Have you ever wondered how the sleek finish on your smartphone or the shiny surface of your laptop is achieved? This article explores the fascinating world of aluminum alloy surface treatments. You’ll learn about the various techniques used to enhance both the durability and appearance of everyday metal products. Get ready to uncover the secrets behind the technology that makes your gadgets both beautiful and long-lasting!

In the mid-19th century, due to the very backward technology of aluminum smelting in France, the ministers of the princes could only use silver tableware at banquets, and only Napoleon II used an aluminum bowl.
With the application of electrolytic aluminum technology, aluminum has become increasingly integrated into public life. The development of aluminum alloy surface treatment technology has made aluminum not only have high practical value but also aesthetic value.

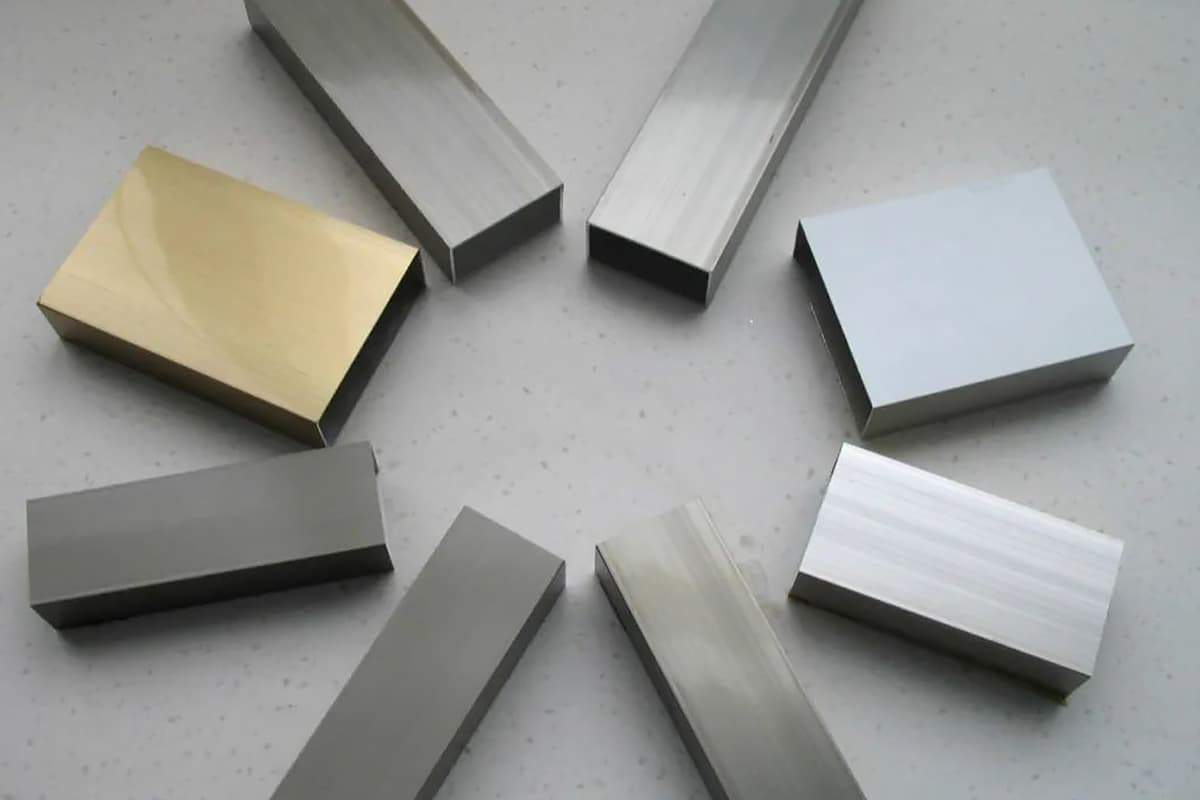
Metal materials are being used more and more in existing products because they can better reflect product quality and highlight brand value. Among many metal materials, aluminum is the first choice of various manufacturers because of its easy processing, good visual effect, and rich surface treatment methods.
Surface Treatment: This process involves the application of a protective layer on the surface of a product, using mechanical and chemical methods. This protective layer maintains stability in the natural environment, enhancing the product’s corrosion resistance, aesthetics, and thus, its value.
The choice of surface treatment type should primarily consider factors like operating conditions, lifespan, aesthetic appreciation, and of course, economic value.

