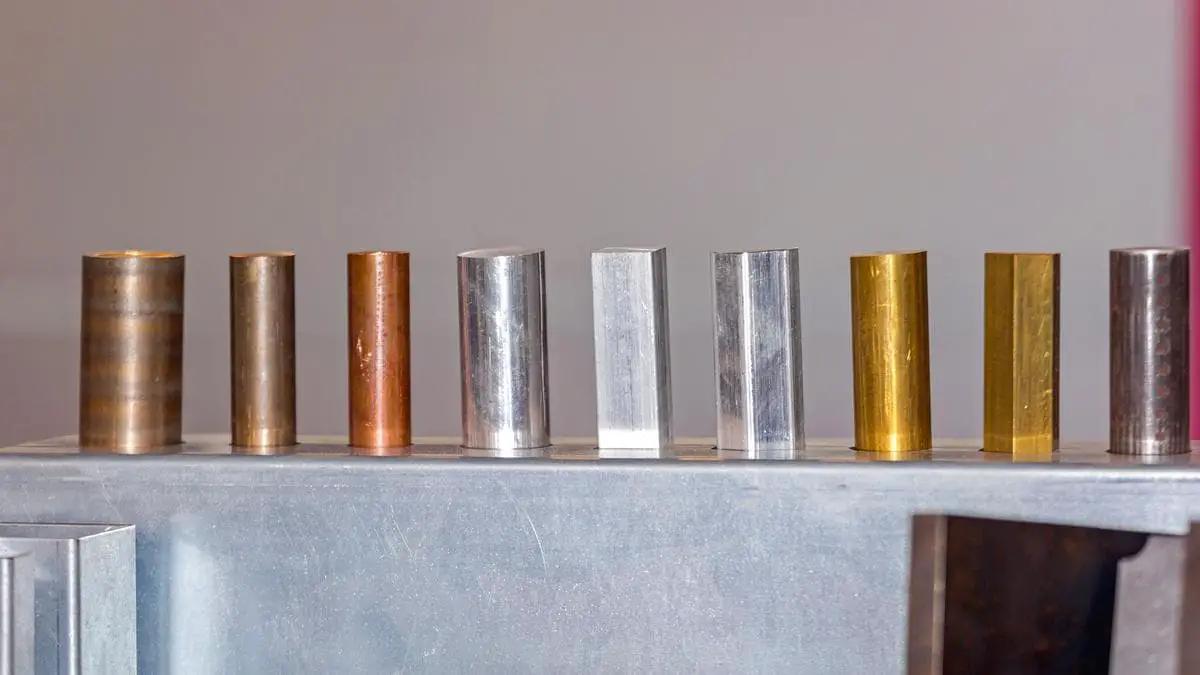
How does sheet metal evolve from raw material to intricate components in our everyday devices? This article dives into the fascinating world of sheet metal fabrication, exploring materials like SPCC, SGCC, and SECC. You’ll discover how different treatments and techniques enhance their properties and applications. Expect to learn about the processes that transform simple metal sheets into durable, versatile parts used in countless industries.

Sheet metal fabrication is a type of processing technology, but a complete definition of it is yet to be established.
Typically, it can be defined as:
Sheet metal fabrication is an extensive cold-working process for metal sheets, typically less than 6mm in thickness.
The process encompasses various techniques, including laser cutting, shearing, punching, cutting, laminating, bending, welding, riveting, splicing, and forming (such as for automobile bodies).
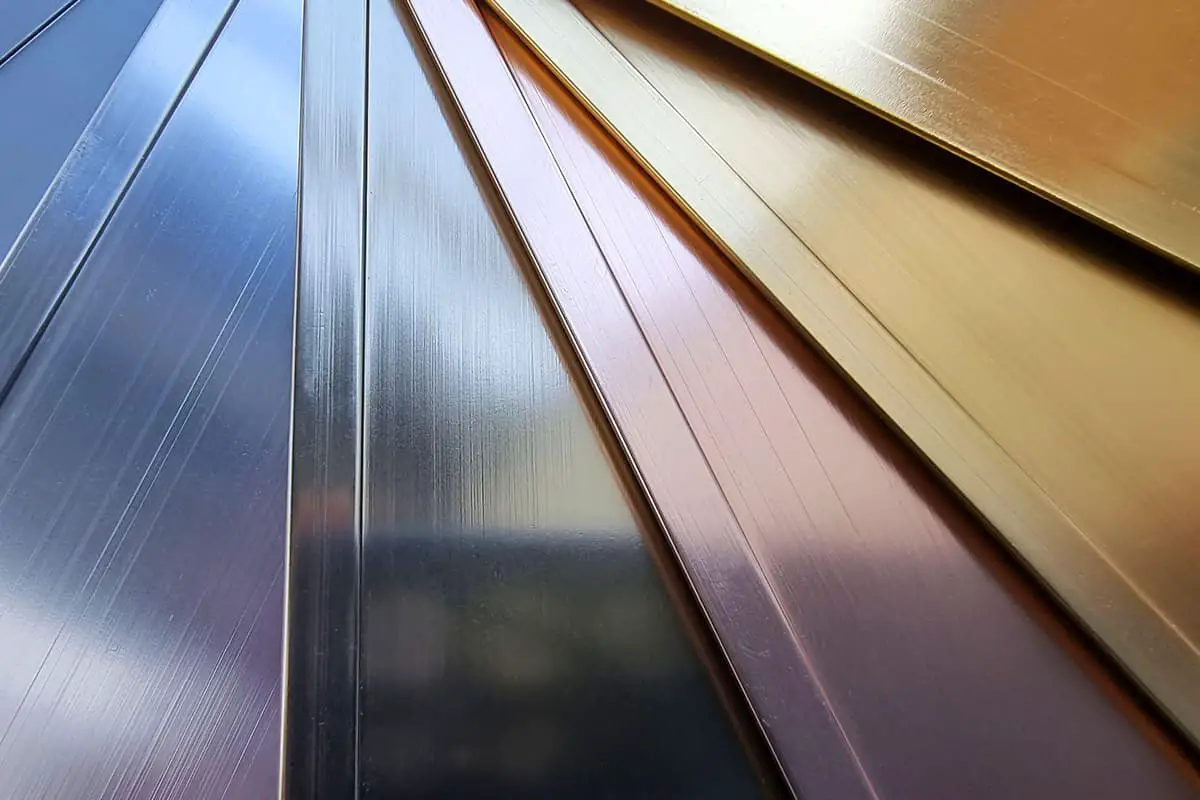
The SPCC cold-rolled sheet is mainly utilized for products that require surface treatment after forming, such as powder coating, paint baking, and electroplating.
The primary objective of using this material is to enhance the surface quality, as SPCC is prone to rust, has an oily surface, and has a dark luster.

