Have you ever considered how crucial proper bearing lubrication is to machine longevity? The right lubrication method can significantly reduce friction, prevent wear, and extend the lifespan of your bearings. In this article, you’ll discover 11 different methods for bearing lubrication, from manual and drip point lubrication to more advanced techniques like spray and jet lubrication. By understanding these methods, you’ll be able to choose the most effective lubrication strategy, ensuring optimal performance and durability for your machinery. Dive in to learn how to keep your bearings running smoothly and efficiently.

Bearing lubrication serves several purposes, including ensuring normal operation of the bearing, avoiding direct contact between the raceway and rolling body, reducing friction and wear within the bearing, extending its service life, and improving its performance.
Additionally, it helps prevent rust and corrosion caused by foreign objects entering the bearing.
In this article, we will introduce 11 commonly used lubrication methods for bearings. We hope this information will be useful in your design process.
The oiling method is the most basic approach for bearing lubrication. When there is insufficient lubricant in the bearing, an oiler can be used to supply oil. However, this method can be challenging to maintain a consistent level of oil, and the risk of neglecting to refill is higher. This method is typically used in light-load, low-speed, or intermittent operations.
To optimize operation, it is best to install a dust cover or ball valve on the lubrication hole and use a filtering device, such as felt, cotton, or wool.
The dripping method is typically used for light to medium load bearings with a peripheral speed of less than 4 to 5 meters per second. A roughly constant quantity of lubricating oil is delivered from a container through holes, needles, valves, etc.
The most classic example is the drip oil cup. The amount of oil dripping can vary greatly depending on the viscosity of the lubricant, the bearing clearance, and the position of the oil supply hole.

The oil ring method involves a ring that is suspended on the shaft and rotates, bringing oil from an oil pool into the bearing. This method is only suitable for lubricating horizontal shafts.
It is appropriate for medium to high-speed bearings with shaft diameters greater than 50mm and works best with a seamless oil ring. When the aspect ratio of the bearing is less than 2, only one oil ring is needed, otherwise, two oil rings are required.
The oil rope method relies on the capillary and siphoning action of the oil rope to introduce lubricating oil from the oil cup into the bearing. This method is mainly used for light to medium load bearings with a peripheral speed of less than 4 to 5 meters per second. The oil rope also serves a filtering function throughout the process.
The oil pad method uses the capillary action of the oil pad to distribute lubricating oil from the oil pool to the surface of the shaft diameter. This method can keep the friction surface clean, but dust can also clog the pores, resulting in insufficient oil supply. The amount of oil supplied by the oil pad method is typically only 1/20th of the amount supplied by oil lubrication.
The immersion method involves submerging a portion of the bearing in lubricating oil. This method is often used for thrust bearings of vertical shafts, but is not suitable for radial bearings of horizontal shafts.
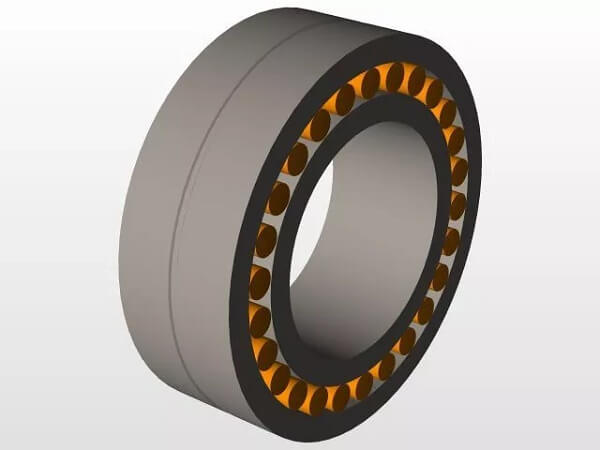

The splash lubrication method involves supplying lubricating oil to the bearing through the flapping of rotating parts in the oil tank. This method is suitable for high-speed bearings.
The atomization method involves spraying the lubricant in a fine mist onto the friction surface. This method is suitable for high-speed bearings.

The pressure lubrication method involves supplying oil to the bearing through the pressure of a lubrication pump. The lubricating oil that flows from the bearing is then collected and returned to the oil pool for recycling. This method is the most stable and efficient method of oil supply and is suitable for high-speed, heavy-load, and critical sliding bearings.
The circulation lubrication method involves delivering filtered oil to the bearing parts using an oil pump. The lubricating oil after passing through the bearing is filtered and cooled before being reused. Because the circulating oil can remove some of the heat and cool the bearing, this method is suitable for high-speed bearing components.
The high-pressure injection method involves using an oil pump to shoot high-pressure oil into the bearing through a nozzle. The oil then flows into the oil groove through the other end of the bearing. This method is necessary when the bearing rotates at a high speed and the surrounding air forms an airflow, making it difficult for general lubrication methods to reach the bearing.
The lubricant must be sprayed into the bearing using high pressure. The nozzle should be positioned between the inner ring and the center of the cage.
After evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of various lubrication methods, the appropriate method can be selected based on the actual operating conditions. The main principles for selection can be summarized as follows:
Bearing lubrication is an ongoing process, and the replacement cycle of the lubricant depends on the conditions of use and the amount of oil. When used in a clean environment with an operating temperature below 50°C and minimal dust, the lubricant should generally be replaced once a year. If the oil temperature reaches 100°C, it should be replaced every three months or sooner.