Have you ever wondered how precise engineering in sheet metal fabrication is achieved? Understanding sheet metal tolerances is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together perfectly in any mechanical project. This article will explore the different types of tolerances used in flat and formed stamping parts, from dimensional deviations to angular tolerances. By the end, you’ll grasp the importance of these tolerances and how they impact the quality and functionality of your metalworking projects. Dive in to learn the key factors that contribute to achieving precision in sheet metal fabrication.
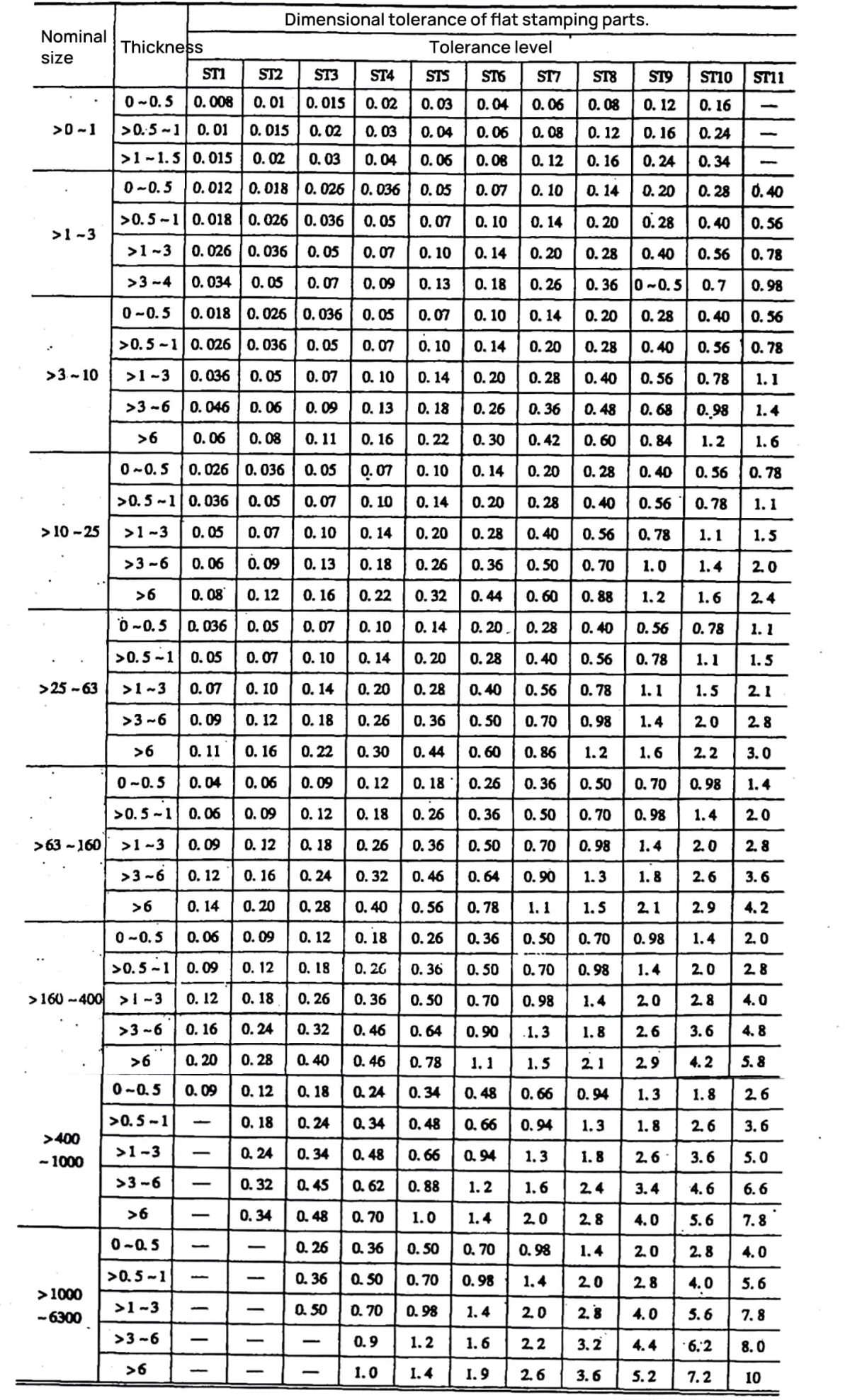
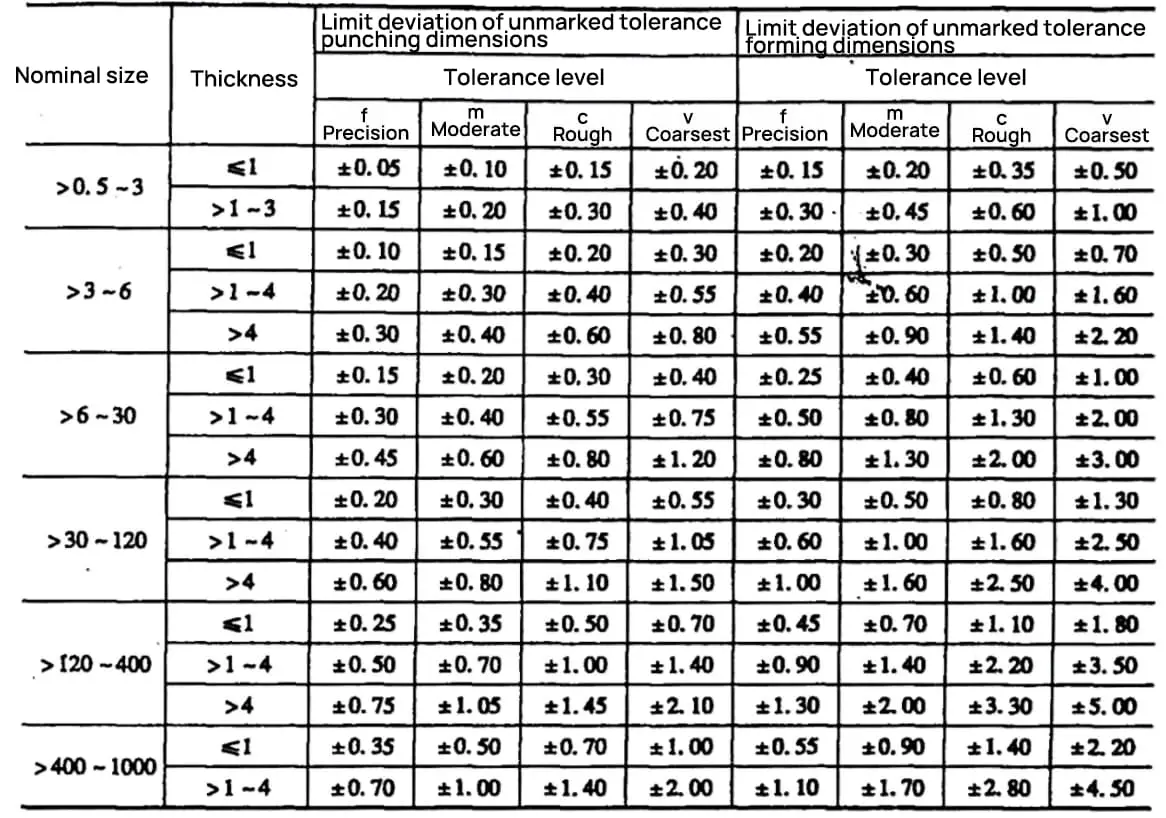
Unit: mm
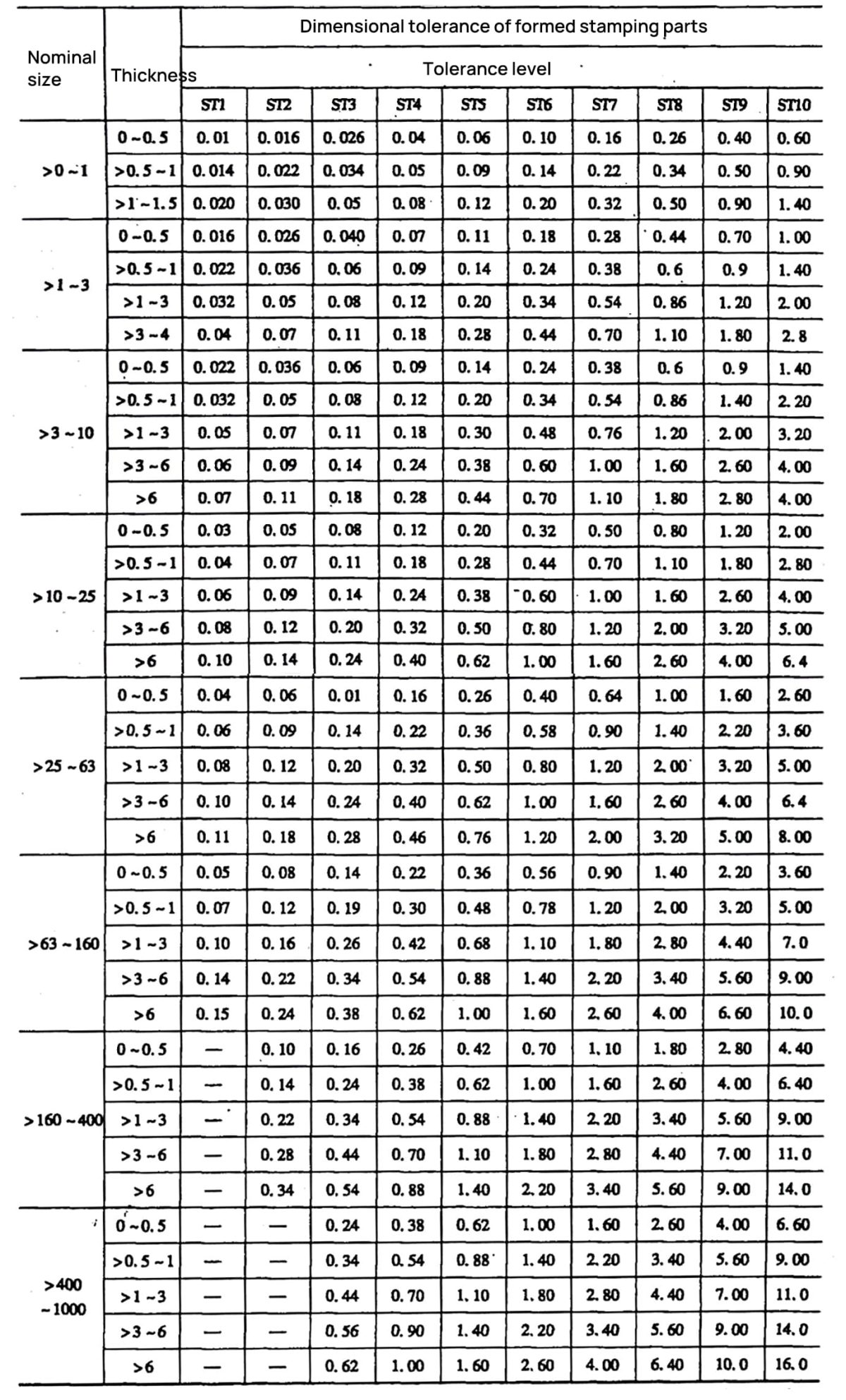
Unit: mm
Note:
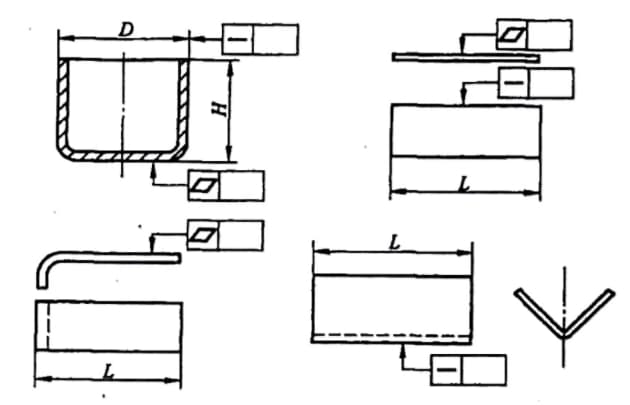
