginning of a legacy in precision engineering and innovation.
In 1958, Makino developed Japan’s first CNC milling machine, setting a new standard in automated machining. By 1966, the company had introduced Japan’s first machining center, further solidifying its position as a leader in the industry.
Makino’s commitment to innovation is exemplified by the establishment of the Makino International R&D Center. With an investment of SGD 75 million, this center aims to enhance human resources and intellectual capital, benefiting not only Makino but also contributing to Singapore’s technological landscape. The center attracts talent from various industries worldwide, serving as a hub for new ideas, technologies, and products, and generating valuable intellectual property.
Makino designs and produces a wide range of advanced machining solutions, including three-axis and multi-axis CNC machine tools, numerical control systems, servo devices, and parts. The company also develops related application software and provides comprehensive product technology and maintenance services.
To meet the rapidly growing processing demands in the Asian market, Makino established Makino Asia Pte Ltd, with its headquarters strategically located in Singapore. This location was chosen due to Singapore’s advantageous economic position and strategic location in Asia. Makino Asia oversees markets in China, India, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Singapore.
Makino Asia has evolved into a comprehensive entity that integrates manufacturing, R&D, product design, and business management. The company is renowned for its advanced processing, manufacturing, and assembly capabilities. Among its notable products are the F and E series machining centers, EDAF and EDGE series EDMs, DUO series, and the latest U3 wire cutting machines.
In 1946, Isamu Amada founded Amada Manufacturing Co., Ltd., initially specializing in sheet metal machinery and cutting products. The company’s first significant innovation came in 1955 when it developed and manufactured a band saw disk named “Contour,” which was launched in 1956.
In 1965, Amada expanded its global footprint by acquiring the Torc-Pac brand in the United States and the Promecam brand in France, subsequently marketing these products under the Amada name. This strategic move facilitated Amada’s rapid growth and established it as a world-renowned brand in the sheet metal industry, particularly in developed markets such as Japan, the United States, and Europe.
Amada has consistently held a dominant position in the international market for sheet metal machinery, boasting a 70% market share in recent years. By 2001, the company achieved sales of 190 billion yen and employed a workforce of 4,400 individuals. Amada operates 83 branches worldwide and sells its products in over 100 countries and regions.
The company offers an extensive range of sheet metal processing machinery—nearly 1,000 varieties—known for their advanced technology and superior performance. In the 1990s, Amada developed the 21st-century intelligent automatic sheet metal processing center, setting new standards for intelligent processing in the global sheet metal industry. This innovation earned the highest technological invention award in Japan.
Amada’s products are highly valued by customers worldwide due to their comprehensive and rational mechanical structure, which ensures top-quality performance. The company’s machinery is designed for efficient and safe operation, providing significant benefits and peace of mind to users. The advanced technology of simulation automation offers users a simplified and highly effective processing experience, contributing to Amada’s impressive annual sales of 200 billion yen globally.
Amada’s main products include:
These products are integral to the company’s reputation as a leader in the sheet metal processing machinery industry.
Komatsu NTC Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of Komatsu Corporation in Japan, was founded in July 1945. As a comprehensive machine tool manufacturer, Komatsu NTC provides a wide range of high-quality, precise metal processing equipment to automobile manufacturers globally. The company has established itself as a leader in the industry through continuous innovation and a commitment to excellence.
In 1983, Komatsu NTC and Toyota Motor Corporation of Japan collaborated to develop the world’s first three-dimensional, five-axis CNC laser cutting machine. This groundbreaking innovation marked a significant advancement in metal processing technology. Over the subsequent decades, the machine has undergone continuous improvement and refinement, driven by extensive user feedback and evolving industry needs. Today, it stands out with its unique technology and advanced features, setting a benchmark in the field.
Komatsu NTC’s machine group is dedicated to the heart of a car, which includes critical components such as the power unit and drive unit, encompassing engines and transmissions. This group is centered around a combination of machine tools, including automatic transfer compound machining machines and various grinding machines. These tools form the backbone of the mass production system for automotive parts, ensuring high precision and efficiency. The machines are widely used both domestically and internationally under the brand name “World Class.”
Beyond providing machining machines, Komatsu NTC contributes to the automotive industry by offering “new hardware” that integrates software solutions such as production systems. The company excels in proposing total solutions based on a deep understanding of the customer’s business foundation. This holistic approach has earned Komatsu NTC deep trust and high evaluation from customers worldwide.
Komatsu NTC’s excellence has been recognized globally. Since 1997, the company has received the “Supplier of the Year” award from General Motors Corporation (GM) for three consecutive years. This achievement is a first for a Japanese industrial machinery manufacturer. The productivity and reliability of Komatsu NTC’s combined machine tools for machining automotive parts have been highly praised, particularly in factories across North America, Central America, and South America.
Aida is a high-tech company that specializes in the research and development, production, and sales of high-speed presses, precision presses, servo presses, and stamping automation. With a history spanning 93 years, Aida is a renowned publicly traded Japanese company known for producing and selling punching machines, industrial robots, and various automatic transmission devices.
Aida’s punching machines, peripheral automation, and plastic forming technology are at the forefront of the global industry. The high-precision, one-piece gantry design of Aida’s machine tools addresses the issue of machine body expansion during loading, enabling the processing of high-precision products. The slider’s left and right dimensions have been expanded for full-length and center guidance, and the use of forced circulation oiling minimizes thermal deformation of the machine body, enhancing precision. The compact design also reduces fuselage deformation and saves space. Additionally, the touch screen interface provides safe and easy operation, further improving production efficiency.
Aida’s forging machinery products include open and closed presses, cold forging presses, high-speed presses, servo presses, large multi-station presses, and peripheral equipment. The company is ranked 23rd in the Gardner World Machine Tool Companies by value and 5th in the metal forming machine tool category.
MAZAK Yamazaki Corporation, established in 1919, is a prominent Japanese manufacturer of machine tools. The company is renowned for its high-speed, high-precision products, which include:
MAZAK Yamazaki has a significant global footprint with nine manufacturing facilities located in:
Additionally, the company has established over 80 customer support bases worldwide through its technical centers and Mazak Technical Service Centers, ensuring comprehensive support and service for its global clientele.
In China, MAZAK Yamazaki operates through two specialized entities:
Products manufactured in Japan are managed by the new company, while sales of products manufactured in China by Mazak Yamazaki are overseen by Ningxia Little Giant Machine Tool Co.
MAZAK Yamazaki’s products are integral to various industries within the machinery sector, providing essential tools for manufacturing and production processes.
MAZAK Yamazaki faces competition from several other well-known Japanese machine tool companies, including:
These companies also contribute significantly to the global machine tool industry, offering a range of products and services that complement and compete with those of MAZAK Yamazaki.