What’s the real difference between cast aluminum and die-cast aluminum? This article dives into the distinct manufacturing processes and properties that set these two types of aluminum apart. From the methods used in casting to their heat treatment capabilities and applications in various industries, you’ll discover the key factors that influence the choice between cast and die-cast aluminum. Get ready to understand how these differences impact the strength, quality, and usability of aluminum parts in everyday products.

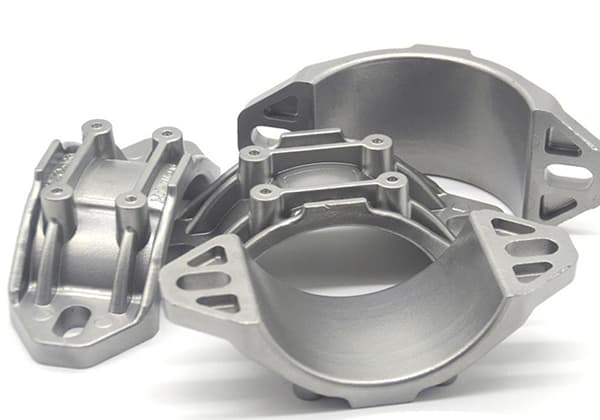
Cast aluminum” generally refers to aluminum castings made through the casting process, while “die-cast aluminum” refers to aluminum castings made through high-pressure die-casting. The primary difference between the two is the casting process used.

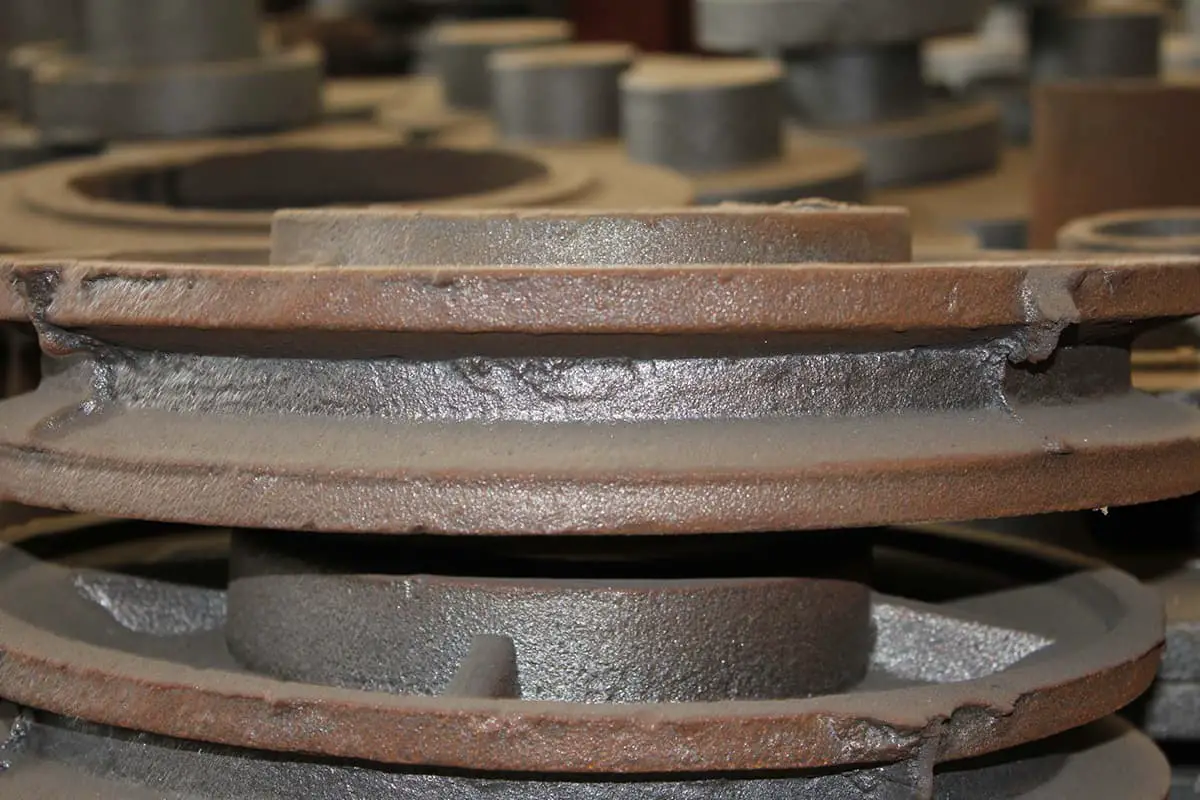
In the casting process, methods such as sand casting, dewaxing casting, gravity casting, low-pressure casting, ceramic mold casting, and gypsum mold casting are used. The die casting process, on the other hand, is a type of high-pressure die casting produced using a cold chamber die casting machine.
