Have you ever wondered what makes your car’s engine parts so durable and efficient? This article unveils the secrets behind casting aluminum alloys, the unsung champions of automotive engineering. Learn how these alloys, with their unique properties and classifications, shape the future of vehicle manufacturing and performance. Get ready to explore the fascinating world of aluminum alloys!

Aluminum alloys that can be directly obtained parts through metal casting processes, aluminum alloy castings. The content of alloying elements in such alloys is generally higher than that in the corresponding wrought aluminum alloys.
Casting aluminum alloys have the same alloy system as wrought aluminum alloys, with the same strengthening mechanisms (except strain hardening). Their main difference lies in: the maximum content of the alloying element silicon in casting aluminum alloys exceeds that in most wrought aluminum alloys.
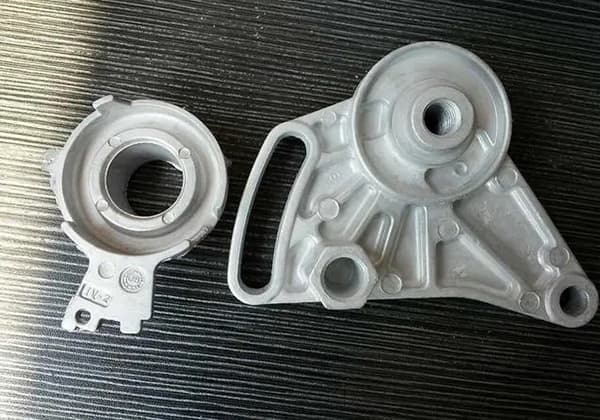
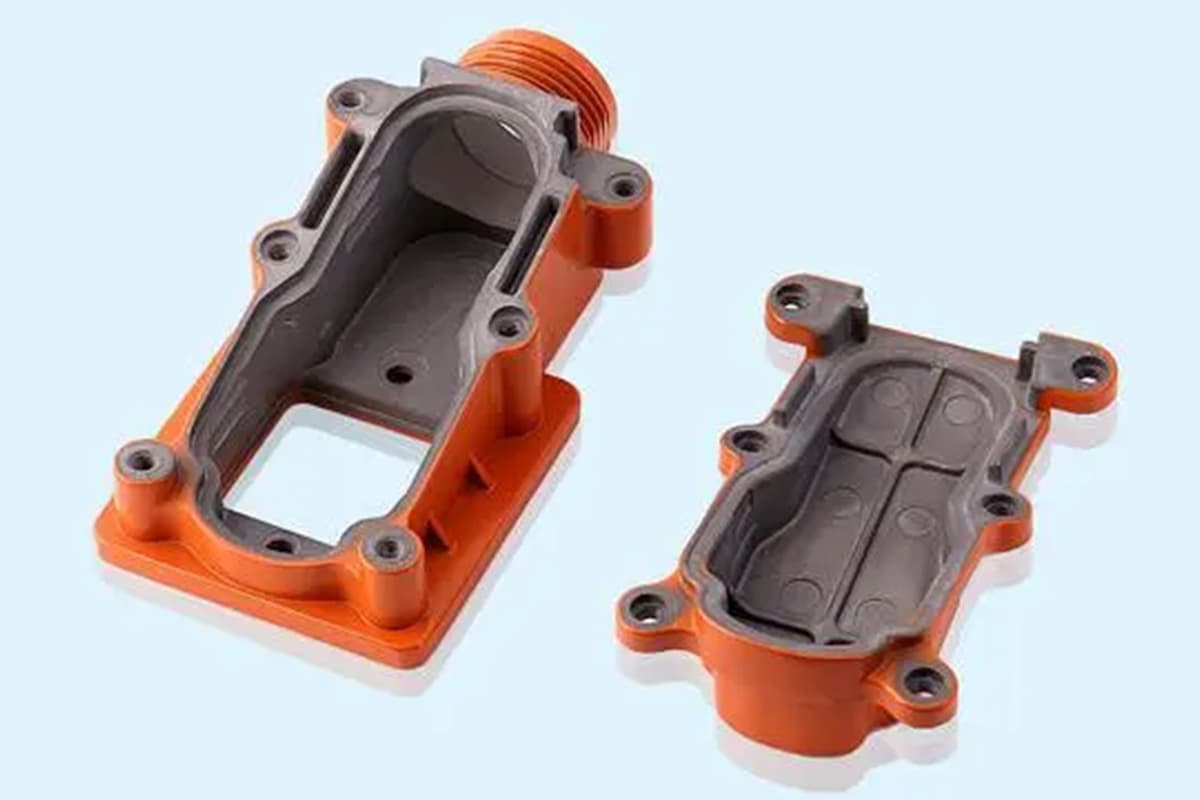
In addition to containing strengthening elements, casting aluminum alloys must also contain a sufficient amount of eutectic elements (usually silicon) to give the alloy considerable fluidity, facilitating the filling of shrinkage gaps during casting. Casting aluminum alloys are widely used in automobiles, such as engine cylinder heads, intake manifolds, pistons, hubs, and power steering housings.
