Ever wondered why some metal sheets come out perfectly flat while others warp and distort? This article reveals the secrets behind cutting forces in rotary plate shears. You’ll learn how different angles and clearances affect the quality and efficiency of metal shearing. Get ready to uncover the mechanics that ensure precision in every cut!
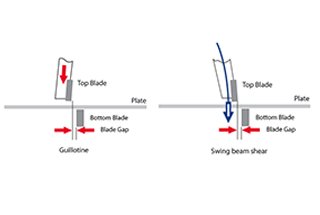
Compared to ordinary plate shears, most rotary plate shears adopt an oblique blade design. This design is advantageous because it allows for a more efficient shearing process. The oblique blade reduces the shearing force required and minimizes the deformation of the sheet metal.
Rotary plate shears are widely used in the industry due to several key benefits:
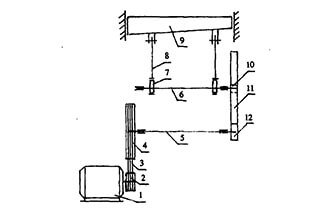
In the shearing process, the blade support of the swing beam shearing machine undergoes a rotary motion. This rotary motion is essential as it changes the cutting angle and shear clearance of the blade during the process. The varying cutting angle and shear clearance help in achieving a clean and precise cut.
One of the challenges in the design of rotary shears is the calculation of the sheet metal cutting force. The current design methodology often calculates the cutting force based on the assumption of straight motion of the blade support. However, in reality, the blade support undergoes rotary motion. This discrepancy can lead to inaccurate calculations of cutting force, resulting in design size deviations and potentially affecting the normal performance of the machine.
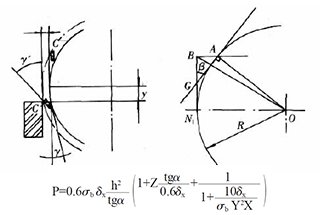
The cutting force calculation for inclined blade shear with blade support in straight motion primarily uses the Norshari Formula, developed by a former Soviet scholar. This formula is crucial for determining the force required in the shearing process, particularly for machines with straight-moving blade supports.
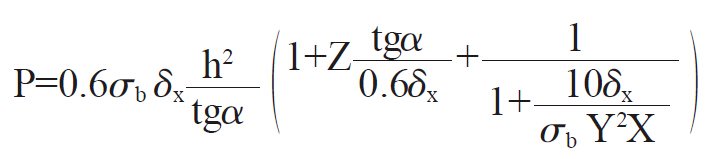
In the cutting force formula:
The Norshari Formula does not account for the changing shear relief angle during the shearing process and assumes a fixed shear clearance. Consequently, it is only applicable to shears with blade support that moves in a straight motion.
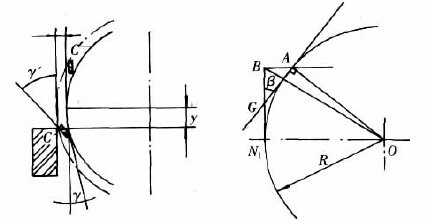
During the shearing process, the relief angle can vary within the range of γ±β. The quality of the plate shear and the force required are highly sensitive to the shear clearance. A larger shear gap increases the proportion of the pulling function, leading to poorer shear quality. For medium thickness plate cutting, the shear clearance should ideally be controlled between 8% to 12%.
For rotary shearing machines, achieving the required γ±β is challenging due to the simplified blade installation process. When the shear gap exceeds the experienced value, it leads to a change in shear force. An increase in shear clearance results in a higher relative value of shear sidewise clearance, thereby increasing the force required for shearing.
A prominent pulling function during the cutting process increases shear force and power loss, causes plastic deformation of the plate, increases friction between the blade and plate, and reduces the cutter’s service life. Therefore, when calculating the cutting force for rotary shearing machines, it is recommended to choose a higher relative value of shear blade sidewise clearance and a higher blade dulling coefficient.
The calculation of shear force for a shearing machine typically uses a technical formula. Most calculations are based on ordinary Q235 steel plates, with conversion factors for different materials:
For a 10mm thick and 6000mm long Q235 steel plate:
Shear Force=10×6000×23.5=1410000 N=141 Tons
For a Q345 steel plate:
Shear Force=141×1.4=197.4 Tons
For a 304 stainless steel plate:
Shear Force=141×2=282 Tons