Have you ever wondered why some materials bend while others snap? This blog post explores the fascinating world of material properties, focusing on elasticity, stiffness, strength, and hardness. By the end, you’ll understand how these properties impact everything from machine parts to everyday objects.
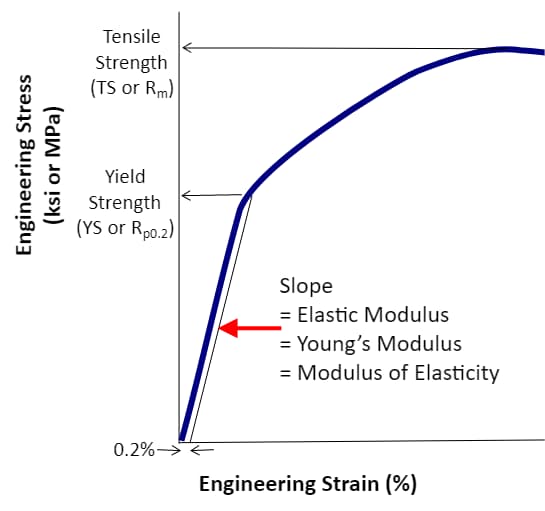
Elastic model is an important performance parameter of materials.
There are many parameters used to measure materials, among which elastic modulus, stiffness, strength, and hardness are the most common, but many people do not fully understand these parameters.
Let’s review these concepts to better understand the relationships between them.
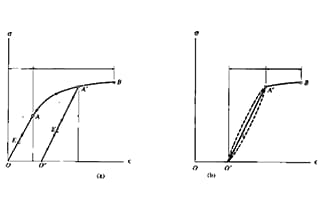
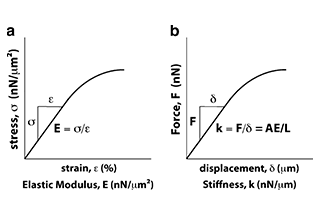
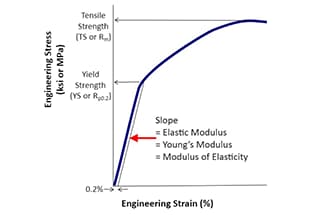
Elastic modulus represents the elasticity of materials. The greater the elastic modulus, the greater the material’s ability to resist deformation. In the elastic range, stress divided by strain becomes a positive proportional relationship, satisfying Hooke’s law, and its ratio is the elastic modulus.
Elastic modulus is an inherent property of materials and reflects the bonding strength between atoms, molecules, or ions. The chemical composition, crystal structure, and temperature of the material affect the elastic modulus. Generally, the higher the temperature of the material, the lower the elastic modulus. For example, when forging parts, it is better to heat the parts first to reduce the elastic modulus and yield strength of the material, rather than forging directly at room temperature.
The heat treatment of metal materials includes overall heat treatment (annealing, quenching, tempering, normalizing) and surface heat treatment (carburizing, nitriding, high, medium, and low-frequency quenching, anodizing of aluminum alloy, etc.).
Heat treatment can improve the yield strength and tensile strength of materials. However, it has little effect on the elastic modulus, which changes by about 5%.
In engineering applications, the elastic modulus is usually used as a constant.

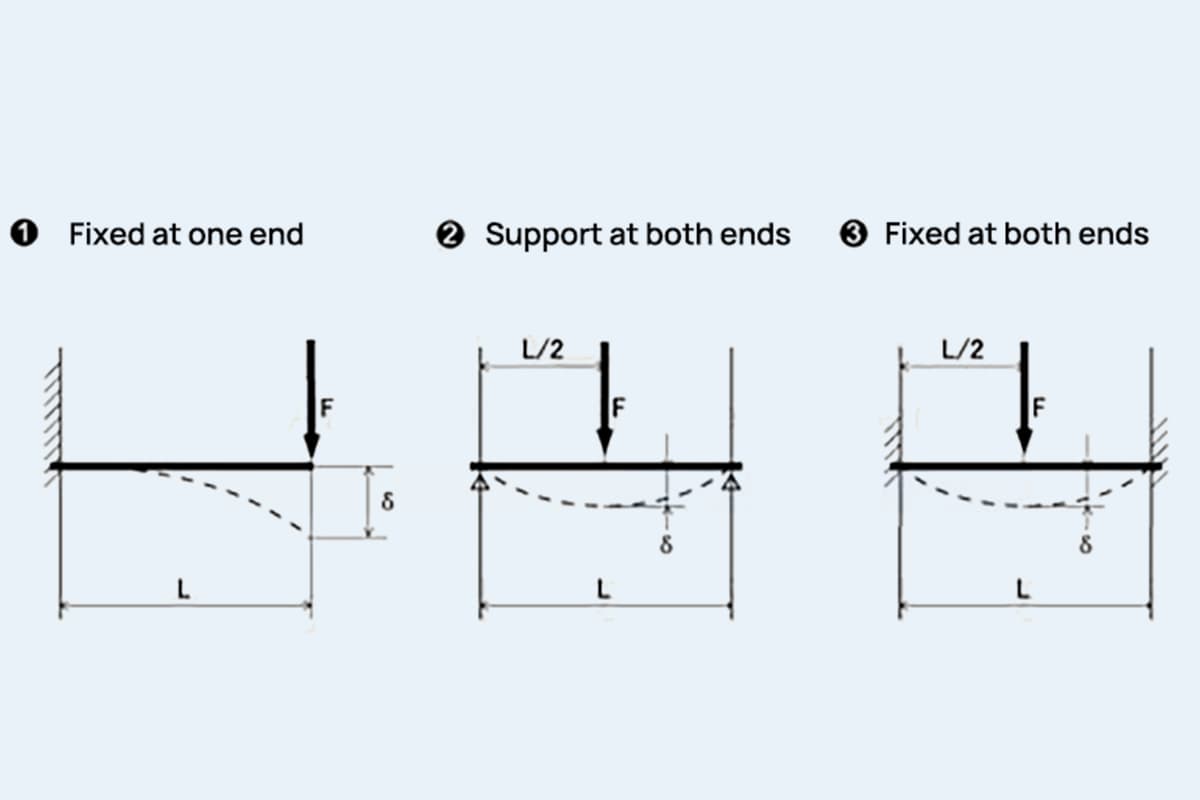
The stiffness of a part refers to its ability to resist elastic deformation under external forces. It depends on the geometry of the part, such as the stiffness of rods with different cross-sections, as well as the material selection of the part itself. For the same structure, a greater elastic modulus results in greater stiffness of the structure.
