Have you ever wondered what keeps you safe and moving smoothly inside an elevator? In this article, we delve into the intricate structure and operating principles of elevators, exploring their main components and systems. From the traction machine to the safety devices, you’ll discover how elevators function seamlessly. Learn how different systems work together to ensure safety, efficiency, and comfort. Get ready to gain a deeper understanding of the technology behind one of the most essential conveniences in modern buildings.
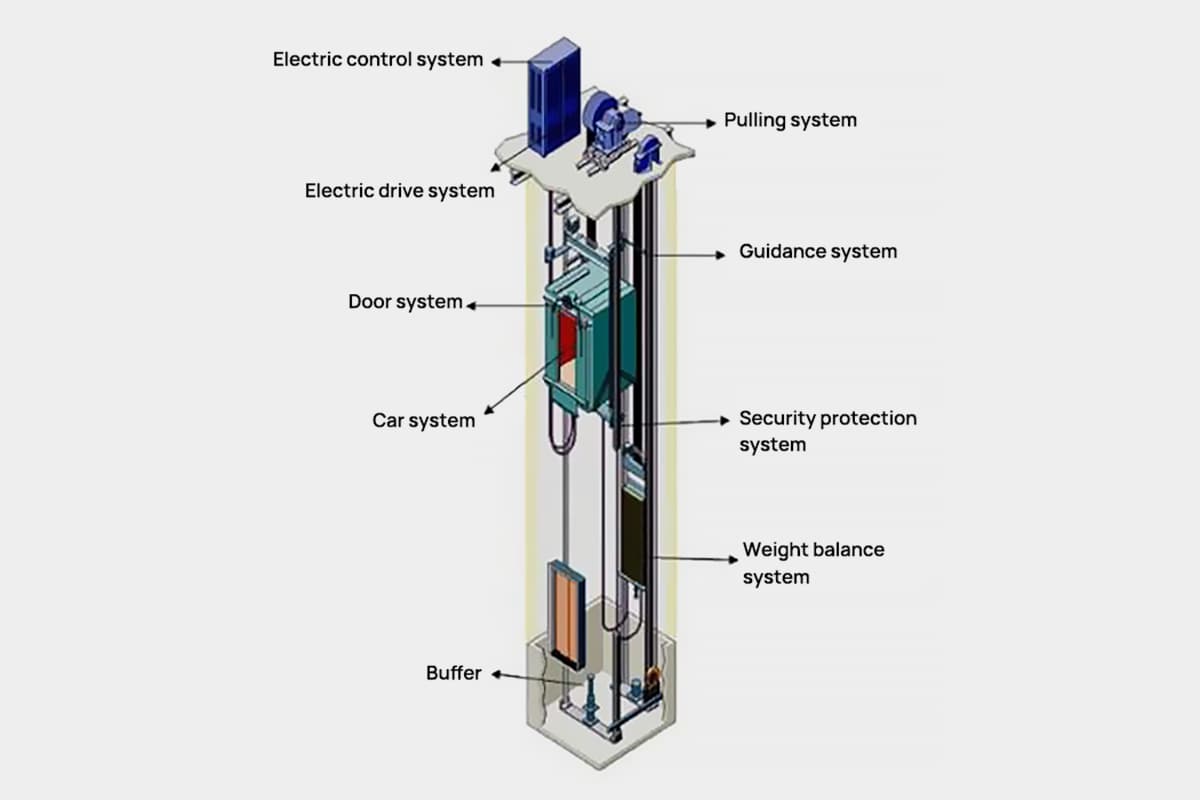
Elevators are generally divided into two categories: elevators with machine rooms and machine room-less elevators.
As the name suggests, machine room-less elevators do not have a machine room. The traction machine for this type of elevator is installed on the guide rail and load-bearing beam, while the control cabinet and other equipment are fixed on the well wall.
Elevators with machine rooms, which include small machine room elevators and regular machine room elevators, typically have the machine room located at the top, taking up more space compared to machine room-less elevators. The following will focus on the basic structure of elevators with machine rooms.
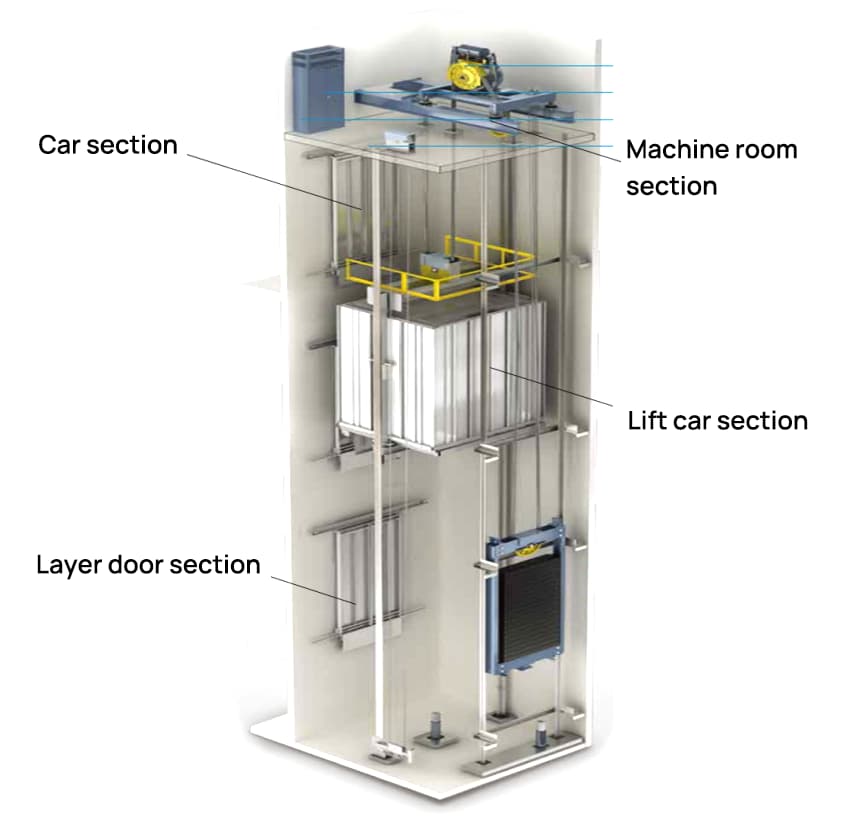
1. Machine Room Section
This includes the traction machine, speed limiter, control cabinet, power cabinet, and exhaust equipment.
