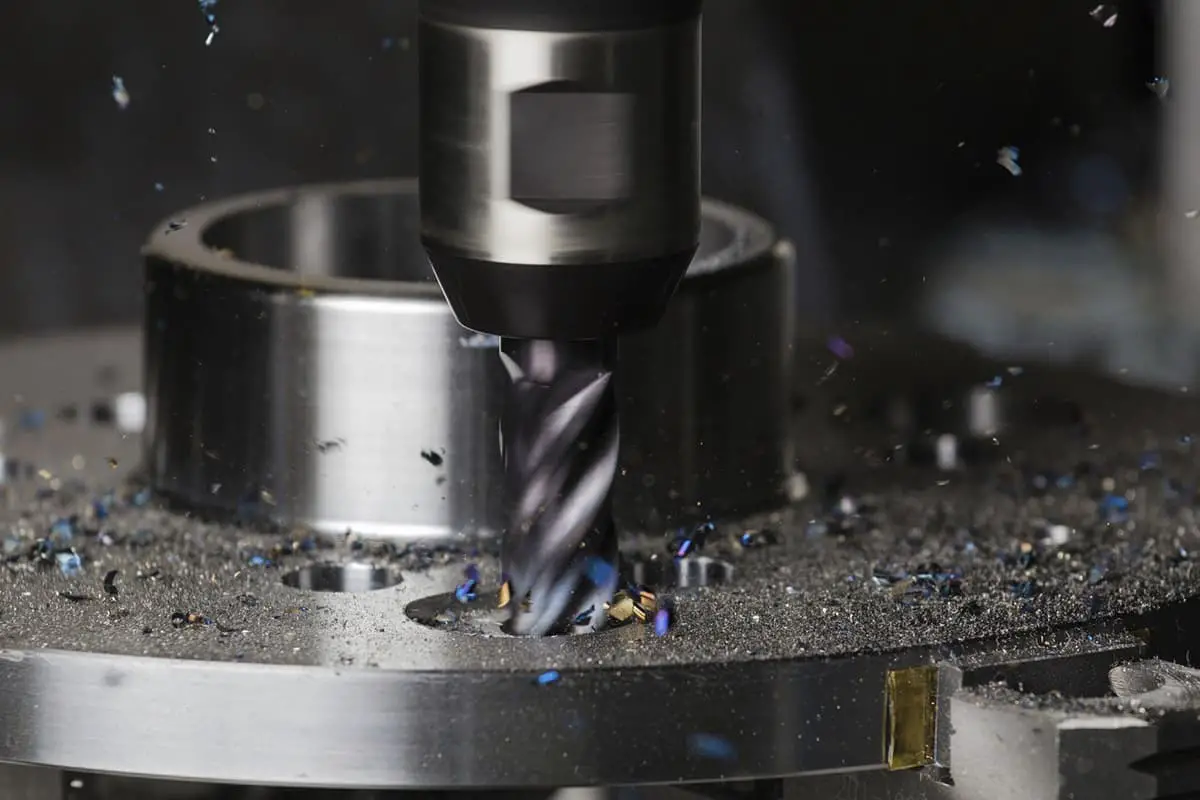
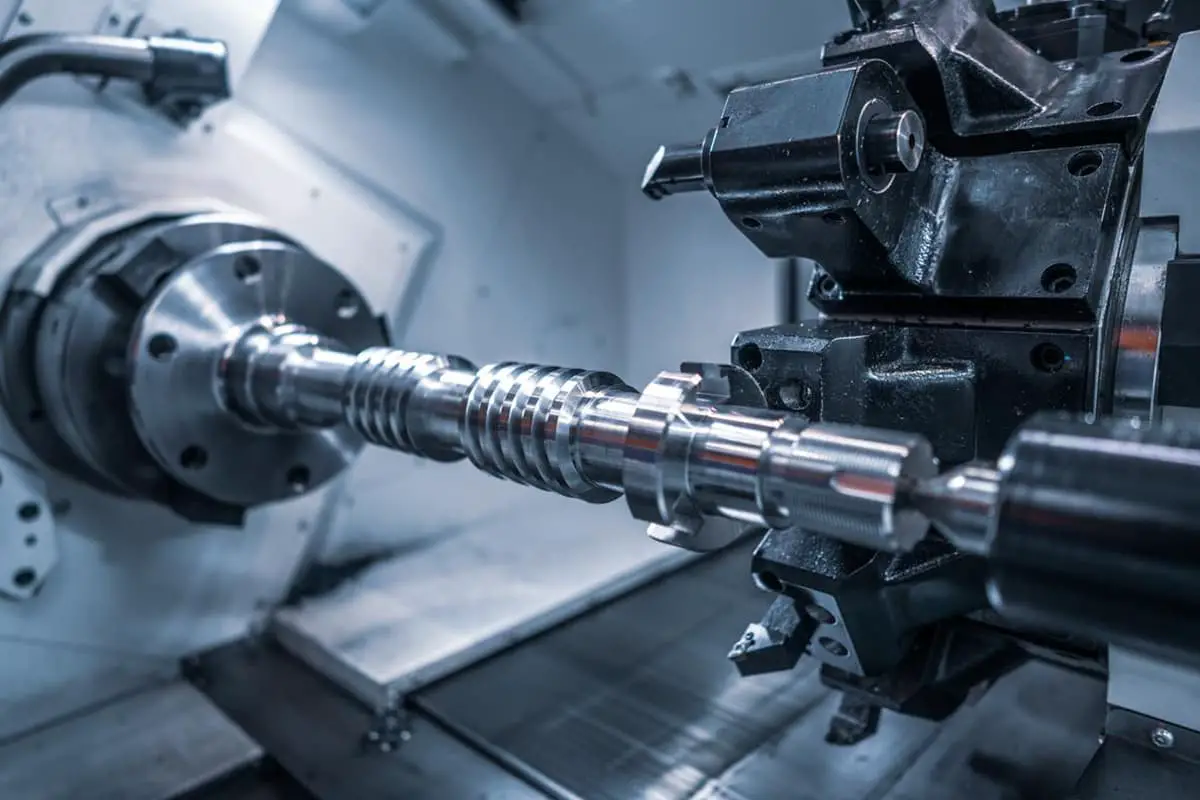
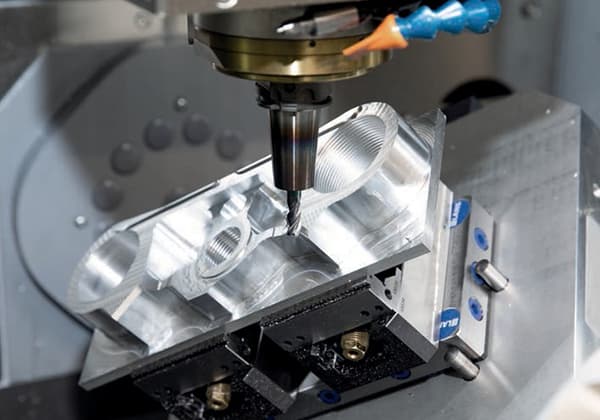
Have you ever wondered what the secret is behind high-precision machining? In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of tool holders, exploring their types, features, and best practices. Our expert mechanical engineer will guide you through the intricacies of tool holders, helping you understand how they impact machining accuracy and efficiency. Get ready to learn valuable insights that can take your machining skills to the next level!

According to the taper of the tool hole of the machining center spindle, it is usually divided into two categories:
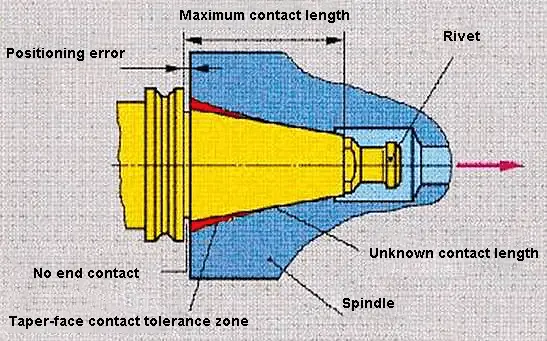
7:24 means that the taper of the tool holder is 7:24, which is a single taper surface positioning with a longer taper shank.
The tapered surface serves two important functions at the same time, which are the precise positioning of the tool holder relative to the spindle and the clamping of the tool holder.

Advantages:
The non-self-locking design allows for quick tool loading and unloading. The cost of the tool holder is relatively low since the taper angle can be machined to a high degree of accuracy, ensuring a precise connection.
Disadvantages:
During high-speed rotation, the tapered hole at the front end of the spindle will expand. The amount of expansion increases with the increase in rotation radius and speed, which decreases the taper connection rigidity. The axial displacement of the tool holder will also change under the action of the drawbar tension. After each tool change, the radial dimension of the to
There are usually five standards and specifications for universal tool holders with a taper of 7:24:
HSK vacuum tool holder with a taper of 1:10
Tensioning Method.