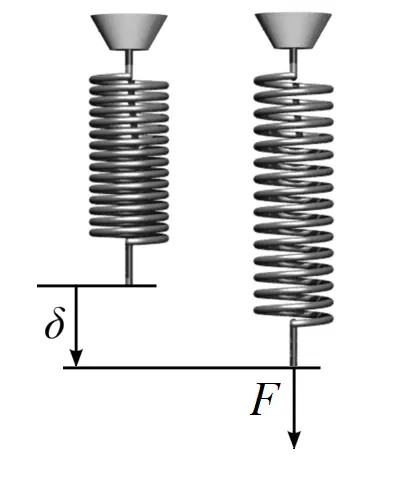
In engineering applications, stiffness is related to the accuracy of parts, such as the spindle of a machine tool.
When the machine tool is in operation, it is important that the spindle does not deform after being stressed, as this can affect the machining accuracy.
Therefore, when designing the spindle of a machine tool, both the structure and the elastic modulus of the material should be taken into consideration.
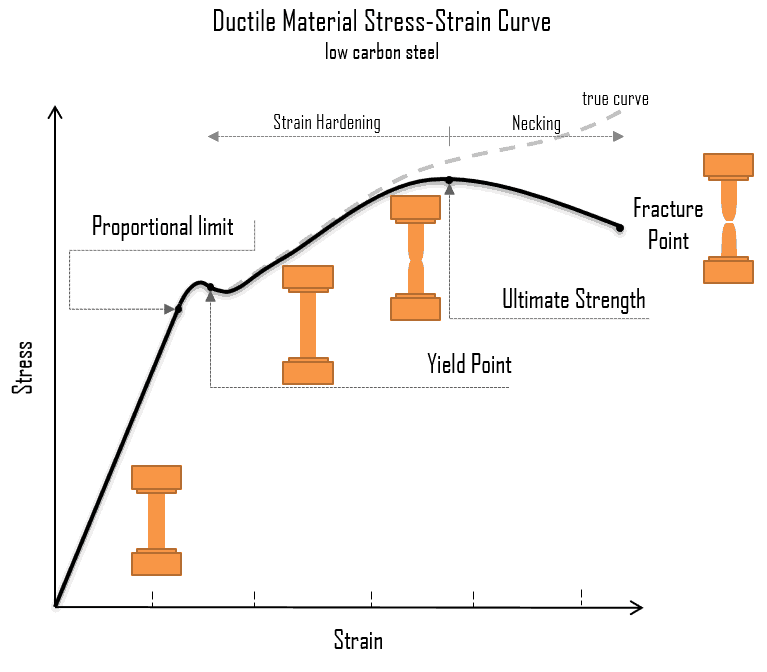
Strength is used to measure the bearing capacity of the part itself.
For brittle materials, we use tensile or compressive ultimate strength to judge whether parts fail.
For elastic materials, we use yield strength to judge whether the parts are permanently deformed, and tensile strength to judge whether the parts are broken.

Hardness refers to the ability of materials to resist hard objects pressing on the surface. Measuring hardness involves using indenters to press on the surface of parts, and determining the hardness of materials based on the indentation depth on the surface of the parts.
Therefore, hardness represents the ability of a material to resist plastic deformation, and the higher the strength limit of a material, the higher its hardness.
The hardness value is determined by the initial plastic deformation resistance and the continuous plastic deformation resistance. The higher the strength of the material, the higher its plastic deformation resistance, and the higher its hardness value.
There is no relationship between elastic modulus and hardness.
Hardness measures the ability of a material to resist plastic deformation, and the elastic modulus is the material constant of the material itself.