The surface treatment process consists of pre-treatment, film formation, post-film treatment, packaging, warehousing, and shipping. The pre-treatment includes mechanical and chemical processes.
Mechanical processes include sandblasting, shot blasting, grinding, polishing, and waxing. These aim to eliminate uneven surfaces and rectify any adverse appearance.
Chemical treatment helps remove oil and rust from the product surface while forming a layer that enables better bonding with the film-forming substances, transforming it into a reactive metal body. This ensures the coating has a stable state, improving the bonding strength of the protective layer and consequently protecting the product.
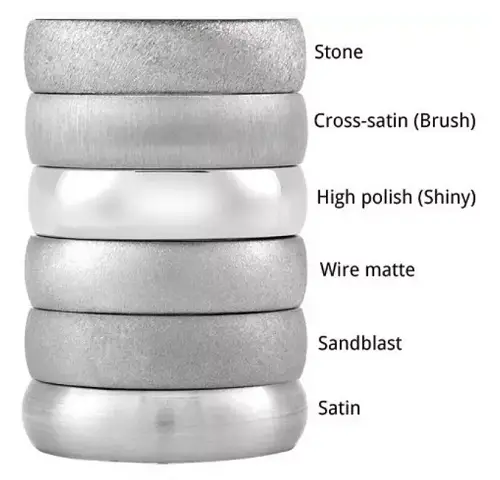
Common surface treatment methods for aluminum materials include chromium (Ge) treatment, painting, electroplating, anodizing, electrophoresis, and other processes in chemical treatment. Mechanical treatments consist of wire drawing, polishing, sandblasting, grinding, and more.
Aluminum alloy sheets can be categorized into non-painted and painted products, according to their surface treatment methods.
1. Non-painted products:
(1) They can be subdivided into hammer-patterned aluminum sheets (with irregular patterns), embossed sheets (with regular patterns), and pre-dull and anodized aluminum surface treatment sheets.
(2) These products do not undergo paint treatment on their surface, so their appearance requirements are not high, and they are comparatively less expensive.
2. Painted products:
(1) Classification:
Depending on the painting process, they can be classified into spray-painted and pre-rolled painted sheets;
Based on the type of paint used, they can be classified into polyester, polyurethane, polyamide, modified silicone, epoxy resin, fluorocarbon, and others.
(2) Among the various coatings, the primary performance difference lies in their resistance to the sun’s UV rays. The most commonly used coating on the front is fluorocarbon paint (PVDF), which has a strong UV resistance; on the back, polyester or epoxy resin coating can be chosen as the protective paint.
Let’s take a look at the surface finishing process of aluminum and aluminum alloys in our daily products.
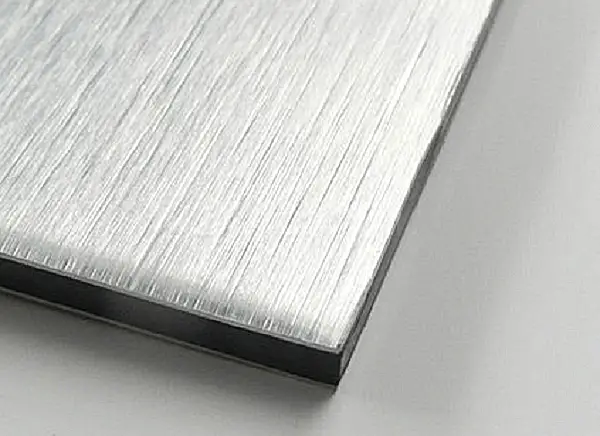

Metal wire drawing is a manufacturing process in which sandpaper is used to repeatedly scrape the surface of the material to produce a series of fine lines.
Drawing can be divided into straight drawing, random drawing, swirl drawing, and thread drawing.
The metal wire drawing process can create fine lines on the surface of the material, producing a silky and matte finish. The resulting product combines both style and technology.