Divided into four categories based on the main elements other than aluminum in the composition: silicon, copper, magnesium, and zinc.
1. Aluminum-silicon alloy
Also known as “silumin” or “silicon-aluminum”. It has good casting performance and wear resistance, a small coefficient of thermal expansion, and is the most varied and widely used alloy in casting aluminum alloys, containing 10% to 25% silicon.
Silicon-aluminum alloys, sometimes with the addition of 0.2% to 0.6% magnesium, are widely used in structural parts, such as shells, cylinder bodies, boxes, and frames. Sometimes the addition of an appropriate amount of copper and magnesium can improve the mechanical properties and heat resistance of the alloy. This type of alloy is widely used in the manufacture of components such as pistons.
2. Aluminum-copper alloy
Alloys containing 4.5% to 5.3% copper have the best strengthening effect, and the appropriate addition of manganese and titanium can significantly improve room temperature, high temperature strength, and casting performance. Mainly used for making sand castings that bear large dynamic and static loads and have uncomplicated shapes.
3. Aluminum-magnesium alloy
The casting aluminum alloy with the smallest density (2.55g/cm³) and the highest strength (around 355MPa) contains 12% magnesium for the best strengthening effect. The alloy has good corrosion resistance in the atmosphere and seawater, good comprehensive mechanical properties and machinability at room temperature, and can be used for parts such as radar bases, aircraft engines, propellers, landing gear, as well as decorative materials.
4. Aluminum-zinc alloy
To improve performance, silicon and magnesium elements are often added, commonly referred to as “zinc silumin”. Under casting conditions, the alloy has a quenching effect, that is, “self-quenching”. It can be used without heat treatment, and the castings have higher strength after modification heat treatment. After stabilization treatment, the dimensions are stable, commonly used for making models, templates, and equipment supports.
Alloy codes are composed of the Chinese pinyin letters “ZL” that represent cast aluminum, followed by three Arabic numerals.
The first numeral after “ZL” denotes the alloy series, with 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively standing for aluminum-silicon, aluminum-copper, aluminum-magnesium, and aluminum-zinc alloy series.
The second and third numerals after “ZL” denote the sequence number of the alloy.
High-quality alloys are denoted with an “A” after their code.
| Alloy Types | Al-Si System | Al-Cu System | Al-Mg System | Al-Zn System |
| Alloy Designations | ZL1XX | ZL2XX | ZL3XX | ZL4XX |
| Code | Title | Code | Title |
| S | Sand Casting | K | Shell Molding Casting |
| J | Die Casting | Y | Pressure Die Casting |
| R | Investment Casting | B | Heat Treatment |
In order to obtain high-quality precision castings of various shapes and specifications, the aluminum alloys used for casting generally have the following characteristics.