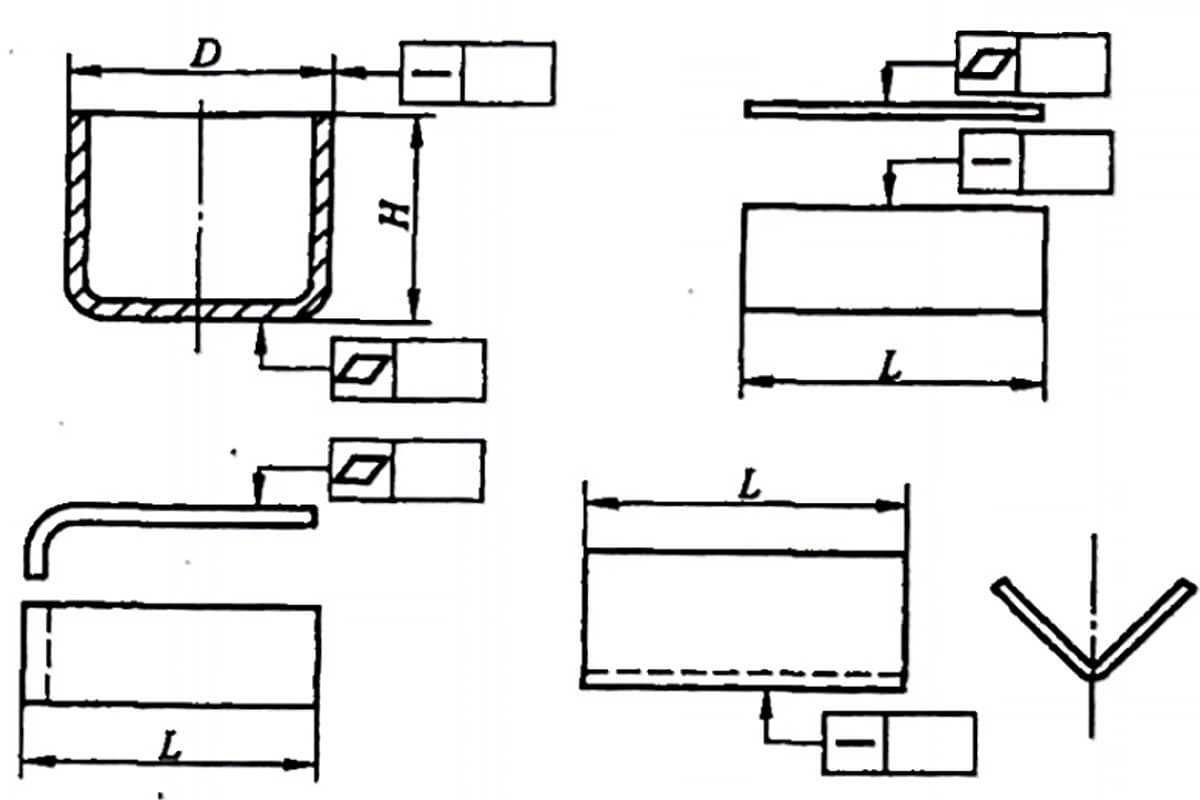
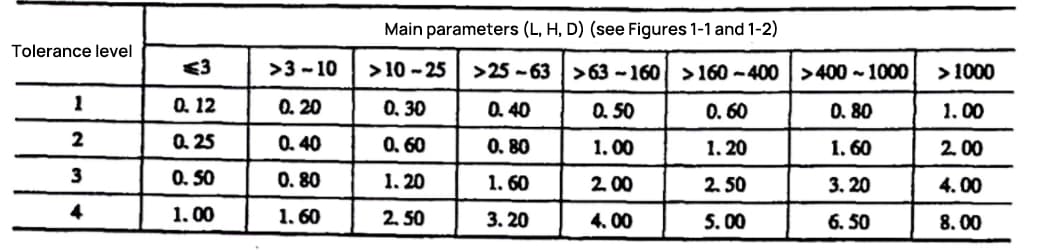
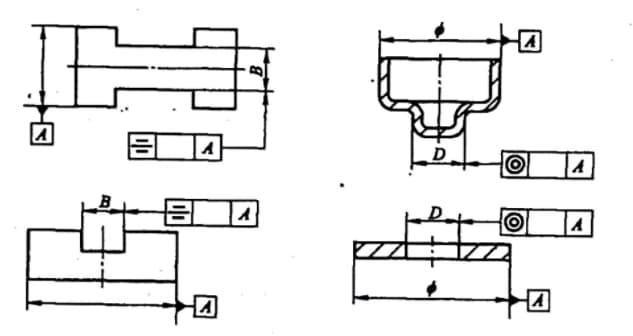
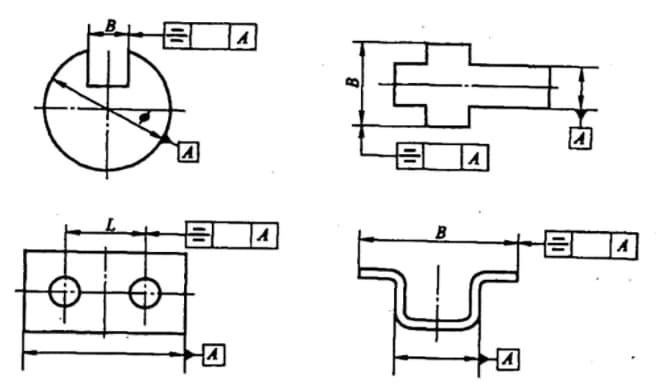
Coaxiality, symmetry, and primary parameters (L, H, D) are indicated in firgure below.