The aluminum grades used in the two processes are different, with ZL representing cast aluminum alloys in China’s national standard GB and YL representing cast aluminum alloys.
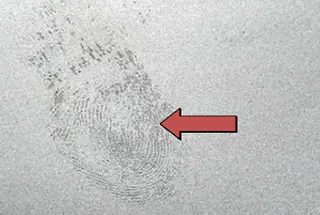
Cast aluminum castings can typically be strengthened through heat treatment, with T6 heat treatment being the most common method. However, die castings are not suitable for T6 heat treatment due to the large amount of gas densely distributed within them. This is because the temperature of T6 heat treatment is close to the melting point of aluminum alloys and the gas in the die casting will expand and be forced out of the casting surface, leading to surface damage and rendering the casting unusable.
Due to the dot protrusion after the gas runs out, the appearance of the casting is seriously damaged and cannot be used.
Aluminum alloy gravity casting and aluminum alloy low-pressure casting belong to the metal mold casting process and are used to produce aluminum castings. The molds are made of hot work die steel, such as H13.
These casting processes can produce the same brand of cast aluminum alloy, with similar pouring temperature and mold opening time, as well as compactness, strength, and other mechanical properties of the aluminum castings.
However, there are still differences between aluminum alloy gravity casting and aluminum alloy low-pressure casting in terms of forming principle, aluminum casting structure, labor intensity, batch number, development time, etc., as shown in the figure below.
| Forming principle | Aluminum casting structure | labour intensity | Minimum batch | Development time | Mold cost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum alloy gravity casting | Using gravity | Complex and diverse | high | 100 | short | less |
| Aluminum alloy low pressure casting | Using air pressure | single | commonly | 500 | long | Higher |
According to the comparison shown above, aluminum alloy gravity casting is ideal for producing products with multiple varieties, small batch sizes, short development cycles, and high quality requirements, while aluminum alloy low-pressure casting is ideal for products with large batch sizes, thin walls, and structures that are suitable for the low-pressure casting process.
The long development cycle of the latter benefits the improvement of production technology throughout the manufacturing process.
A typical product produced through aluminum alloy low-pressure casting is an automobile wheel rim. Its structure is well-suited for the low-pressure casting process and the high volume of production allows sufficient time to improve production technology.
In contrast, typical products produced through aluminum alloy gravity casting are industrial robot castings. These aluminum castings require small production batches, high product quality, and a short development cycle. The aim is to produce high-quality aluminum castings without any pores or sand holes in a very short time.
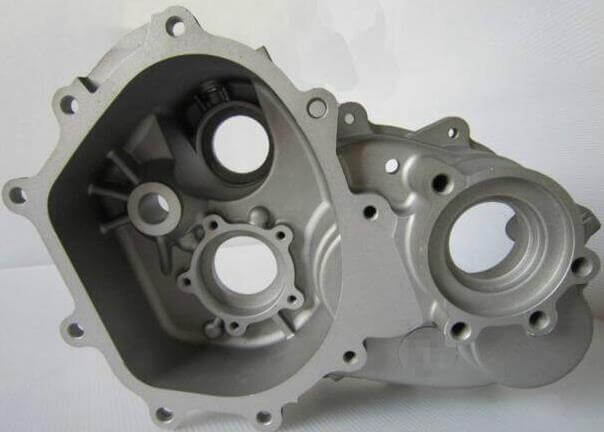
Aluminum die casting is a widely used manufacturing process that offers several advantages in creating parts and components for various industries. This process involves forcing molten aluminum into a mold cavity under high pressure to create complex shapes that might be challenging to produce through other methods, such as extrusion or machining.
There are different alloys of aluminum used in die casting, the most common being 383 and 413. These aluminum alloys exhibit characteristics such as high operating temperatures, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties. Furthermore, they provide excellent stiffness, strength-to-weight ratios, and effective EMI and RFI shielding capabilities.
The die casting process itself comprises several steps. First, the mold cavity, also known as the die, is prepared with a release agent to facilitate part removal after solidification. Then, the molten aluminum is injected into the mold cavity under extreme pressure. After the aluminum solidifies, the die opens, and the aluminum casting is ejected. The process allows for high-volume and efficient production of aluminum parts, leading to reduced costs compared to other manufacturing techniques.