1. Good fluidity for filling narrow grooves and slits
2. Lower melting point than general metals, but can meet the requirements of most situations
3. Good thermal conductivity, the heat of molten aluminum can be quickly transferred to the mold, resulting in a shorter casting cycle
4. Hydrogen and other harmful gases in the melt can be effectively controlled through treatment
5. When casting aluminum alloys, there is no tendency for hot brittleness cracking and tearing
6. Good chemical stability, strong corrosion resistance
7. Not prone to surface defects, castings have good surface smoothness and gloss, and are easy to undergo surface treatment
8. The processability of cast aluminum alloys is good, they can be cast using die casting, permanent mold, green sand and dry sand molds, lost foam gypsum casting molds, and can also be formed using vacuum casting, low pressure and high pressure casting, squeeze casting, semi-solid casting, centrifugal casting, etc., to produce various castings of different uses, varieties, specifications, and performances.
| Heat Treatment Condition Code | Heat Treatment Condition Categories | Characteristics |
| F | As-cast Condition | —— |
| T1 | Artificial Aging | For wet sand molds, metal molds, and particularly die-cast parts, partial solid solution effects are noticed due to the rapid cooling speed. Aging treatment can increase strength and hardness, and improve machinability. |
| T2 | Annealing | Eliminate the stress generated in the casting process to enhance dimensional stability and improve the plasticity of the alloy. |
| T4 | Solution Heat Treatment with Natural Aging | By implementing solution strengthening through heating, insulation, and rapid cooling, we can enhance the mechanical properties of alloys, particularly improving the alloy’s ductility and its corrosion resistance at room temperature conditions. |
| T5 | Solution Heat Treatment with Partial Artificial Aging | Following solution treatment, an incomplete artificial aging process is carried out, which is conducted at lower temperatures or over shorter durations. The aim is to further enhance the strength and hardness of the alloy. |
| T6 | Solution Heat Treatment with Complete Artificial Aging | The highest tensile strength can be achieved, though at the expense of reduced ductility. Aging is carried out at elevated temperatures or over an extended period of time. |
| T7 | Solution Heat Treatment with Stabilization Treatment | Enhancing the structural and dimensional stability of castings, as well as the corrosion resistance of the alloy. Primarily used for components operating at elevated temperatures, the stabilization treatment temperature can approach the working temperature of the casting. |
| T8 | Solution Heat Treatment with Softening Treatment | After solution treatment, casting parts with high plasticity and excellent dimensional stability are obtained by utilizing temperatures above stabilization treatment. |
| T9 | Cold and Hot Cycle Treatment | Fully eliminate internal stress in castings and stabilize dimensions. Used for high-precision castings. |
ZL101 is known for its simple composition, easy melting and casting, good casting performance, good air tightness, and relatively good welding and cutting processing performance, but its mechanical properties are not high.
It is suitable for casting various parts with thin walls, large areas, complex shapes, and low strength requirements, such as pump housings, gearboxes, instrument shells (frames), and parts on household appliances. It is mainly produced by sand casting and metal casting.

The addition of a small amount of Ti to ZL101 refines the grain and strengthens the alloy’s structure, resulting in comprehensive properties that are higher than those of ZL101 and ZL102, as well as good corrosion resistance.
It can be used as high-quality castings for general load-bearing structural components in engineering, as well as various structural components on motorcycles, automobiles, household appliances, and instrument products. Its usage is currently second only to ZL102. Sand casting and metal casting are commonly used for production.
This alloy’s main characteristic is good fluidity, with other properties similar to ZL101, but with better air tightness than ZL101.
It can be used to cast various complex-shaped thin-walled die-castings and low-strength thin-walled, large-area, and complex-shaped metal or sand-cast parts. Whether it is a die-casting or a metal/sand casting, it is the most commonly used aluminum alloy in civilian products.
Due to its large number of working crystals and the addition of Mn, which counteracts the harmful effects of Fe mixed into the material, this alloy has good casting performance, excellent air tightness, corrosion resistance, and relatively good welding and cutting processing performance.
However, its heat resistance is poor.
It is suitable for producing complex-shaped, large-sized dynamic structural parts with large loads, such as turbocharger housings, cylinder heads, cylinder liners, and other parts. It is mainly produced by die-casting, but sand casting and metal casting are also commonly used.