Type NT tool holders are tightened by a drawbar on conventional machines, which is also known domestically as ST.
The other four tool holders are tightened on the machining center through a spigot at the end of the tool holder.
Universality.
(1) At present, the most widely used tool holders in China are DIN 69871 (JT) and Japanese MAS BT.
2) DIN 69871 tool holders can also be mounted on machines with ANSI/ASME spindle taper bores.
(3) The international standard IS0 7388/1 tool holder can also be installed on DIN 69871, ANSI/ASME spindle tapered bore machine tools. So in terms of versatility, the IS0 7388/1 tool holder is the best.
HSK vacuum tool holders rely on the elastic deformation of the tool holder, not only the tool holder with a taper of 1: 10 in contact with the 1:10 taper of the machine tool spindle bore, but also the flange face of the tool holder is in close contact with the spindle face.
This double-sided contact system is superior to a 7:24 universal tool holder in terms of high-speed machining, connection rigidity and overlap accuracy.
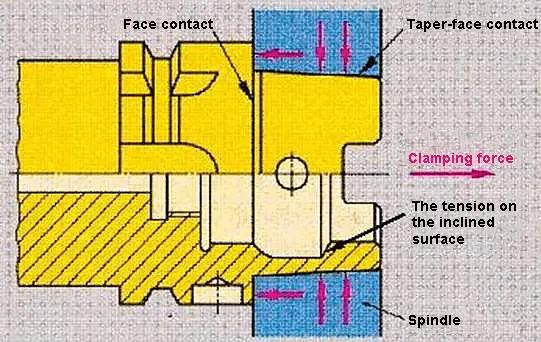

The HSK vacuum tool holder can improve the rigidity, stability, and product accuracy during high-speed machining, and also shorten the time of tool replacement, which is essential for high-speed machining. It is suitable for machine tool spindle speeds of up to 60,000 rpm. The HSK tool system is being widely used in the aerospace, automotive, and precision mold industries, among others.
HSK tool holders are available in types A, B, C, D, E, and F, with types A, E, and F being commonly used on machining centers with an automatic tool change (ATC) process.
The biggest difference between Type A and Type E:
(1) Type A has a transmission groove, but Type E does not. Therefore, Type A has a relatively larger transfer torque, which can handle heavy cutting. The torque transmitted by Type E is relatively small, so it can only handle light cutting.
(2) Type A tool holder has manual fixing holes and direction grooves, in addition to the transmission groove, resulting in relatively poor balance. Type E does not have these features, making it more suitable for high-speed processing.
The mechanisms of Type E and Type F are identical. The difference between them is that for handles with the same name (such as E63 and F63), the taper of the Type F handle is one size smaller. This means that both E63 and F63 have a flange diameter of φ63, but the F63 taper is only the same size as the E50. Therefore, the F63 will rotate faster (with a smaller spindle bearing) compared to the E63.
It is mainly used for straight tool holders such as drills, milling cutters and taps, or tool clamping.
The elastic deformation of the circlip is 1mm, and the clamping range is 0.5~32mm in diameter.


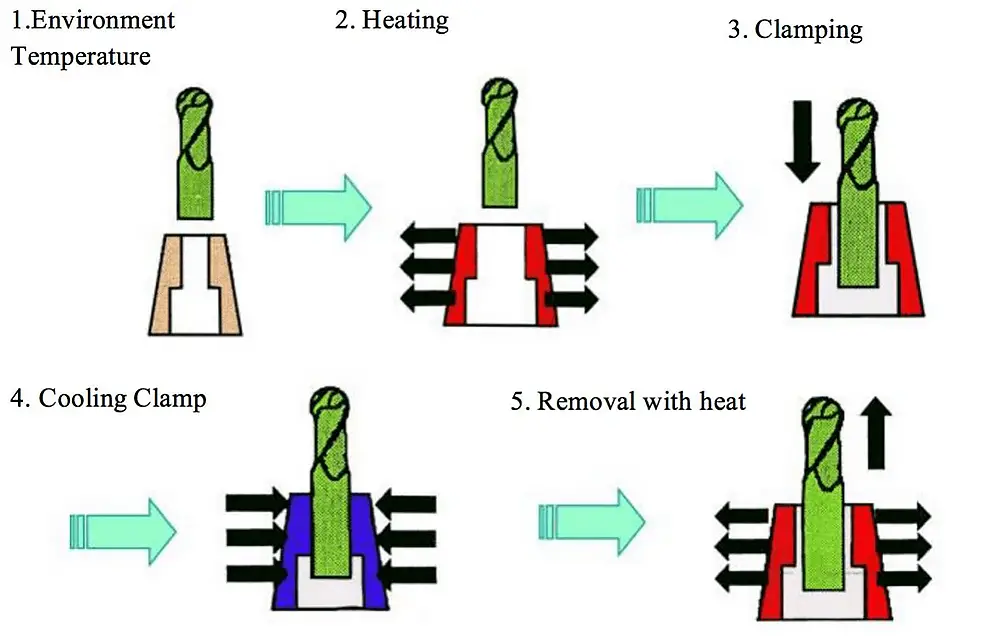
Sensing heating technology is used to heat the tool clamping part of the tool holder, causing it to expand in diameter. The cold shank is then inserted into the hot tool holder. This results in a high clamping force and good dynamic balance, making it suitable for high-speed machining.