Some essential factors to consider during the aluminum die casting design include:
In conclusion, aluminum die casting is an efficient manufacturing process suitable for producing complex and intricate parts. With its multiple benefits and versatile applications, it remains a popular choice in industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to consumer electronics and beyond.
In aluminum die casting, high pressure plays a significant role in creating precise and high-quality parts. Molten aluminum is forced into the mold cavity using high pressure, ensuring that the material completely fills the mold and reaches every detail of the complex shape. This pressure helps to produce a part with tight tolerances and a smooth surface finish.
Once the molten aluminum fills the mold cavity, it begins to solidify and take the shape of the desired part. During this solidification process, it is crucial to avoid the formation of cavities and voids that can compromise the part’s structural integrity and performance. To ensure a flawless casting, proper temperature control, venting, and pressurization are important factors in preventing unwanted cavities and defects.
Draft and parting lines are two critical aspects of the die casting process that influence the quality of the final product. Draft refers to the angle or taper applied to the mold’s sidewalls to facilitate the ejection of the solidified part. Adequate draft ensures a smooth removal of the part without causing damage or distortion.
Parting lines, on the other hand, are the lines where two halves of the mold meet. Proper placement and design of parting lines are essential to minimize flash (excess material) and achieve a clean, accurate final product.
Aluminum die casting is known for its capability to create complex shapes with intricate details. Features such as holes and windows, bosses, and ribs can be easily achieved by incorporating them into the mold design. This versatility allows for the production of lightweight and high-strength components used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Careful design and planning, combined with the efficient use of high pressure and solidification control, enable the production of aluminum die cast parts with complex geometries and excellent performance.
Cast aluminum parts are known for their lightweight nature, making them an excellent choice for many applications. They have a good strength-to-weight ratio, ensuring a balance between durability and ease of use. The hardness of cast aluminum parts varies depending on the specific alloy used. However, most aluminum die casts have considerable tensile strength, providing resistance to deformation and breaking under load.
Aluminum die casts exhibit high operating temperatures, making them suitable for applications requiring resistance to heat. Their thermal conductivity is also notable, allowing for efficient heat transfer and rapid cooling when needed. In addition, cast aluminum parts provide excellent electrical conductivity, acting as effective shields against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) in electronic devices.
One of the key benefits of using cast aluminum parts is their exceptional corrosion resistance. This makes them suitable for use in harsh environments where they may be exposed to moisture or corrosive substances. In addition, aluminum die casts are wear-resistant, ensuring their longevity and reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacement.
Aluminum die casting is an efficient process, as it allows for high-volume production of parts with complex geometries. Tolerances of ±0.002″ to ±0.004″ can generally be achieved for aluminum casting, providing accurate and consistent results. This efficiency makes it an ideal choice for industries requiring large quantities of precision components, such as automotive and aerospace.
Die cast aluminum is a versatile material, finding applications in a wide range of industries because of its favorable mechanical properties and ease of manufacturing. In this section, we will explore the uses of die cast aluminum in various sectors, including automotive, industrial, and electronics.
Automotive Industry: The automotive sector benefits significantly from die cast aluminum parts, as they contribute to weight reduction and improved fuel efficiency. The lightweight and durable properties of aluminum make it an ideal material for automobile components such as engine blocks, transmission housings, and structural parts of a vehicle’s chassis. Additionally, aluminum alloys can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for automotive applications where heat dissipation is crucial.
Industrial Applications: In the industrial sector, die cast aluminum plays an essential role in manufacturing equipment and machinery. Due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and the ability to withstand varying temperatures, aluminum die cast parts are used in various applications such as heavy machinery, pumps, valves, and industrial tools. These properties enable manufacturers to reduce material costs, enhance performance, and extend the lifespan of their equipment.
Electronic Connectors and Housings: Aluminum die casting is widely used in the electronics industry to produce complex shapes and designs for connectors and housings. The material’s excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, along with its low cost, make it ideal for producing parts used in RF filter boxes, heat dissipation, and networking equipment. Aluminum die cast housings also provide excellent EMI shielding, ensuring that electronic devices function efficiently and reliably.
In summary, die cast aluminum offers numerous advantages in various industries, including automotive, industrial, and electronics. Its impressive properties, such as lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and conductivity, make it an ideal choice for manufacturing durable, efficient, and cost-effective components.