Have you ever struggled with choosing the right laser cutting nozzle for your project? Selecting the optimal nozzle is crucial for achieving clean, precise cuts and maximizing efficiency. In this article, we’ll explore the key factors to consider when making this decision and provide expert insights to help you make an informed choice. Discover how the right nozzle can elevate your laser cutting results to new heights.
In the realm of laser cutting, the efficiency and quality of the cut are paramount. One often overlooked yet critical component in this process is the laser cutting nozzle. Despite its small and inconspicuous appearance, the nozzle plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance. This article delves into the significance of selecting the right nozzle and provides insights into making an informed choice.
The laser cutting nozzle serves several essential functions:

The quality of the nozzle used in a laser cutting head makes a significant difference in the performance and results achieved. Several key factors are directly impacted by the nozzle material and precision:
A high-quality nozzle serves critical functions:
Therefore, the nozzle quality has a direct effect on both the service life of the cutting head and the cut quality of the workpiece.
The nozzles provided by the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) of the cutting head tend to command premium prices. This has created a strong demand for more affordable third-party nozzles.However, not all third-party suppliers have the manufacturing capabilities to produce nozzles that match the quality and precision of OEM consumables. As the prices of fiber laser cutters have become more competitive in recent years, there is increased price pressure on accessories like nozzles as well.
Pursuing the lowest possible price while neglecting quality considerations for critical components like nozzles is likely to be counterproductive. Using inferior nozzles increases the risk of:
The selection and maintenance of nozzles in laser cutting machines are critical for ensuring optimal performance and precision. Improper selection or poor maintenance of nozzles can lead to several adverse consequences, significantly impacting the cutting process and the quality of the final product. Here are the key consequences:
Nozzles play a crucial role in directing the laser beam and the assist gas to the cutting area. If the nozzle design is not appropriate or if it is not well-maintained, the precision of the laser beam can be compromised. This can lead to inaccuracies in the cutting path, resulting in parts that do not meet the required specifications.
The assist gas, typically oxygen or nitrogen, is essential for the cutting process as it helps in removing molten material from the cut and prevents oxidation. An improperly selected nozzle can restrict the gas flow rate, leading to insufficient gas supply at the cutting point. This can cause poor cut quality and increased dross formation on the edges of the cut material.
The nozzle must ensure a stable and directed airflow to maintain a clean and precise cut. If the nozzle is not designed correctly or is damaged, the airflow can become turbulent and unstable. This instability can disrupt the cutting process, leading to irregular cuts and increased roughness on the cut edges.
The laser cutting process relies on the efficient melting and removal of material. Improper nozzle selection can affect the laser’s ability to focus accurately on the material, leading to inefficient melting. This inefficiency can cause incomplete cuts, especially in thicker materials, making it difficult or even impossible to achieve the desired cut depth.
When the nozzle fails to direct the assist gas properly, molten debris can accumulate around the cutting area. This debris can adhere to the surface of the material, causing defects and requiring additional post-processing to clean up. Excessive molten debris can also damage the nozzle and other components of the laser cutting machine.
Thicker materials require precise and powerful laser cutting capabilities. An improperly selected nozzle can hinder the laser’s ability to penetrate and cut through thicker materials effectively. This can result in incomplete cuts, increased wear on the laser cutting machine, and potential damage to the material being processed.
Selecting a nozzle that is too large

Selecting a nozzle that is too small

In the context of sheet metal processing, particularly in laser cutting and similar applications, nozzle design plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency and quality of the cutting process. There are primarily two types of nozzle designs utilized based on the gas flow rate:
1. Low-Speed Nozzle
A low-speed nozzle is characterized by a gas flow rate that is lower than the speed of sound. These nozzles are typically used in applications where high precision and control over the cutting process are required. However, they may not be as effective in cutting thicker or more viscous materials due to their lower gas velocity.
2. High-Speed Nozzle
A high-speed nozzle operates with a gas flow rate that is close to the speed of sound. The working principle of a high-speed nozzle is akin to the exhaust mechanism of a rocket or jet engine, where the gas is accelerated as it passes through the nozzle. This acceleration effect enhances the cutting performance, especially for viscous materials, by providing a more concentrated and powerful gas jet.
Several factors influence the performance of both low-speed and high-speed nozzles:
The pressure of the gas within the cutting head cavity is critical. Higher gas pressure can improve the cutting speed and quality by ensuring a more focused and powerful gas jet.
The diameter of the nozzle affects the flow rate and the concentration of the gas jet. A smaller diameter can produce a more concentrated jet, which is beneficial for precision cutting, while a larger diameter may be used for cutting thicker materials.
The internal shape of the nozzle determines how the gas is directed and accelerated. A well-designed internal shape can minimize turbulence and maximize the efficiency of the gas flow.
The shape of the nozzle outlet also plays a significant role in the cutting process. A properly shaped outlet can ensure a uniform gas flow and reduce the chances of irregularities in the cut.