The diamond carving knife is mounted on the spindle of a high-speed engraving machine (typically 20,000 rpm) to carve parts, generating a highlighted area on the surface of the product.
The brightness of the highlighted area is affected by the speed of the milling bit. The faster the speed, the brighter the light, while the slower the speed, the darker the light and it is easy to produce knife marks.
High-gloss high-light cutting is especially used in mobile phones, such as the iPhone 5. In recent years, some high-end TV metal frames have adopted high-gloss milling technology, combined with anodizing and wire drawing technology, making the TV appear fashionable and technologically advanced.

Two-color anodization refers to the process of anodizing a product and imparting a different color to a particular area.
The two-color anodizing process is complicated and costly; however, the contrast between the two colors can better reflect the high-end and unique appearance of the product.

Anodization refers to the electrochemical oxidation of a metal or alloy. It is the process of forming an oxide film on the surface of an aluminum article (anode) and its alloy under corresponding electrolyte and specific process conditions due to the application of current.
Anodizing can not only solve the defects of aluminum surface hardness and wear resistance, but also prolong the service life of aluminum and enhance its appearance. It has become an indispensable part of aluminum surface treatment and is the most widely used and highly successful process.
Primarily, anodizing is applied to aluminum, leveraging electrochemical principles to create an Al2O3 (aluminum oxide) film on the surface of aluminum and its alloys. This oxide film possesses special attributes like protection, decoration, insulation, and abrasion resistance.
Process: Single or gradient color: Polishing/Sandblasting/Wire drawing → Degreasing → Anodizing → Neutralization → Dyeing → Sealing → Drying

Applicable to stainless steel, aluminum alloys, etc., electrophoresis imparts various colors to the product while preserving the metallic luster. Concurrently, it enhances the surface properties and has good anti-corrosion performance.
Process: Pre-treatment → Electrophoresis → Drying
Technical features:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Moderate defect coverage ability; die-casting parts require high pre-treatment for electrophoresis.

