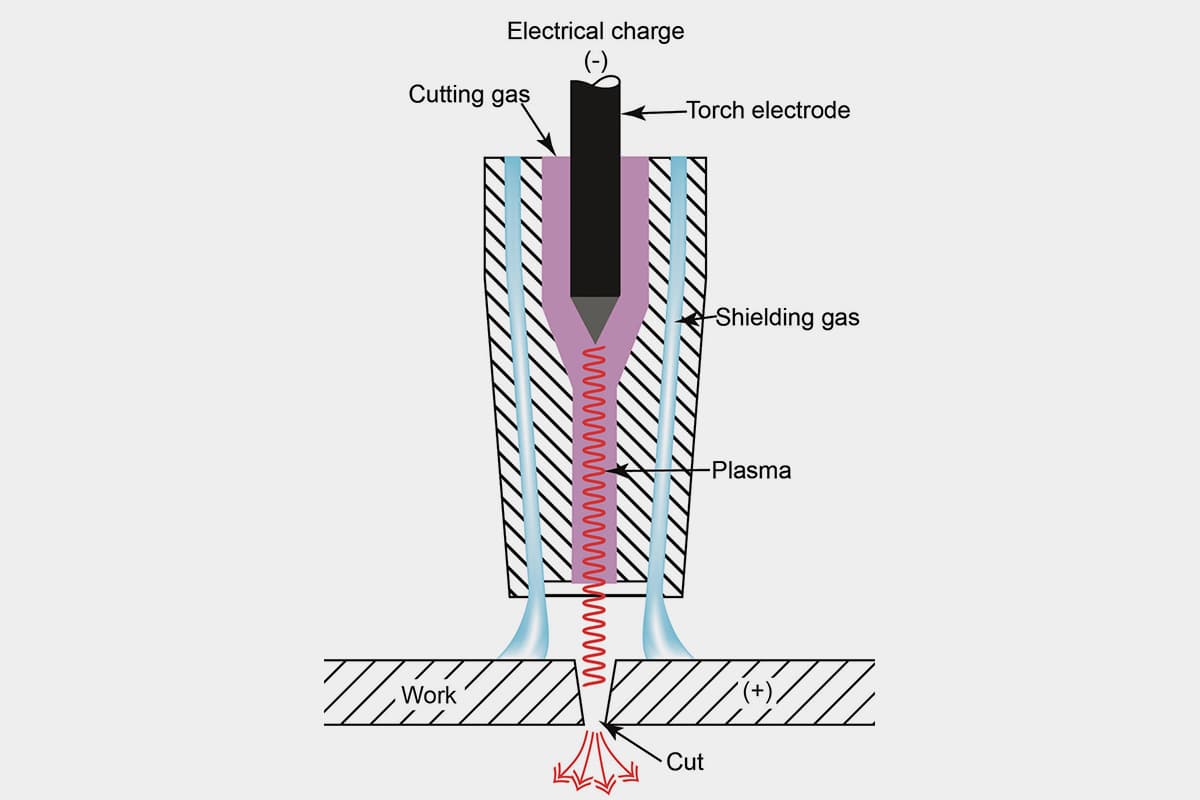
Is your plasma cutter acting up, and you can’t figure out why? Whether it’s a broken torch or unstable arcs, this guide tackles common plasma cutter issues head-on. From power problems to airflow issues, you’ll discover practical troubleshooting steps to get your machine back in top shape. Read on to learn how to diagnose and fix your plasma cutter, ensuring smooth and efficient operation every time.


| No. | Problem Symptoms | Cause of the Problem | Troubleshooting Method |
| 1 | The power indicator light does not turn on after switching on the “Power Switch” of the plasma cutting machine main unit. | The “Power Indicator Light” is broken. | Replace |
| 2A fuse is broken. | Replace | ||
| No input three-phase 380V voltage. | Repair | ||
| Input power phase loss. | Use a multimeter to check the three-phase power supply. | ||
| The power switch is broken. | Replace | ||
| Control board or main unit is broken. | Repair | ||
| 2 | After connecting the input power, the fan of the plasma cutting machine does not rotate, but the power indicator light is on. | Phase loss in the three-phase input power. | Use a multimeter to check the three-phase power supply. |
| The fan blade is jammed by a foreign object. | Remove foreign objects. | ||
| The fan power plug is loose. | Replug it. | ||
| The fan lead is broken. | Repair | ||
| The fan is damaged. | Repair or replace. | ||
| 3 | After connecting the input power, the power indicator light is on and the fan is normal, but there is no airflow ejected after turning on the “Test Air” switch. | No input compressed air. | Inspect and repair the air source and supply pipeline. |
| Air filter pressure reducing valve fails, the pressure gauge indicates 0, and the “insufficient air pressure” indicator light is on. | Adjust the pressure of the pressure reducing valve or replace the pressure reducing valve. | ||
| The “Test Air” switch is broken. | Replace | ||
| The electromagnetic valve in the main unit is broken. | Repair or replace. | ||
| The gas supply pipeline is leaking or broken. | Maintenance | ||
| 4 | When the “Test Air” switch on the main panel is turned on, airflow is ejected, but the machine does not respond when the torch switch is pressed. | The plasma torch switch is broken or the connection line is broken. | Repair or replace. |
| The “Cutting” switch on the plasma cutting machine panel is broken. | Repair or replace. | ||
| The control board of the cutting machine main unit is broken. | Repair or replace. | ||
| The host control transformer or related circuits and components are damaged. | Maintenance | ||
| The cutting machine is in a protective state due to temperature or other reasons. | Wait for the temperature to normalize. | ||
| The water circuit is not working properly, causing low water pressure protection. | Check the water circuit and water pressure valve. | ||
| 5 | When the plasma torch switch is pressed, there is airflow from the nozzle, but neither “High Gear” nor “Low Gear” can cut. | Phase loss in the input power. | Maintenance |
| Air pressure is less than 0.45Mpa. | Adjust the pressure of the pressure reducing valve. | ||
| The input air flow is too small. | Ensure 0.3m3/min. | ||
| Poor contact between the cutting ground wire and the workpiece. | Re-clamp or replace. | ||
| Electrode nozzle or other parts in the torch are damaged. | Replace with new parts. | ||
| The cutting method is incorrect. | Place the nozzle and workpiece correctly. | ||
| The cable of the plasma cutting machine’s torch is broken. | Replace or reconnect properly. | ||
| The gap in the “spark discharger” in the main unit is too large or short-circuited. | Ensure a gap of about 0.5mm. | ||
| Some components in the main unit are damaged, such as: pressure controller, etc. | Repair or replace. | ||
| The control board in the main unit is damaged. | Repair or replace. | ||
| The torch of the plasma cutting machine is damaged. | Replace | ||