Due to the addition of Cu and a reduction in Si content, this alloy’s casting and welding performance are worse than ZL104, but its room temperature and high-temperature strength and cutting processing performance are better than ZL104, with slightly lower plasticity and poorer corrosion resistance.
It is suitable for use as complex-shaped, large-sized, and heavily loaded dynamic structural components such as turbocharger housings, cylinder heads, cylinder liners, and other parts.
ZL105A reduces the impurity element Fe content of ZL105 and increases the alloy’s strength, resulting in better mechanical properties than ZL105. High-quality castings are commonly used for production.
The addition of a small amount of Ti and Mn, as well as an increase in Si content, improves the casting and high-temperature performance of this alloy, making it better than ZL105 in terms of air tightness and corrosion resistance.
It can be used as structural components for general loads and parts that require good air tightness and work at higher temperatures. Sand casting and metal casting are mainly used for production.
ZL107 has excellent casting and air tightness performance, good mechanical properties, average welding and cutting processing performance, and slightly poorer corrosion resistance.
It is suitable for producing structural components that withstand general dynamic or static loads and parts that require air tightness. Sand casting is commonly used for production.

Due to its high Si content and the addition of Mg, Cu, and Mn, ZL108 has excellent casting performance, a small coefficient of thermal expansion, good wear resistance, high strength, and good heat resistance. However, it has slightly lower corrosion resistance.
It is suitable for producing pistons for internal combustion engines and other parts that require wear resistance, as well as parts that require stable dimensions and volume. It is mainly produced by die-casting and metal casting, but sand casting can also be used.
This is a complex alloy of Al-Si-Cu-Mg-Ni, with an increased Si content and the addition of Ni to provide excellent casting and air tightness performance, as well as high-temperature strength, improved wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. The linear expansion coefficient and density are also significantly reduced.
It is suitable for producing pistons for internal combustion engines and parts that require wear resistance and stable dimensions and volume. Metal casting and sand casting are mainly used for production.
ZL111 is a complex alloy with the addition of Mn and Ti, providing excellent casting performance, good corrosion resistance, air tightness, and high strength. Its welding and cutting processing performance is average.
It is suitable for casting complex-shaped, heavily loaded dynamic structural components (such as aircraft engine components, water pumps, oil pumps, impellers, etc.) and parts that require good air tightness and work at higher temperatures. Metal casting and sand casting are mainly used for production, but die-casting can also be used.
ZL114A is a complex alloy with the addition of Mn and Ti, providing excellent casting performance, good corrosion resistance, air tightness, and high strength. Its welding and cutting processing performance is average.
It is suitable for casting complex-shaped, heavily loaded dynamic structural components (such as aircraft engine components, water pumps, oil pumps, impellers, etc.) and parts that require good air tightness and work at higher temperatures. Metal casting and sand casting are mainly used for production, but die-casting can also be used.
ZL115 has good casting performance and high mechanical properties, mainly used as heavy-duty engineering structural components and other parts such as valve housings and impellers. Sand casting and metal casting are mainly used for production.
ZL116 is a complex alloy of Al-Cu-Mg with the removal of Zn and Sb from ZL115 and the addition of trace elements Ti and Be. The alloy’s grain is refined, and the harmful effects of Fe impurities are reduced, providing good casting and air tightness performance as well as high mechanical properties.
It is suitable for casting dynamic structural components that withstand large loads, such as parts on aircraft and missiles, and various parts with good comprehensive properties in civilian products. Sand casting and metal casting are mainly used for production.
ZL117 is a complex alloy of Al-Cu-Mg with a hypereutectic structure and a high Si content of 19-22%, with the addition of trace element Mn and rare earth element RE. It has excellent casting performance, good room temperature and high-temperature strength, low coefficient of thermal expansion, and is a high-level wear-resistant material consisting of many hard primary Si particles distributed on a soft matrix.