This is a process that forms a ceramic surface film layer by applying high voltage in an electrolytic solution (generally a weak alkaline solution). It is the result of physical discharge and electrochemical oxidation.
Process: Pre-treatment → Hot water wash → MAO → Drying
Technical features:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Currently, color options are limited, with only black, grey, etc., being mature; vibrant colors are challenging to achieve. The cost is primarily affected by high electricity consumption, making it one of the most expensive surface treatments.
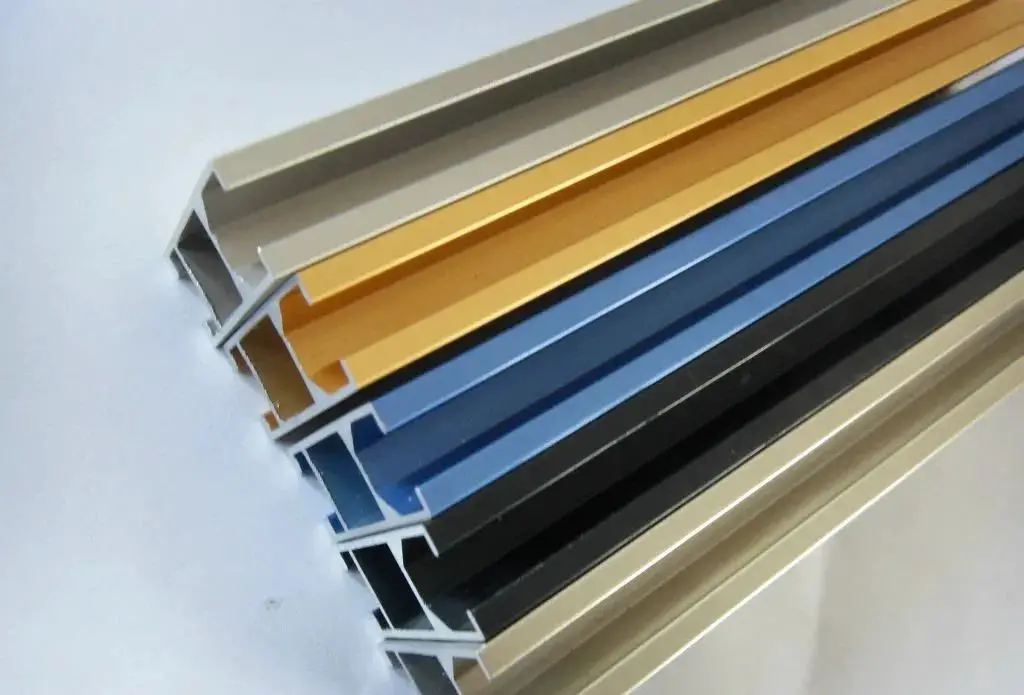
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is an industrial manufacturing process, a technique primarily used to deposit thin films through physical processes.
Process: Pre-cleaning for PVD → Vacuum furnace loading → Target cleaning and ion cleaning → Coating → End of coating, cooling and unloading → Post-processing (polishing, AFP)
Technical features:
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) can deposit high-hardness, high-wear-resistant metal ceramic decorative coating on the metal surface.
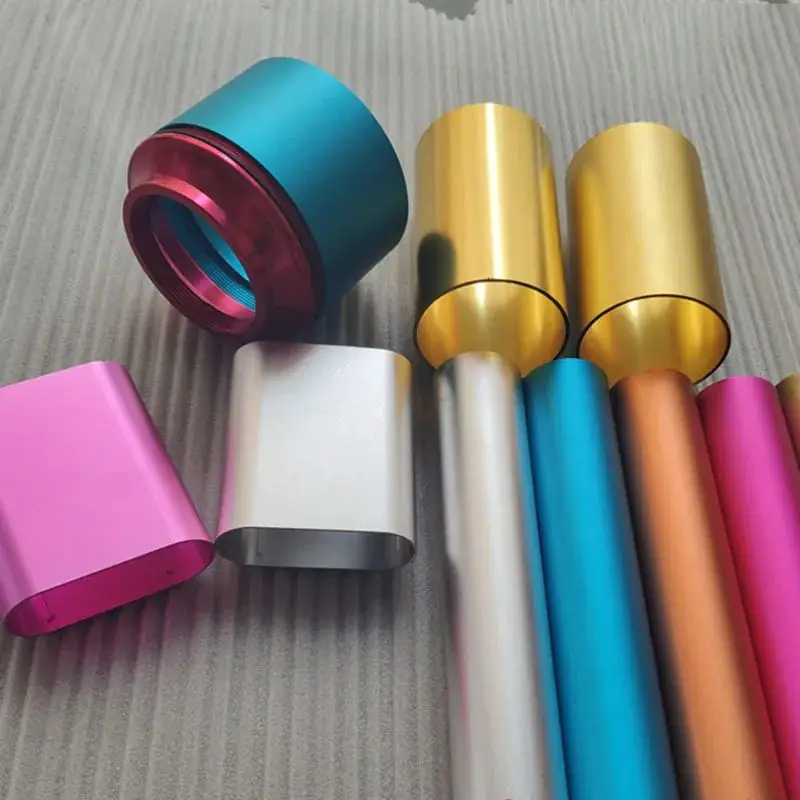

Electroplating is a technique that uses electrolysis to coat the surface of a metal with a thin layer of metal film, thereby providing protection against corrosion and enhancing wear resistance, electrical conductivity, reflectivity, and aesthetics.
Process flow: Pretreatment → Cyanide-free Alkaline Copper → Cyanide-free White Copper-Tin → Chromium Plating
Technical Features:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Poor environmental protection, high risk of environmental pollution.