Unit: mm
Unit: mm
Note:
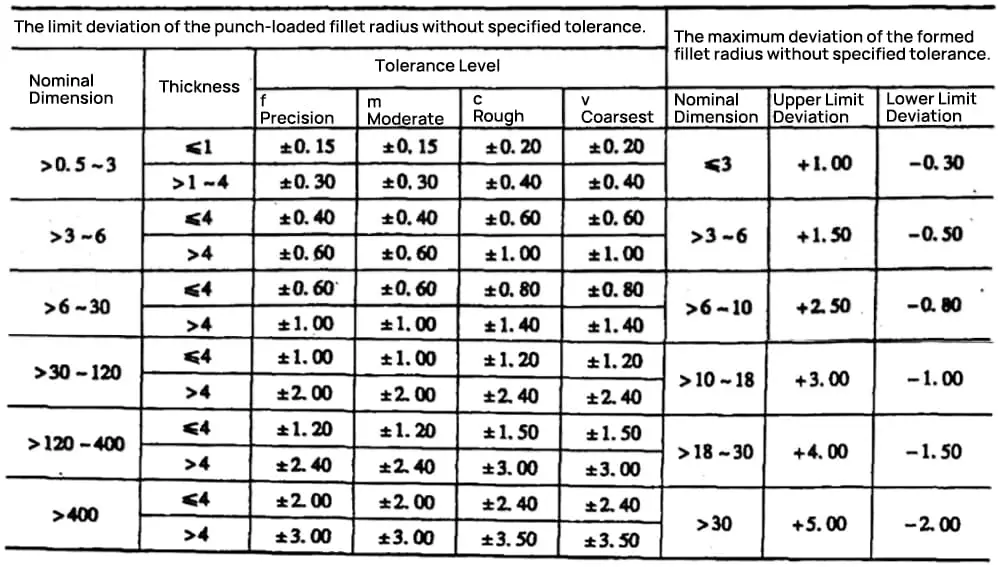
Unit: mm
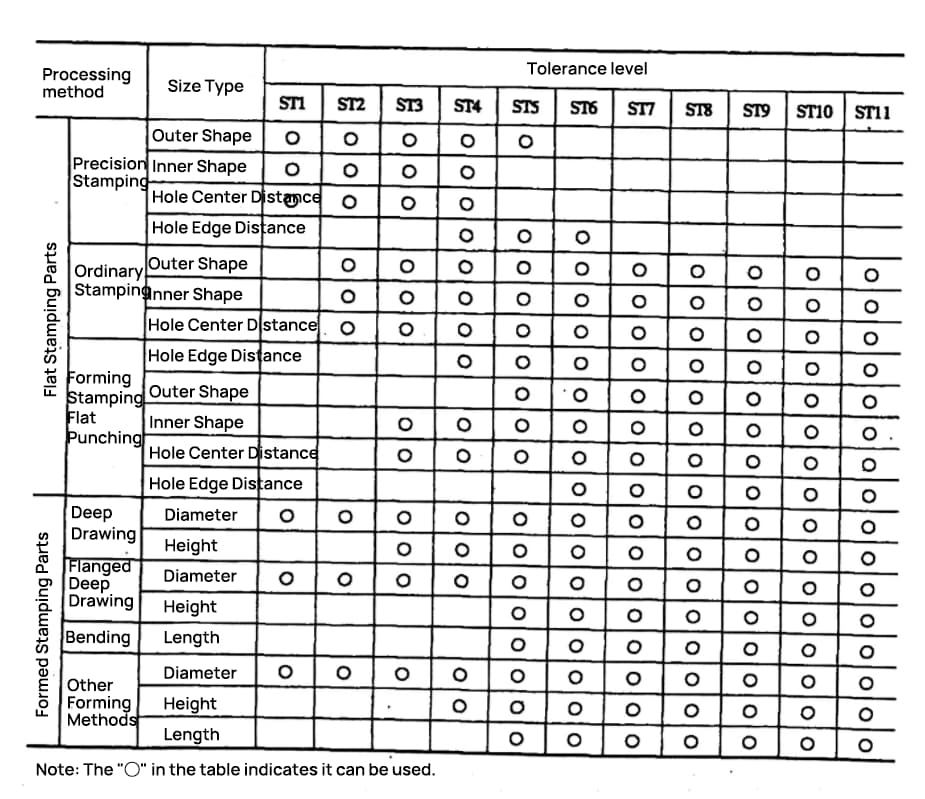
Unit: mm