It is suitable for casting pistons for internal combustion engines, brake pads, and other wear-resistant parts with stable dimensions and volume, as well as high-strength structural components. Metal casting is mainly used for production, but sand casting can also be used.
In addition, the Aviation Industry Corporation of China has also developed three aluminum-silicon alloys (ZL112Y, ZL113Y, and ZL117Y). ZL112Y and ZL113Y are Al-Si-Cu die-casting alloys, both with good casting performance, air tightness, and high mechanical properties, suitable for casting parts that require high strength and working temperatures and good air tightness, as well as other wear-resistant parts such as pistons with stable dimensions, volume, and good heat transfer performance.
Die-casting is mainly used for production, but sand casting and metal casting can also be used. Unlike ZL108, the Si content is reduced, and the Cu content that enhances solid solution strengthening and precipitation hardening is increased, resulting in better room temperature and high-temperature performance than ZL108.

ZL201 has good room temperature and high-temperature mechanical properties, moderate plasticity, average welding and cutting processing performance, poor fluidity with a tendency towards hot cracking, and poor corrosion resistance.
It is suitable for casting structural components that work at relatively high temperatures (200-300℃) or parts that bear large dynamic or static loads at room temperature, as well as parts that work at low temperatures (-70℃). Sand casting is mainly used for production.
ZL201A greatly reduces the content of impurities Fe and Si compared to ZL201, resulting in higher room temperature and high-temperature mechanical properties. It has good cutting and welding performance but poor casting performance.
It can be used for parts that work at 300℃ or bear large dynamic or static loads at room temperature. Sand casting is mainly used for production.
ZL202 has relatively good casting performance and high-temperature strength, hardness, and wear resistance, but poor corrosion resistance.
It is suitable for casting parts that work at a temperature of 250℃ and bear small loads, such as cylinder heads. Sand casting and metal casting are mainly used for production.
ZL203 has a lower Si content which results in slightly poorer fluidity, greater tendency toward hot cracking, and poorer corrosion resistance. However, it has good high-temperature strength, welding, and cutting processing performance.
It is suitable for casting parts that work at a temperature below 250℃ and bear small loads or parts that bear large loads at room temperature, such as instrument parts and crankcase bodies. Sand casting and low-pressure casting are mainly used for production.
ZL204A is a high-purity, high-strength cast Al-Cu alloy, with good plasticity and welding and cutting processing performance, but poor casting performance.
It is suitable for casting structural components that bear large loads, such as support bases and support arms. Sand casting and low-pressure casting are mainly used for production.
ZL205A is currently the strongest aluminum alloy in use in the world. It has good plasticity and corrosion resistance, excellent cutting and welding performance, but poor casting performance.
It is suitable for casting structural components that bear large loads and some parts with low airtightness requirements. Sand casting, low-pressure casting, and metal casting can be used.
ZL207 has very high high-temperature strength with average casting performance, welding and cutting processing performance, and low room temperature strength.
It is suitable for casting various structural components that work under 400℃, such as valve shells on aircraft engines and some heat-resistant components in the petroleum industry. Sand casting and low-pressure casting are mainly used for production.
ZL209 has higher tensile strength, yield point, and high-temperature strength than ZL201A with good welding and cutting processing performance, but poor casting performance and elongation.
It is suitable for casting various wear-resistant components that work at higher temperatures, such as parts on internal combustion engines. Sand casting is mainly used for production.
ZL301 is the most corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy currently available with good cutting processing performance, relatively good welding performance, high strength, good anodizing performance, but complex casting process, cumbersome operation, and easy to produce defects such as looseness and hot cracking.
It is suitable for casting various parts with large loads in corrosive media such as seawater working at a temperature of 150℃, such as various components in marine vessels, pump housings, impellers, frames in the petroleum industry. Sand casting is mainly used for production.
ZL303 has better high-temperature strength than ZL301, good corrosion resistance (slightly worse than ZL301), excellent cutting processing performance, good welding performance, better casting performance than ZL301, cannot be heat-treated, resulting in much lower mechanical properties than ZL301.