The technology also provides high repeatability accuracy within 2μm and radial runout within 5μm, and has good resistance to stains and interference during machining.
However, only one tool of a specific shank diameter can be installed for each tool holder specification, and a set of heating equipment is also required.
The principle of pyrocondensational tool holder clamping:

Comprehensive evaluation and comparison of tool holders
| Evaluation | Spring clamp type | Hydraulic type | Pyrocondensational type |
| Structure Diagram | 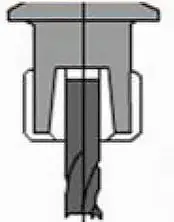 | 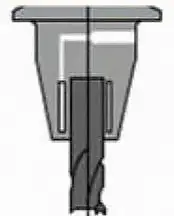 | 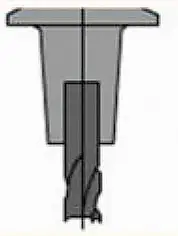 |
| Versatility | be used in all processes; highly versatile | limited for high-speed machining; high maintenance costs | excellent performance in a wide range of high-speed machining applications |
| Toolholder beating | quality spring clip <10µm | >5µm | about 3µm |
| Rigid | good | good | |
| Dynamic Equilibrium | good | general | good |
| Vibrations | no advantage | can absorb vibrations | no advantage |
| Convenience | accuracy depends on the operator | clamping structure is easily damaged | standardized operation |
| Cost | general | expensive | Cheaper than Hydraulic type |
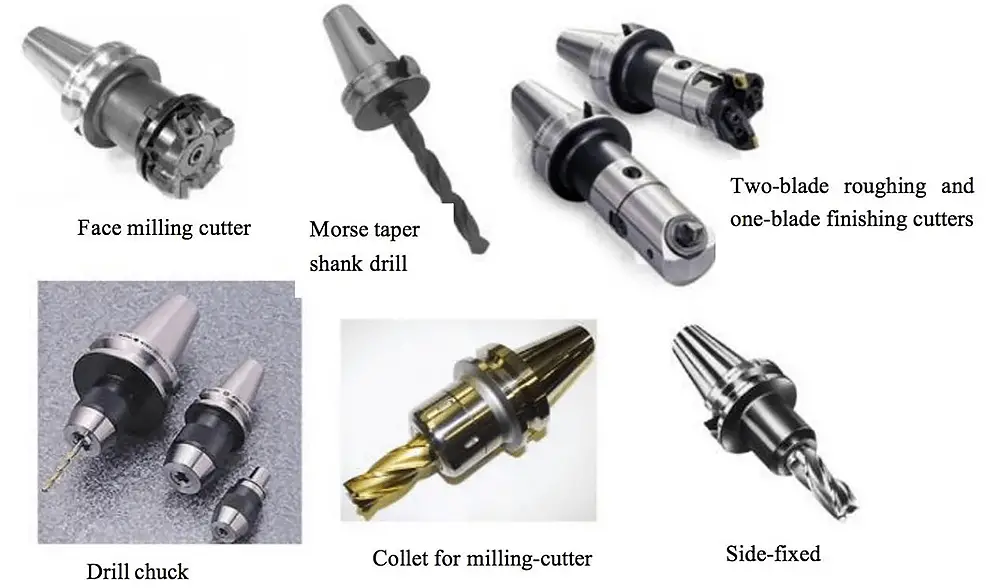
Other types of tool holders

When choosing a tool holder, several key factors should be considered to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with your machinery:
To prolong the life of your tool holders and maintain their performance, follow these steps:
By considering these factors and following proper maintenance practices, you can ensure that your tool holders remain in good condition, providing reliable and accurate performance in your machining operations.