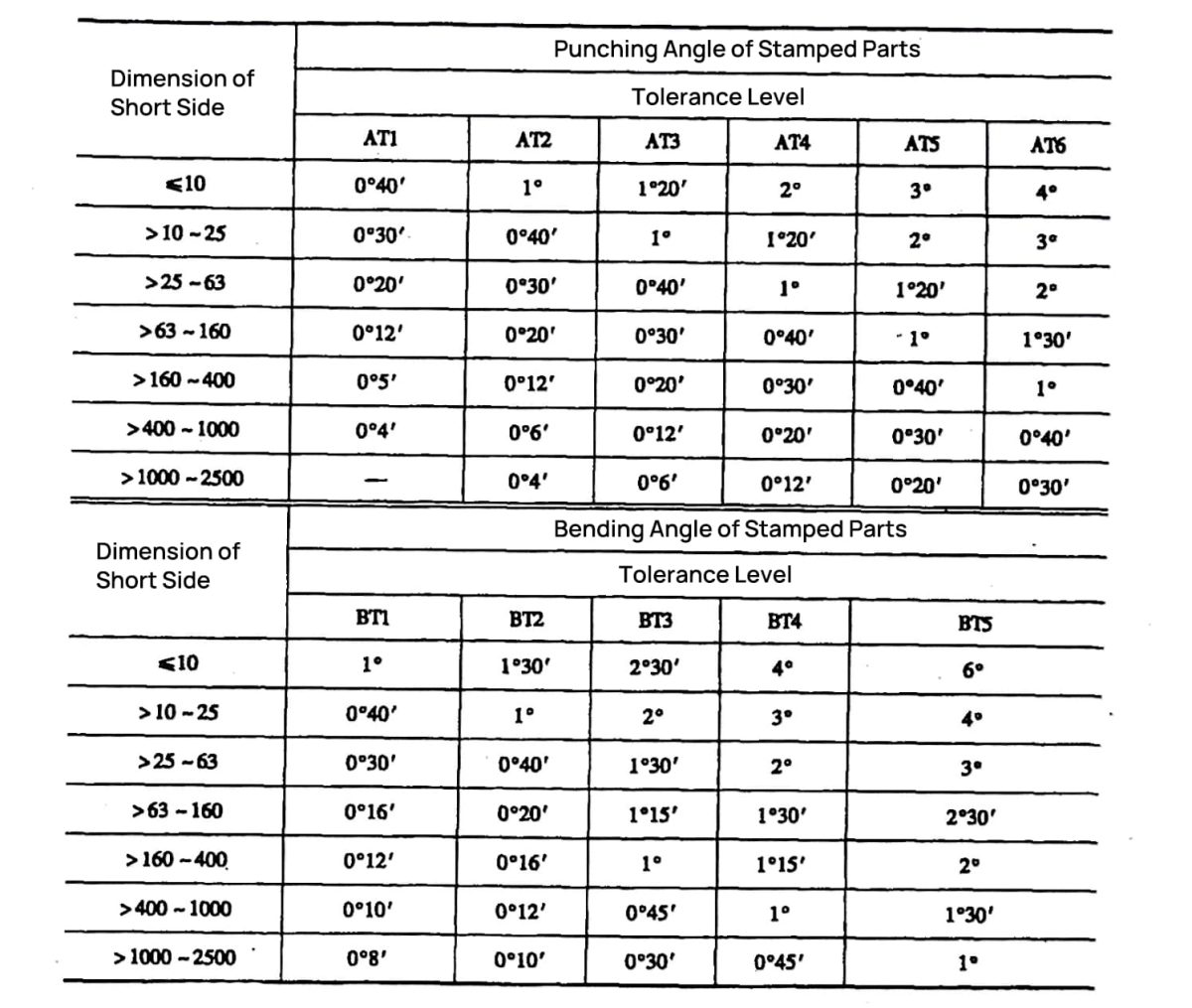
Note:
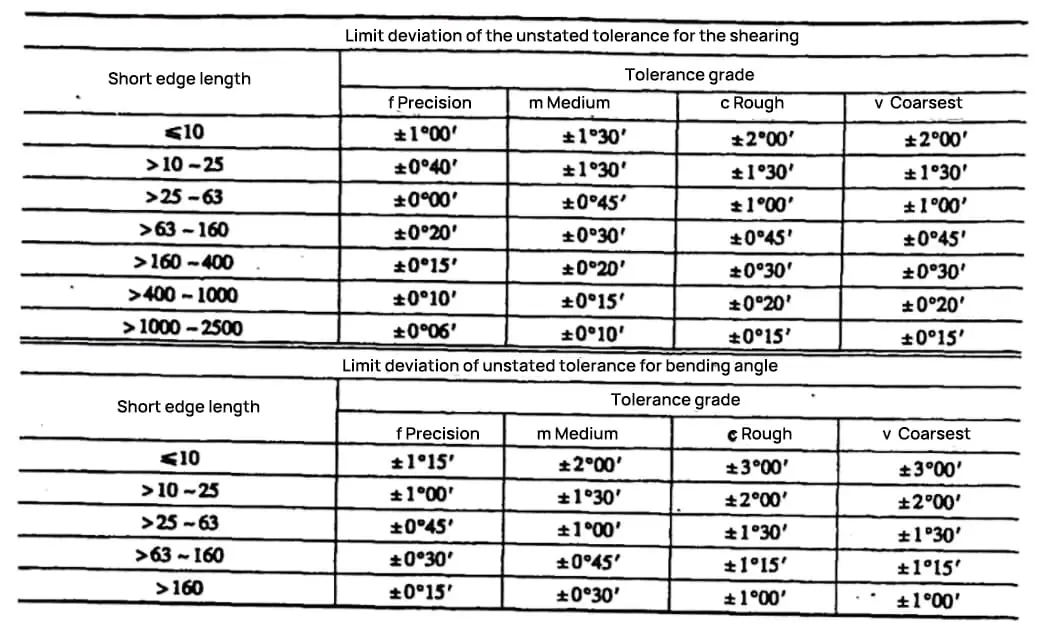
Unit: mm
Unit: mm
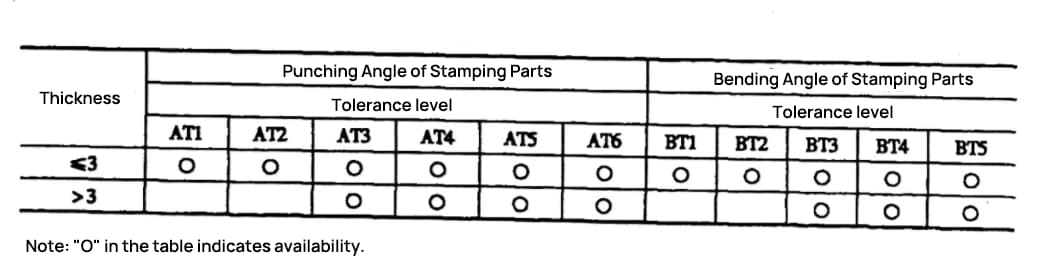
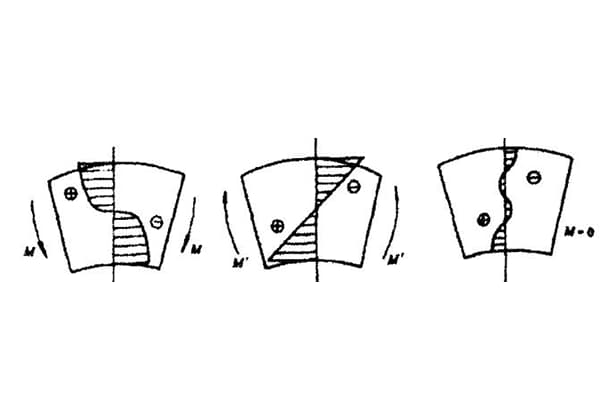
The primary parameters (L, H, D) for flatness and straightness are indicated as shown in Figures 1-3.
Unit: mm