Fig. 1 SPCC coil

Fig. 2 SPCC cold-rolled sheet
The purpose of using ordinary zinc and high zinc galvanized steel plates is to prevent corrosion on the surface of the steel and to extend its lifespan.
The steel plate is coated with a layer of zinc metal, referred to as a galvanized sheet.
The surface of SGCC zinc plates has a smooth and refined appearance.

Fig. 3 SGCC galvanized sheet
Surface Characteristics: The surface of SGCC high zinc plates has a rough spangle, with black zinc spots present on the surface and a dark color.

Fig. 4 SGCC with ordinary zinc
The surface of SECC electrolytic plates is finer compared to others.
In terms of rust resistance, under the same thickness of zinc coating, the rust resistance of electro-galvanized (electrolytic plate) is better due to a more stable density of zinc on the surface after electrolysis compared to high-temperature galvanizing.
Surface Characteristics: The surface is smooth, flat, and not easily damaged, with a silvery-gray to bluish color.
SECC is resistant to fingerprints, but the surface is coated with oil and baking paint, leading to poor adhesion and a need for polishing.
SECC without oil coating is not resistant to fingerprints and has a rough surface with a dark color.

Fig. 5 SGCC with high zinc
SGLCC aluminum zinc clad plates are made of 55% aluminum, 43.4% zinc, and 1.6% silicon, and are solidified at around 600°C.
These plates are suitable for use in harsh environments, as they have excellent corrosion and weather resistance, and are guaranteed to have a service life of over 20 years.
Surface Characteristics: The surface of SGLCC plates is white gray with a spangle pattern and a dark luster.
The spangle pattern can range from large spangles to medium spangles to small spangles.

Fig. 6 SECC electrolytic plate
Al
Aluminum is a lightweight metal with a low melting point.
Pure aluminum is prone to oxidation, but it has good tensile strength.
Surface Characteristics: The surface of aluminum has drawn lines, a gray-white color, a light feel, and a dark luster.

Fig. 7 SGLCC aluminum zinc clad plate (1)

Fig. 8 SGLCC aluminum zinc clad plate (2)
Tinplate (SPTE) is a type of low carbon steel coated with tin (SN).
Features: The good plasticity and formability of low carbon steel are retained in this material.
Typically, the thickness of tinplate does not exceed 0.6mm.
Purpose: Tinplate is used as a shield to prevent magnetic interference and as a material for punching a limited number of parts.
Spring steel, which is a medium carbon steel, contains elements such as Mn, Cr, and Si, among others.
Characteristics: This material has the ability to produce substantial elastic deformation, making it ideal for absorbing shocks or impacts. It can also store energy for use in completing work.
The color of spring steel is gray-white, with a bright surface and a soft feel.

Fig. 9 SPTE tinplate
Stainless steel is made of acid-resistant steel that can withstand corrosion from the atmosphere, acid, alkali, and salt.
To achieve rust and corrosion resistance, there are various alloys available, depending on the type and content of the alloy.
Features of stainless steel include: good corrosion resistance, good brightness, high strength, and some elasticity.
Surface treatment is typically performed to improve the surface quality of the plate, as the raw plate often has poor surface quality. This treatment can include wire drawing.

Fig. 10 SUS stainless steel

Fig. 11 Brushed
Copper is a transition element, with the chemical symbol Cu and atomic number 29.
Pure copper is a soft metal that has a reddish-orange color with a metallic luster when cut. Its elemental form is purplish red.
Due to its good ductility, high thermal conductivity, and conductivity, copper is a widely used material in the production of cables, electrical and electronic components.
It can also be used as a building material and can be formed into various alloys, such as bronze and brass, which have excellent mechanical properties and low resistivity.
Furthermore, copper is a durable metal that can be recycled multiple times without affecting its mechanical properties.

Fig. 12 Red copper

Fig. 13 Pure copper








