Have you ever wondered how a simple element like nitrogen can transform steel’s properties? This blog explores nitrogen’s profound impact on steel’s microstructure, mechanical strength, and more. Discover how nitrogen can enhance steel’s durability and performance, making it indispensable in various applications. Prepare to uncover the fascinating role of nitrogen in revolutionizing steel technology!

① Nitrogen, similar to carbon, can dissolve in iron to form an interstitial solid solution.
② Nitrogen enhances the size of the austenite phase zone in steel, which is a robust element for forming and maintaining stability in austenite.
Its impact is around 20 times that of nickel, and it can partially replace nickel in steel.
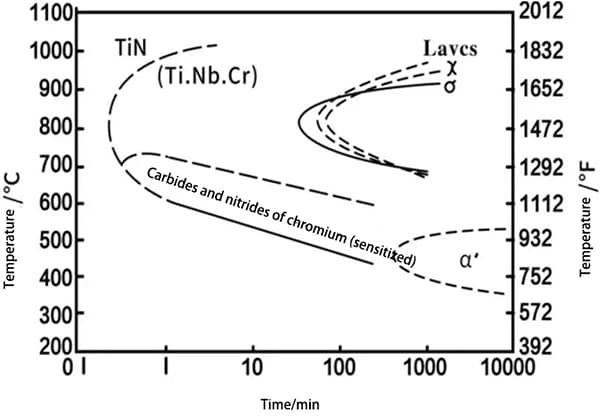
③ Nitrogen, along with elements such as chromium, aluminum, vanadium, titanium, and others that infiltrate the steel surface, can form highly stable nitrides. These nitrides serve as surface hardening and strengthening elements.
④ Nitrogen makes the structure of high chromium and high chromium nickel steel more compact and solid.
⑤ Excessive residual nitrogen content in steel can result in macrostructural porosity or holes in the structure.

① Nitrogen has a solid solution strengthening effect and enhances the hardenability of steel.
② In nitrogen-containing ferritic steel, precipitation hardening may occur as a result of the formation of ultra-microscopic nitrides during tempering, following rapid cooling or prolonged exposure to room temperature.
Nitrogen can also lead to strain aging in low-carbon steel.
As the strength and hardness of steel increase, its toughness decreases and its susceptibility to notch sensitivity increases.
The brittleness of steel caused by nitrogen is comparable to that of phosphorus and has a much greater impact than phosphorus.
Nitrogen is also a significant contributor to blue embrittlement in steel.
③ The strength and impact toughness of high chromium steel and high chromium nickel steel are enhanced without sacrificing plasticity.
④ The creep strength and high temperature rupture strength of the steel are also improved.
① The presence of nitrogen does not have a substantial impact on the corrosion resistance of stainless steel.
② If the nitrogen content exceeds 0.16% by mass, the steel’s resistance to oxidation will decline.
③ Nitrogen-containing steel has a higher rate of hardening due to cold deformation.
④ Nitrogen can decrease the tendency of grain growth in high chromium ferrite steel and enhance its welding capabilities.
① Nitrogen is commonly used as an alloying element in steel, with a content typically ranging from less than 0.3% (by mass) to a maximum of 0.6% in specific circumstances.
② It is primarily utilized in nitrided quenched and tempered steel, ordinary low-alloy steel, stainless acid-resistant steel, and heat-resistant non-spalling steel. Among these, heat-resistant non-spalling steel can be used to produce components for steam turbines.