Have you ever wondered about the versatile material that shapes our modern world, from sleek car bodies to sturdy building roofs? In this captivating blog post, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of sheet metal, exploring its properties, types, and applications. Our expert mechanical engineer will guide you through the intricacies of this essential material, revealing how it has become indispensable in countless industries. Get ready to discover the hidden marvels of sheet metal and gain a newfound appreciation for its significance in our daily lives.


Sheet metal is metal that has been formed into thin, flat pieces, usually through an industrial process. It is generally produced in sheets less than 6 mm thick. Sheet metal is one of the fundamental forms used in metalworking, and it can be cut and bent into a variety of different shapes.
Sheet metal is available in a variety of materials, standard sizes, and thicknesses, typically ranging from 0.5 to 6 millimeters. It is commonly used in a wide array of applications, from car bodies and airplane wings to building roofs and HVAC ductwork.
Creating objects from sheet metal involves specialized tools and techniques, such as hammers, snips, digital imaging, and laser welding. Sheet metal work requires skill and craftsmanship to shape the metal into the desired forms.
Sheet metal is known for its ductility, allowing it to be formed into numerous shapes without breaking or cracking. Its malleability is crucial when it comes to manufacturing, as it permits the material to be bent, stretched, and stamped during the production process.
The thickness of sheet metal is also an important factor, and it can range from extremely thin to several centimeters. The thickness is usually specified using a gauge number, where a lower gauge represents a thicker material. The use of different thicknesses makes sheet metal suitable for various applications, from lightweight electronic enclosures to heavy-duty machinery parts.
Another key property of sheet metal is its strength-to-weight ratio. This means that it maintains its strength even when reduced in thickness, allowing for lightweight yet robust designs.
There are various materials that can be used to produce sheet metal:
Different materials possess unique properties that make them suitable for specific applications, allowing sheet metal to be a versatile and widely used material in many industries.

Commonly used sheet metal materials can be divided into two categories, which are:
Galvanized steel can be mainly divided into:
Let’s compare the above two galvanized sheets of steel through a table.
| Electro-galvanized sheet (EG/SECC) | Hot-dipped metallic-coated sheet (GI) | |
| Base metal | Cold rolled annealed steel | Cold rolled hard steel plate |
| Pre-treatment | Electroplating | Hot dip |
| Zinc plating | Hard plating for thick | Hard plating for thin |
| Plating surface | The zinc layer is adsorbed on the surface of the steel, and the surface is smooth and free of zinc spangle. | Solidified structure of zinc layer, may have zinc spangle or not. |
| Plating organization | Pure zinc coating | The outermost layer is pure zinc and the inner layer is iron-zinc alloy. |
| Mechanical performance | Same as the base metal | After annealing, it has age hardening; the material is soft. |
| Max material thickness | Common material thickness can be seen | 0.6-1.5mm |
| Corrosion resistance | Thin coating, poor | The plating is thick and good. Can be added with anti-fingerprint coating |
| Price | Expensive | Cheap |
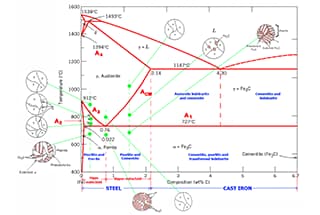
It is a general term for stainless acid-resistant steel, which resists corrosion from atmospheric, acid, alkali, salt, and other media.
To achieve stainless corrosion resistance, the amount of chromium (Cr) should not be less than 13%. In addition, nickel (Ni) or molybdenum (Mo) may be added to enhance the effect.
Because of the various types and content of alloys, there are many types of stainless acid-resistant steel.
See also:

Stainless Steel Features:
Stainless Steel Material Properties:
Austenitic Stainless Steel:
See also:
Sheet metal is characterized by its light weight, high strength, conductivity (which makes it suitable for electromagnetic shielding), low cost, and good production efficiency.
It has found widespread use in various industries, such as electronics, communications, automobiles, and medical devices. For instance, it is a crucial component in computer cases, mobile phones, and MP3 players.
As the application of sheet metal continues to expand, the design of sheet metal parts has become a critical aspect of product development. Mechanical engineers must be well-versed in the design of sheet metal components to ensure that the parts meet the necessary functional and aesthetic requirements while keeping the stamping die production simple and cost-effective.
There are many sheet metal materials suitable for stamping processing, which are widely used in the electronic and electrical industry. These include:
Ordinary Cold Rolled Sheet (SPCC) – SPCC is a steel material that is produced by continuously rolling steel ingots into steel coils or sheets of the desired thickness using a cold rolling mill. However, the surface of SPCC is not protected and can easily oxidize when exposed to air, particularly in humid environments where rust appears more quickly. To avoid this, the surface must be painted, plated, or otherwise protected during use.
Galvanized Steel Plate SECC – SECC is a type of galvanized steel that is produced from general cold-rolled steel coils. After undergoing degreasing, pickling, electroplating, and other post-treatment processes, it becomes an electro-galvanized product that offers excellent corrosion resistance and a decorative appearance. It is widely used in the electronics, household appliances, and furniture industries, for example, in computer chassis.
Hot Dip Galvanized Steel Plate (SGCC) – SGCC is a material that is produced by hot rolling or cold rolling, washing, and annealing the semi-finished product. The material is then immersed in a molten zinc bath at a temperature of around 460°C to produce a zinc-coated material. SGCC is harder than SECC but has poor ductility, a thicker zinc layer, and poor weldability.
Stainless Steel SUS301 – This type of steel has a lower content of chromium compared to SUS304 and has poor corrosion resistance. However, it can be cold-processed to obtain good tensile strength and hardness and has good elasticity, making it ideal for use in elastic springs and anti-EMI applications.
Stainless Steel SUS304 – SUS304 is one of the most widely used stainless steels and contains nickel, which provides better corrosion and heat resistance than chromium-containing steels. It has very good mechanical properties and does not undergo hardening during heat treatment and has no elasticity.
Generally speaking, the basic equipment for sheet metal processing includes a shearing machine, a CNC punching machine, a laser cutting machine, a plasma cutting machine, a water jet cutting machine, a press brake machine, a drilling machine, and various auxiliary equipment such as an uncoiler, a leveling machine, a deburring machine, and a spot welding machine.
Typically, the most important four steps in sheet metal processing are shearing, punching/cutting/folding/rolling, welding, and surface treatment.
Sheet metal is also sometimes referred to as “plate metal.” The process of shaping metal plates into the desired form and size is accomplished through plastic deformation by manual or die stamping. More complex parts can be formed through welding or a small amount of mechanical processing. Examples of sheet metal parts include chimneys, sheet metal furnaces, and automobile shells.
Sheet metal processing involves the use of metal plates to create parts such as chimneys, iron drums, oil tanks, ventilation pipes, elbow heads, round places, funnel shapes, and more. This process requires certain geometric knowledge and involves cutting, bending and buckling, bending and forming, welding, and riveting.
Sheet metal parts are thin hardware parts that can be processed through stamping, bending, stretching, and other means. They have a constant thickness throughout processing and are different from cast parts, forged parts, or machined parts. Examples of sheet metal parts include the iron shell of an automobile and some stainless steel kitchen utensils.
Modern sheet metal technology includes filament winding, laser cutting, heavy processing, metal bonding, metal drawing, plasma cutting, precision welding, roll forming, metal sheet bending, die forging, water jet cutting, and precision welding.
Surface treatment is an important part of the sheet metal processing process because it prevents rust and enhances the appearance of the product. The surface pre-treatment removes oil stains, oxide scales, and rust, prepares the surface for post-treatment, and the post-treatment mainly includes spray (bake) painting, plastic spraying, and plating an anti-rust layer.
3D software such as Solidworks, UG, Pro/E, SolidEdge, Topsolid, and CATIA have sheet metal parts and are mainly used to obtain data required for sheet metal processing through the editing of 3D graphics. This data provides information for the CNC punching machine/laser, plasma, water jet cutting machine/combination machine and CNC bending machine.
In the sheet metal manufacturing process, the first step to perform is cutting. Various techniques are used to cut sheet metal, such as shearing, laser cutting, plasma cutting, and waterjet cutting. Shearing is a simple mechanical process that utilizes a blade to trim the edges or make straight cuts. In contrast, laser cutting employs a focused laser beam that easily melts through the metal, resulting in precise cuts and minimal material waste.
After cutting, bend the sheet metal to create the desired shape. Some common bending methods include air bending, bottoming, and coining. Air bending, the most popular technique, involves applying force to the metal using a punch and die, and it offers high precision and flexibility. Bottoming and coining, on the other hand, require more force but ensure that the metal bends accurately to predefined angles.
Stamping is another crucial step in the manufacturing process where a die and a press are used to create raised or indented sections on the sheet metal. Techniques like embossing, coining, and flanging are common in stamping. These methods add complex details and patterns to the metal surface. Stamping can also be combined with cutting, offering versatility and expanding the range of final products I can create.
Lastly, perform forming to shape the sheet metal further. Forming processes include roll forming, stretch forming, and deep drawing. Roll forming involves passing the metal through a series of rollers to create a continuous profile while maintaining the material’s integrity. During stretch forming, attach the sheet metal to a tensioned machine and apply pressure to achieve the desired shape without causing any defects. Deep drawing, on the other hand, pulls the metal into a die cavity, creating deep, hollow shapes with uniform walls.
Overall, these manufacturing processes allow me to efficiently create a wide range of sheet metal products that cater to various industries and applications.
In my experience, working with sheet metal offers several advantages. First, it provides a remarkable weight-to-strength ratio, making it ideal for various industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction. Additionally, sheet metal is highly customizable, allowing for easy manipulation and modification to fit specific design requirements. This flexibility contributes to minimal waste generation during the manufacturing process, making it an eco-friendly choice.
Another advantage I’ve found is that sheet metal offers excellent conductive properties, making it efficient for electrical and thermal applications. It’s also highly resistant to corrosion, ensuring durability and long-term reliability.
Despite its advantages, there are a few downsides to using sheet metal. One major concern I’ve encountered is its susceptibility to warping and distortion during the fabrication process. High temperatures and mechanical stress can potentially compromise its structural integrity, leading to costly repairs or product failure.
Another issue that I’ve faced is the risk of injury during handling and fabrication due to sharp edges and burrs. Proper safety protocols must be implemented to minimize chances of accidents while working with sheet metal.
Lastly, while sheet metal provides versatility in manufacturing, it may not be suitable for every application. Its thin walls can limit its strength and rigidity, making it unsuitable for heavy-duty or high-pressure projects.