It is suitable for casting parts such as aircraft engines, missiles, internal combustion engines, chemical pumps, oil pumps, petrochemical gas pump housings, rotors, blades that bear medium loads in corrosive media such as seawater, chemical industry, and gas. Pressure casting and sand casting are mainly used.
ZL305 has better casting performance and more stable tissue after natural aging than ZL301 and ZL303 due to the addition of Zn and the reduction of Mg content. The tendency to form looseness and hot cracking is small because of the addition of trace elements Ti and Be, resulting in good comprehensive properties and strong stress corrosion resistance.
However, its mechanical properties at high temperatures are poor. It is suitable for casting parts that bear large loads and work in corrosive media such as seawater, chemicals, and gas below 100℃, such as aircraft, internal combustion engines, chemical pumps, oil pumps, petrochemical gas pump housings, rotors, blades. Sand casting is mainly used for production.
ZL401 has excellent casting performance, a small tendency towards shrinkage and hot cracking, high mechanical properties, good welding and cutting processing performance, but high specific gravity, low plasticity, and poor corrosion resistance.
It is mainly used for pressure casting and casting molds, templates, and structural components on aircraft, internal combustion engines, vehicles, and other products that work at temperatures not exceeding 200℃ and bear medium loads. Pressure casting, sand casting, and metal casting can be used.
| Alloy Series | Country | Alloy Grade | WB/% | Standard Specifications | ||||
| Si | Cu | Mg | Fe | Al | ||||
| AI-Si series | China | YL102 | 10.0-13.0 | <0.6 | <0.05 | <1.2 | Allowance | GB/T15115-94 |
| Japan | ADC1 | 11.0-13.0 | <1.0 | <0.30 | <1.2 | JISH5302-82 | ||
| America | 413 | 11.0-13.0 | <1.0 | <0.35 | <2.0 | ASTMB85-82 | ||
| Russia | AJ12 | 10.0-13.0 | <0.6 | <0.10 | <1.5 | TOCT2685-82 | ||
| Germany | AlSil2 | 11.0-13.5 | <0.10 | <0.05 | <1.0 | DIN1725 | ||
| AI-Si-Mg series | China | YL104 | 8.0-10.5 | <0.30 | 0.17-0.30 | <1.0 | Allowance | GB/T15115-94 |
| Japan | ADC3 | 9.0-10.0 | <0.60 | 0.40-0.60 | <1.3 | JISH5302-82 | ||
| America | 360 | 9.0-10.0 | <0.60 | 0.40-0.60 | <2.0 | ASTMB85-82 | ||
| Russia | AJl4 | 8.0-10.5 | <0.10 | 0.17-0.30 | <1.0 | TOCT2685-82 | ||
| Germany | AlSil0Mg | 9.0-11.0 | <0.10 | 0.20-0.50 | <1.0 | DIN1725 | ||
| AI-Si-Cuseries | China | YL112 | 7.5-9.5 | 3.0-4.0 | <0.30 | <1.2 | Allowance | GB/T15115-94 |
| YL113 | 9.6-12.0 | 1.5-3.5 | <0.30 | <1.2 | ||||
| Japan | ADC10 | 7.5-9.5 | 2.0-4.0 | <0.30 | <1.3 | JISH5302-82 | ||
| ADC12 | 9.6-12.0 | 1.5-3.5 | <0.30 | <1.3 | ||||
| America | 380 | 7.5-9.5 | 3.0-4.0 | <0.10 | <1.3 | ASTMB85-82 | ||
| 383 | 9.5-11.5 | 2.0-3.0 | <0.10 | <1.3 | ||||
| Russia | AJl6 | 4.5-6.0 | 2.0-3.0 | <0.10 | <1.5 | TOCT2685-82 | ||
| Germany | AlSi8Cu3 | 7.5-9.5 | 2.0-3.5 | <0.30 | <1.3 | DIN1725 | ||
| AI-Mg series | China | YL302 | 0.80-1.30 | <0.10 | 4.5-5.5 | <1.2 | Allowance | GB/T15115-94 |