Powder coating is a process where a powder coating device (electrostatic powder sprayer) sprays the powder coating onto the surface of the workpiece. Under electrostatic action, the powder uniformly adheres to the surface of the workpiece, forming a powdered coating. After high-temperature leveling and baking, the powdered coating turns into a final coating with varying effects depending on the type of powder coating used.
Process flow: Piece mounting → Electrostatic dust removal → Coating → Low-temperature leveling → Baking
Technical Features:

Wire drawing is a surface treatment method that forms linear striations on the surface of a product through grinding, creating a decorative effect. Depending on the pattern of the striations after wire drawing, it can be divided into: straight line drawing, random line drawing, wave pattern, and spiral pattern.
Technical Features: Wire drawing treatment can give the metal surface a non-mirror-like metallic luster, while also eliminating minor defects on the metal surface.

Sandblasting is a process that uses compressed air as the power to form a high-speed jet stream, which blasts the blasting material at high speed onto the surface of the workpiece to be processed, causing changes in the exterior surface or shape of the workpiece and achieving a certain level of cleanliness and different levels of roughness.
The process involves cleaning and roughening the metal surface using high-velocity sand flow.
This method of aluminum surface treatment can achieve a certain degree of cleanliness and different levels of roughness on the surface of the workpiece, which improves the mechanical properties of the workpiece’s surface.
As a result, the workpiece’s fatigue resistance is improved, the coating’s adhesion is increased, the durability of the coating film is prolonged, and the coating’s leveling and decoration are also facilitated.
This process is often seen in various Apple products and is increasingly used in the manufacturing of TV sets or middle frames.
Technical Features:

Polishing is a modification process performed on the workpiece surface using a flexible polishing tool and abrasive particles or other polishing mediums.
Depending on the polishing process: rough polishing (basic polishing process), medium polishing (fine machining process) and fine polishing (glossing process), selecting the appropriate polishing wheel can achieve the best polishing effect and increase polishing efficiency.
It improves the dimensional accuracy or geometric precision of the workpiece, achieves a smooth surface or mirror-like gloss, and can also remove gloss.
Mechanical, chemical, or electrochemical methods are used to reduce the surface roughness of the workpiece to obtain a bright, flat surface.
The polishing process is mainly divided into mechanical polishing, chemical polishing, and electrolytic polishing.
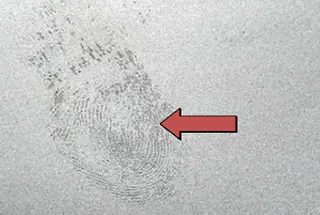
Aluminum parts can be mechanically polished and electrolytically polished to achieve a mirror effect close to that of stainless steel, giving people a feeling of high-grade simplicity and fashionable future. Of course, this surface finish is prone to fingerprints and requires more care.

Etching, often referred to as photochemical etching, involves removing the protective film from the area to be etched after exposure and development, making contact with a chemical solution during etching, to dissolve and corrode, forming embossed or hollowed-out shaping effects.
Process flow:
Exposure method: The engineer opens the material size according to the graphics – Material preparation – Material cleaning – Drying → Film sticking or coating → Drying → Exposure → Development → Drying – Etching → Film removal → OK
Screen printing method: Material cutting → Cleaning the plate (stainless steel and other metal materials) → Screen printing → Etching → Film removal → OK
Technical Features:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
The corrosive liquid used during etching (acid, alkali, etc.) is mostly harmful to the environment.