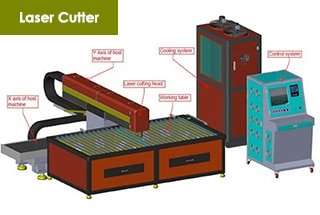
Laser cutting is currently recognized as one of the most efficient, high-quality, and precise methods of metal processing. Various factors affect laser cutting, and the nozzle is one of them. Selecting the appropriate nozzle when cutting different materials can simplify the processing. But how can we correctly choose the right nozzle? Let’s take a look today.
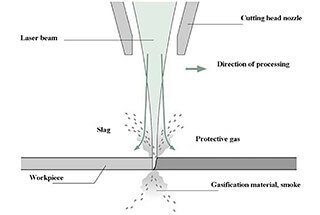
The nozzle, also known as the copper nozzle, is one of the very important components in laser cutting. Located at the lower end of the cutting head, both the laser beam and auxiliary gas act on the cutting material through the nozzle. Its main function is to gather the auxiliary gas and form high pressure, releasing it onto the surface and into the kerf of the cutting material. This blows away the parent material that has melted and vaporized during the cutting process, leaving a clean kerf. At the same time, it prevents pollutants like molten slag and dust from bouncing back up, thus protecting the internal lens.
To achieve better cutting sections, it is necessary to control the concentricity of the laser beam and the nozzle center, which is one of the important factors affecting cutting quality. Therefore, the nozzle must be coaxial with the laser beam to get better cutting sections.
When the nozzle center and the laser beam center are not coaxial, the effects on cutting quality are as follows:

To achieve better cutting sections, it is necessary to control the concentricity of the laser beam and the nozzle center, which is one of the important factors affecting cutting quality. Therefore, the nozzle must be coaxial with the laser beam to get better cutting sections.
To verify whether the laser beam and the nozzle are coaxial, the following steps are required for testing:

If the hole is in the center of the circle, this means that the laser beam and the nozzle are coaxial, and no adjustment is needed. If the hole is not coaxial with the center of the circle, or if the hole cannot be seen (the laser beam hits the inner wall of the nozzle), you need to adjust the adjustment screw on the laser cutting head. Repeat steps 1-3 until the laser hole coincides with the center of the nozzle.
Single layer nozzles are characterized by relatively slow gas flow speeds. They are commonly used for cutting metals such as stainless steel, aluminum alloy, and copper. These nozzles typically utilize nitrogen as the auxiliary gas. The slower gas flow is suitable for these materials as it helps in achieving cleaner cuts without excessive oxidation.
Double layer nozzles, on the other hand, have faster gas flow speeds, making them suitable for high-speed cutting applications. They are often used for cutting carbon steel and generally employ oxygen as the auxiliary gas. The high-speed gas flow enhances the cutting efficiency, but it also causes the cutting surface to turn black due to oxidation.
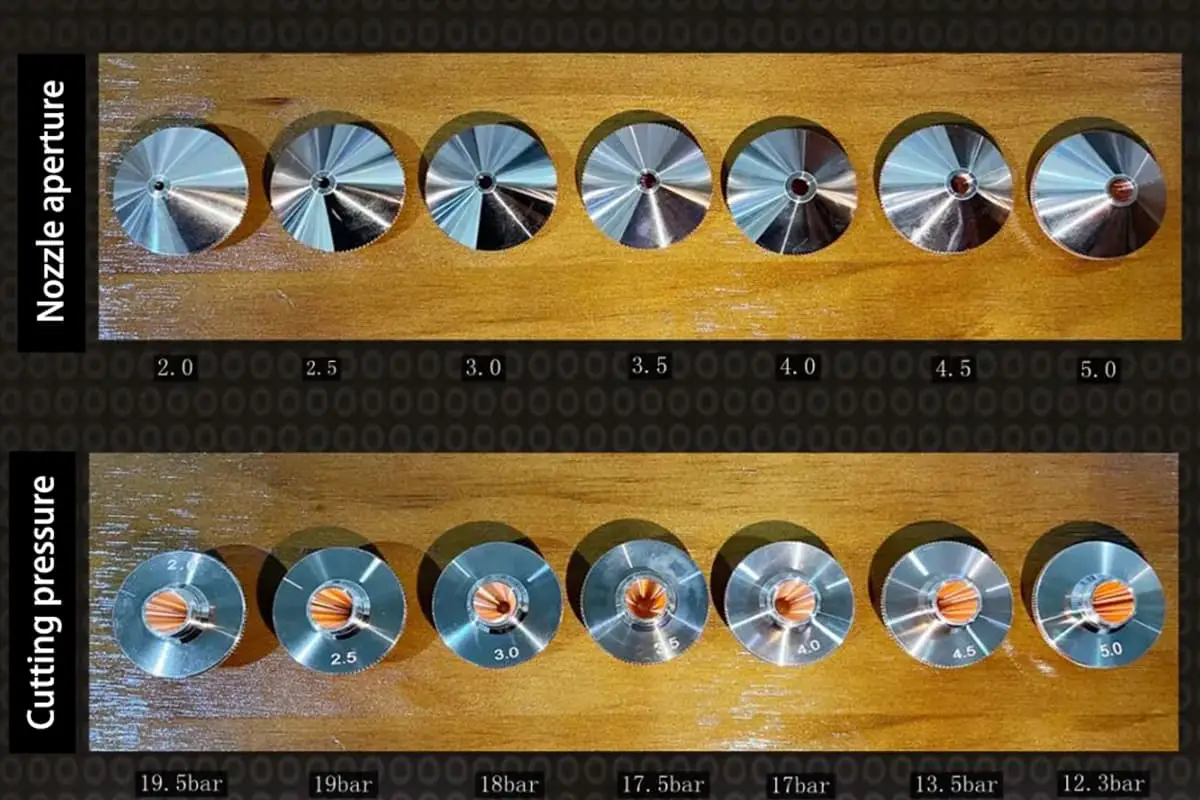
The size of the nozzle opening is crucial as it determines the gas flow speed acting on the cutting material, which in turn affects the removal of molten material. Here are some key points to consider:
Nozzles are commonly made from two materials:
The aperture size of the nozzle determines the gas flow rate and the shape of the gas field. Recommendations based on material thickness are as follows:

There are several types of nozzles commonly used in industrial applications. Here are some of the most common ones:
Single-Layer Nozzle – S

Features: Conical inner wall with high gas flow rate for slag blowing.
Purpose: Melting cutting of materials such as stainless steel and aluminum plate.
Double-Layer Nozzle – D

Features: Double-layer composite nozzle with an added inner core on the basis of a single-layer nozzle.
Purpose: Double-layer 2.0 or larger for carbon steel sand cutting
High-speed Double-Layer Nozzle – E

Features: The nozzle has a pointed shape, and the three holes on the edge of the inner core are larger than those of a regular double-layer nozzle.
Purpose: It is mainly used for high-power, high-speed, and high-quality cutting of carbon steel up to 20mm thickness with a smooth and bright surface finish.
High-speed Single-Layer Nozzle – SP

Features: The nozzle has a pointed shape, with a conical inner wall that features a stepped design.
Purpose: It is mainly used for high-power, high-speed cutting of carbon steel with a thickness above 20mm, resulting in a smooth and bright surface finish. It is also suitable for oxygen-focusing cutting applications.
High-speed Single-Layer Nozzle – SD

Features: The nozzle has a pointed shape with a conical inner wall and a larger nozzle orifice area.
Purpose: It is mainly used for high-speed cutting of carbon steel with a thickness above 20mm, resulting in a smooth and stable cutting performance with better cutting quality.
Boost Nozzle – B

Features: Improved from a single-layer nozzle, the nozzle has a step layer at the nozzle orifice.
Purpose: It can be used for high-power cutting of stainless steel and carbon steel with nitrogen or compressed air at low pressure.
For a BLT 12kW laser cutting head, the focal point must be calibrated when paired with different nozzles. Here are the recommended focal points for various nozzles:
Proper installation and calibration of the nozzle are critical to ensure optimal performance and cutting quality. Incorrect installation or calibration can lead to poor cutting results, increased wear on the machine, and potential damage to the workpiece. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for nozzle installation and calibration to achieve the best results.
When selecting nozzles for laser cutting carbon steel with oxygen, the power of the laser and the thickness of the material are critical factors. Below are the suggested nozzles based on the laser power and material thickness:
| Laser | Cutting thickness (bright surface cutting of carbon steel with oxygen) | Suggested nozzle |
|---|---|---|
| Low power laser (≤6000W) | 16-20mm | 1.4D-1.6D general conical nozzle |
| High power laser (≥6000W, using Raycus 12kW as an example) | 3-12mm | 1.2E dual-layer high-speed nozzle |
| 12-14mm | 1.2B-1.4E dual-layer high-speed nozzle | |
| 16-20mm | 1.4E-1.6E dual-layer high-speed nozzle | |
| 22-35mm | SP1.4-SP1.8 single-layer high-speed nozzle or 1.4E-1.8E dual-layer high-speed nozzle | |
| 35-40mm | SP1.6-SP1.8 single-layer high-speed nozzle or 1.6E-1.8E dual-layer high-speed nozzle |
The quality of nozzles available on the market can vary significantly. It is recommended to carefully distinguish the nozzles according to the specifications provided above and to purchase through reputable and regular channels to ensure optimal performance and cutting quality.
By adhering to these recommendations, you can achieve efficient and high-quality cutting results for carbon steel using laser technology.