| Japan | ADC5 | <0.30 | <0.20 | 4.0-8.5 | <1.8 | JISH5302-82 | ||
| America | 518 | <0.35 | <0.25 | 7.5-8.5 | <1.8 | ASTMB85-82 | ||
| Russia | AlMg9 | <0.50 | <0.05 | 7.0-10.0 | <1.0 | DIN1725 | ||
(GB/T 1173-2013)
| Alloy Grade | Alloy Code | Casting Method | Alloy Condition | Tensile Strength Rm/MPa | Elongation Ratio A/% | Brinell Hardness HBW. |
| ≥ | ||||||
| ZAlSi7Mg | ZLl01 | S、R、J、K | F | 155 | 2 | 50 |
| S、R、J、K | T2 | 135 | 2 | 45 | ||
| JB | T4 | 185 | 4 | 50 | ||
| S、R、K | T4 | 175 | 4 | 50 | ||
| J、JB | T5 | 205 | 2 | 60 | ||
| S、R、K | T5 | 195 | 2 | 60 | ||
| SB、RB、KB | T5 | 195 | 2 | 60 | ||
| SB、RB、KB | T6 | 225 | 1 | 70 | ||
| SB、RB、KB | T7 | 195 | 2 | 60 | ||
| SB、RB、KB | T8 | 155 | 3 | 55 | ||
| ZAlSi7MgA | ZL101A | S、R、K | T4 | 195 | 5 | 60 |
| J、JB | T4 | 225 | 5 | 60 | ||
| S、R、K | T5 | 235 | 4 | 70 | ||
| SB、RB、KB | T5 | 235 | 4 | 70 | ||
| JB、J | T5 | 265 | 4 | |||
| SB、RB、KB | T6 | 275 | 2 | 80 | ||
| JB、J | T6 | 295 | 3 | 80 | ||
| ZAlSi12 | ZL102 | SB、JB、RB、KB | F | 145 | 4 | 50 |
| J | F | 155 | 2 | 50 | ||
| SB、JB、RB、KB | T2 | 135 | 4 | 50 | ||
| J | T2 | 145 | 3 | 50 | ||
| ZAlSi9Mg | ZL104 | S、R、J、K | F | 150 | 2 | 50 |
| J | T1 | 200 | 65 | |||
| SB、RB、KB | T1 | 230 | 2 | 70 | ||
| J、JB | T6 | 240 | 2 | 70 | ||
| ZAlSi5Cu1Mg | ZL105 | S、J、R、K | T1 | 155 | 65 | |
| S、R、K | T5 | 215 | 1 | 70 | ||
| J | T5 | 235 | 70 | |||
| S、R、K | T6 | 225 | 70 | |||
| S、J、R、K | T7 | 175 | 1 | 65 | ||
| ZAlSi5Cu1MgA | ZL105A | SB、R、K | T5 | 275 | 1 | 80 |
| J、JB | T5 | 295 | 2 | 80 | ||
(GB/T 1173-2013)
| Alloy Type | Alloy Grade | Alloy Code | Casting Method | Alloy State | Tensile Strength Rm/MPa | Elongation Ratio A/% | Brinell Hardness HBW. |
| ≥ | |||||||
| Al-CuAlloy | ZAlCu5Mg | ZL201 | S、J 、R、K | T4 | 295 | 8 | 70 |
| S、J 、R、K | T5 | 335 | 4 | 90 | |||
| S | T7 | 315 | 2 | 80 | |||
| ZAlCu5MgA | ZL201A | S、J 、R、K | T5 | 390 | 8 | 100 | |
| ZAlCul0 | ZL202 | S、J | F | 104 | — | 50 | |
| S、J | T6 | 163 | — | 100 | |||
| ZAlCu4 | ZL203 | S、R、K | T4 | 195 | 6 | 60 | |
| J | T4 | 205 | 6 | 60 | |||
| S、R、K | T5 | 215 | 3 | 70 | |||
| J | T5 | 225 | 3 | 70 | |||
| ZAlCu5MnCdA | ZL204A | S | T5 | 440 | 4 | 100 | |
| ZAlCu5MnCdVA | ZL205A | S | T5 | 440 | 7 | 100 | |
| S | T6 | 470 | 3 | 120 | |||
| S | T7 | 460 | 2 | 110 | |||
| ZAlR5Cu3Si2 | ZL207 | S | T1 | 165 | — | 75 | |
| J | T1 | 175 | — | 75 | |||
| Al-MgAlloy | ZAlMgl0 | ZL301 | S、J、R | T4 | 280 | 9 | 60 |
| ZAlMg5Si | ZL303 | S、J 、R、K | F | 143 | 1 | 55 | |
| ZAlMg8Znl | ZL305 | S | T4 | 290 | 8 | 90 | |
| Al-ZnAlloy | ZAlZn11Si7 | ZL401 | S、R、K | T1 | 195 | 2 | 80 |
| J | T1 | 245 | 90 | ||||
| ZAlZn6Mg | ZL402 | J | T1 | 235 | 4 | 70 | |
| S | T1 | 220 | 4 | 65 | |||
Defect characteristics:
Oxidation slag inclusions are mostly distributed on the upper surface of the castings, at the corners where the mold is not ventilated. The fracture is mostly gray-white or yellow, found through X-ray inspection or during machining, and can also be found during alkali washing, acid washing, or anodization.
