Galvanized steel” refers to the process of coating the surface of a steel plate with zinc to make it less susceptible to corrosion and rust, thus prolonging its service life. Will galvanized steel rust? In our daily life, galvanized steel plates are a common type of steel plate. The cars we drive are made from […]

Galvanized steel” refers to the process of coating the surface of a steel plate with zinc to make it less susceptible to corrosion and rust, thus prolonging its service life.

In our daily life, galvanized steel plates are a common type of steel plate. The cars we drive are made from them and they have a good reputation. But, will they rust?
Why does galvanized steel plate rust?

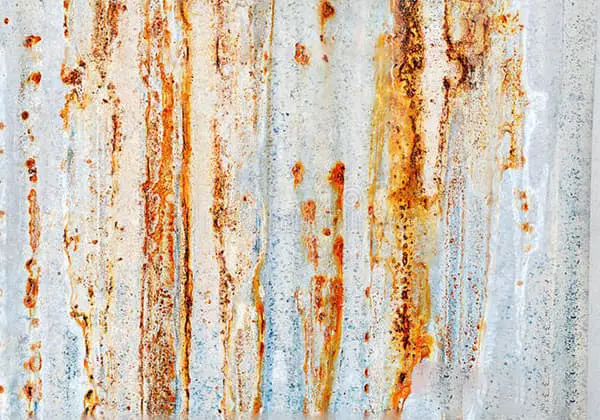
(1). During the entire service life of a galvanized sheet, the first form of corrosion is the oxidation of the zinc coating on the surface, leading to the formation of “white rust.” Over time, the “white rust” on the surface will further react with carbon dioxide and other contaminants in humid air to form “black spots.”
When the galvanized sheet has been in use for an extended period and the corrosion of the galvanized layer is severe, the steel base loses the protective function of zinc, known as “sacrificial corrosion protection,” and begins to oxidize, forming “red rust.”
Once the steel base starts to oxidize, the rate of corrosion accelerates, and the galvanized sheet reaches the end of its service life.
(2). Additionally, there are two special forms of corrosion in galvanized sheets known as “black change.”
One occurs after a period of use, where elements such as lead in the zinc coating cause dull parts of the zinc flake to become blackened. Although the blackened zinc coating still protects the steel base, it does impact its service life. This issue has been improved by using antimony instead of lead in promoting the formation of zinc flakes.
Another situation occurs during the transportation of the galvanized sheet, where low coiling tension causes the steel strip layers to become loose, and parts of the steel coil rubbing against the skid result in oxidation. The white oxide is rubbed off, producing black spots on the galvanized sheet surface, damaging the passivation film, reducing the thickness of the galvanized layer, and shortening its service life, affecting its appearance.
(3). Galvanized steel sheets exhibit excellent corrosion resistance in dry or non-polluting environments. However, in polluted environments, its service life is greatly reduced and must be pre-coated to form a color plate, also known as a color coated plate, before use.
(4). Generally, the corrosion of galvanized steel sheets is not due to uniform corrosion of the galvanized coating on the surface, but rather to the initial corrosion of the coating at points where the coating and substrate are poorly bonded, resulting in severe local corrosion and loss of performance.
In this regard, the adhesion of the zinc coating, especially overall adhesion, is more crucial than the thickness of the zinc coating. If the local adhesion of the zinc coating is poor, even a thicker coating will rust from the poor adhesion, a problem that galvanizing production technicians must recognize, similar to the “bucket principle.”
Generally, the galvanized steel available on the market today includes 80g spangle-free and 60g spangled galvanized sheets.
These materials can provide rust protection for up to three years without spangles in outdoor conditions, while spangled sheets may start to show signs of white rust in about two years.
Properly plated galvanized steel can resist rust for a longer period of time, but will eventually transition from bright white to a light gray color.
However, if the steel is not properly treated before plating, it may develop rust spots or even begin peeling within three to five months.
It is important to note that no material is completely immune to rust.
The performance of aluminum and galvanized plates may vary in different environments, and the quality of aluminized and galvanized steel produced by different factories can also impact their rust resistance.
Even aluminum-zinc plated 200 series stainless steel, which is one grade higher than galvanized sheet, is not immune to rust.
Similarly, 300 series and 400 series aluminum-zinc plated stainless steel, which are even higher grades, can still rust in certain environments.
It should also be noted that the service life of galvanized steel can be affected by the environment in which it is used. If it is in a dry environment for an extended period of time, its lifespan may be longer, but if it is in a consistently wet environment, its lifespan may be shortened.