2. Lift Car Section
This includes the car, safety gear, safety window, door operator, leveling device, and COP control box.
3. Floor Door Section
This includes the hall door, door header, door frame, sliders, rollers, and sill.
4. Well Section
This includes the traction machine, speed limiter, control cabinet, power cabinet, and exhaust equipment.
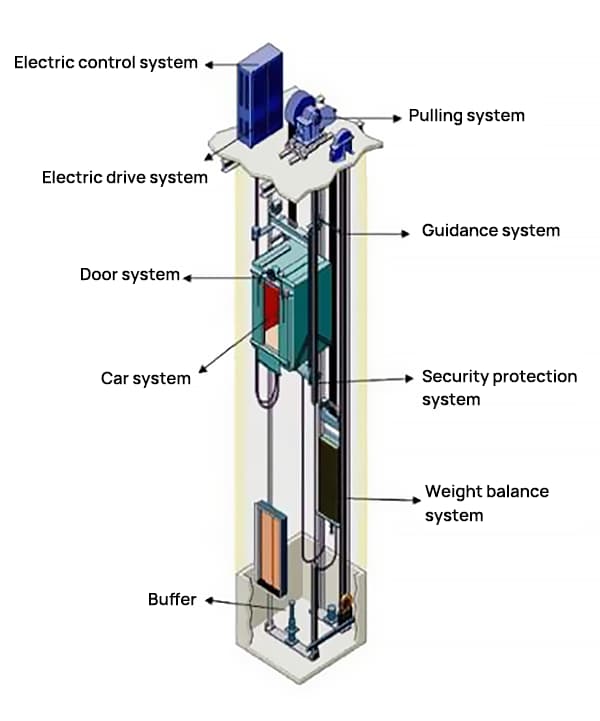
1. Traction System
The primary function of the traction system is to output and transfer power to operate the elevator. It mainly consists of the traction steel wire rope, guide wheel, and counter rope pulley.
2. Guidance System
The guidance system restricts the mobility of the car and counterweight, allowing them to only move up and down along the guide rail. It mainly consists of the guide rail, guide shoe, and guide rail bracket.
3. Lift Car System
The car is the elevator component that transports passengers and goods. It consists of the car frame and car body.
4. Door System
The door system seals the station entrance and car entrance. It consists of the car door, floor door, door operator, and door lock device.
5. Weight Balance System
The main function of this system is to balance the car’s weight and keep the weight difference between the car and counterweight within a limit during the elevator’s operation, ensuring normal traction transmission. The system mainly consists of the counterweight and weight compensation device.
6. Electric Drive System
The electric drive system provides power and controls the speed of the elevator. It consists of traction, power supply system, speed feedback device, motor speed control device, etc.
7. Electric Control System
The main function of the electric control system is to operate and control the elevator. It mainly consists of the control device, position display device, control panel (cabinet), leveling device, selector, etc.
8. Safety System
The safety system ensures safe use of the elevator and prevents accidents that could harm personal safety. It consists of elevator monitoring, elevator floor display, speed limiter, safety gear, buffer, end station protection device, etc.
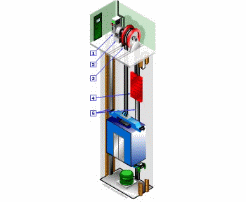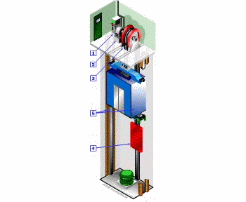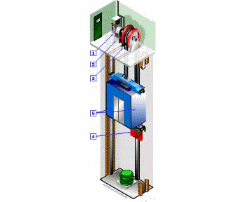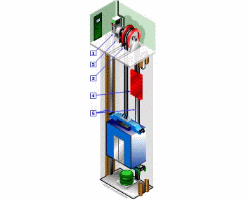
An elevator has a car and a counterweight, connected by a steel wire rope. The traction drive of the driving device (traction machine) enables the elevator car and counterweight to move up and down on the elevator’s internal guide rail.
The guide shoes, fixed on the car, can move up and down along the fixed guide rail installed on the building’s well wall, preventing the car from deviating or swinging during operation.
The normally closed block-type brake releases when the motor is working, allowing the elevator to operate. In case of power failure, it brakes, stopping the car from moving up or down and holding it stationary at the designated floor for passengers and goods to enter or exit.
The car, a box component, carries passengers or other loads, while the counterweight is used to balance the car load and reduce motor power. The compensation device compensates for the tension and weight changes in the traction rope movement, stabilizing the load on the traction motor and allowing the car to dock accurately.
The electrical system controls the elevator’s movement while also completing floor selection, leveling, speed measurement, and lighting tasks. The call indication system constantly displays the car’s direction of movement and its current floor position. Safety devices ensure safe operation of the elevator.