Causes:
Defect characteristics:
The pores inside the casting wall are generally round or oval, with a smooth surface, usually shiny oxide skin, sometimes yellowish like oil. Surface pores and bubbles can be found through sandblasting, and internal pores and bubbles can be found through X-ray or machining, appearing black on the X-ray film.
Causes:
Defect characteristics:
Shrinkage porosity in aluminum castings generally occurs near the inner gate, at the root of the riser where the section is thickest, at the junction of thick and thin walls, and in areas with large, thin walls. The fracture surface appears gray or light yellow in the as-cast condition and turns to light gray, light yellow, or gray-black after heat treatment. On X-ray films, it appears as a cloud-like shape, and severe shrinkage porosity can be detected by methods such as X-ray, fluorescent low magnification fracture examination.
Causes:
(1) Casting crack
Develops along grain boundaries, often accompanied by segregation, is a type of crack formed at higher temperatures. It tends to appear in alloys with significant volume shrinkage and in castings with more complex shapes.
(2) Heat treatment crack
Caused by overheating or burning during heat treatment, often presenting as transgranular cracks. Commonly occurs in alloys that generate stress and have a high coefficient of thermal expansion during overly rapid cooling, or when other metallurgical defects are present.
Causes:
(1) Clean the parting surface, clean the mold cavity, clean the ejector rod; improve the coating, improve the spraying process; increase the clamping force, increase the amount of metal poured. These measures can be implemented by simple operations.
(2) Adjust process parameters, injection force, injection speed, filling time, mold opening time, pouring temperature, mold temperature, etc.
(3) Change materials, choose high-quality aluminum alloy ingots, change the ratio of new materials to recycled materials, improve the melting process.
(4) Modify the mold, modify the pouring system, add internal gates, add overflow grooves, exhaust grooves, etc.
For example, reasons for the generation of flash in die castings include:
(1) Refining role of rare earth in aluminum alloys (Rare earth elements can improve the morphology of inclusions and purify grain boundaries).
(2) Refining effect of rare earth on aluminum alloys (Intentionally inhibiting the growth of columnar and dendritic crystals to promote the formation of fine equiaxed crystals, this process is called grain refinement treatment).
(3) Modification effect of rare earth on aluminum-silicon alloys (In casting Al-Si alloys, the Si phase will grow into blocky or flaky brittle phases under natural conditions, severely cleaving the matrix, reducing the alloy’s strength and plasticity, thus it needs to be changed into a favorable form. Modification treatment transforms the eutectic Si from coarse flaky to fine fibrous or lamellar, thereby improving alloy performance.