| 6 | Contact cutting is possible, but non-contact cutting is not. No sparks are ejected from the nozzle during non-transferred arc testing. | The 15A fuse core is broken. | Replace |
| The air pressure on the pressure reducing valve is too high. | Adjust the pressure. | ||
| Some parts in the torch are damaged. | Replace | ||
| The torch is damp, and the moisture content in the compressed air is too high. | Dry and add a water filter device. | ||
| The arc ignition line is broken. | Replace | ||
| The torch is damaged. | Replace | ||
| 7 | Only one gear can work in both high and low gears. | The thick cut selection switch is broken or the wire is broken. | Replace |
| One of the AC contactors is damaged. | Replace | ||
| The main rectifier is broken or the related wire is broken. | Repair or replace. | ||
| 8 | The plasma arc is unstable when the plasma cutting machine is working. | The air pressure is too low or too high. | Adjust |
| The electrode or nozzle in the torch is burnt. | Replace | ||
| The input AC voltage is too low. | Adjust the input voltage. | ||
| Poor contact between the cutting ground wire and the workpiece. | Re-clamp or replace. | ||
| The cutting movement speed is too slow. | Adjust the cutting speed. | ||
| The spark discharger cannot automatically break the arc. | Discharge normally for 0.5s, then repair. | ||
| Related components in the main unit are not working properly. | Maintenance | ||
| 9 | The cutting thickness does not reach the rated index. | Low input voltage. | Adjust the input voltage. |
| The diameter of the input power line is too small, causing too much line loss. | Increase the input capacity. | ||
| The pressure of the input compressed air is too low or too high. | Adjust the air pressure. | ||
| The flow of compressed air is too small. | Ensure the flow of compressed air. | ||
| The selected gear for cutting thickness is inappropriate. | Switch to high gear. | ||
| The cutting speed is too fast. | Slow down the cutting speed. | ||
| The material of the workpiece does not match. | Adjust the parameters. | ||
| The nozzle hole has been burnt. | Replace the nozzle. | ||
| The electrode is burnt. | Replace | ||
| The nozzle model is incorrect. | Change to the correct model of nozzle. | ||
| There is a gas leak in the air duct. | Repair or replace. | ||
| 10 | The cut is skewed. | The electrode nozzle has been damaged. | Replace |
| The installation position of the electrode nozzle is not concentric. | Reinstall correctly. | ||
| The cutting speed is too fast. | Slow down the cutting speed. | ||
| The nozzle axis is not perpendicular to the workpiece surface. | Adjust to solve. | ||
| 11 | The cut is too wide, resulting in poor cutting quality. | The cutting speed is too slow. | Adjust the speed. |
| The electrode nozzle is burnt. | Replace | ||
| The cutting material and thickness do not match the selected switch gear. | Choose the correct gear. | ||
| The nozzle model is incorrect. | Replace the nozzle with the correct model. | ||
| 12 | The torch of the plasma cutting machine is burnt out. | The metal pressure cap is not tightened. | Regularly inspect the connections of the plasma cutting machine’s torch section to ensure all parts work well together. |
| The conductive connection of the torch is loose and leaking. | |||
| Poor insulation at the torch joint. | |||
| The ceramic protective sleeve on the torch is damaged and not replaced. | |||
| Too much moisture in the compressed air. | |||
| The torch is mistaken when the sectional cutting machine is cutting in parallel. | |||
| The electrode was not replaced in time after it was burnt. | |||
| The water circuit is not normal when the water-cooled torch is working, and the interface is leaking. | |||
| 13 | The rectifier diode often burns out. | The reverse breakdown voltage of the newly replaced diode is too low. | Reverse voltage resistance ≥1600V. |
| Some iron-shell capacitors on the protection capacitor board are damaged. | Replace | ||
| The main rectifier transformer is damaged. | Repair or replace. | ||
| The torch is damaged. | Replace |