How do you get the perfect weld? Understanding the intricacies of adjusting welding machine current and voltage is crucial. This article explores the key factors influencing the ideal settings for CO2 gas shielded welding, including the relationship between welding current, voltage, and wire feeding speed. By mastering these elements, you can achieve a stable arc length and superior welding quality. Dive in to learn how to optimize your welding machine settings for the best results.

CO2 gas shielded welding involves melting the welding wire using welding voltage as the energy source.
The welding wire melts at a faster rate as the voltage is increased.
The welding current is determined by balancing the wire feeding speed with the melting speed.
The selection of welding current should be based on various welding conditions such as plate thickness, welding position, welding speed, material, and other relevant parameters.
For carbon dioxide gas shielded welding, it is crucial to ensure that the welding current matches the welding voltage, and that the wire feeding speed and welding voltage are consistent with the melting capacity of the welding wire. This is necessary to maintain the stability of the arc length during the welding process.
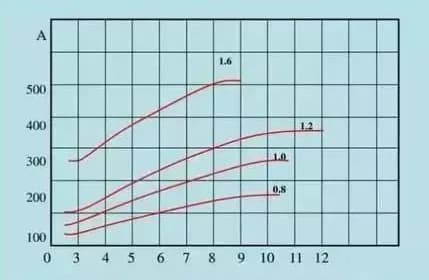
For a given welding wire, increasing the cable size results in a higher wire feeding speed.
Similarly, when the current remains constant, using a thinner welding wire will result in a faster wire feeding speed.
Welding voltage, also known as arc voltage, is responsible for providing the necessary welding energy.
A higher arc voltage translates to greater welding energy, faster melting of the welding wire, and increased welding current.
Arc voltage can be calculated by subtracting the loss voltage of the welding circuit from the output voltage of the welder. This can be expressed using the following formula:
Uarc = Uoutput – Uloss
Assuming that the welding machine has been installed in compliance with the installation requirements, any voltage loss is primarily due to cable extension.
In situations where welding cables need to be extended, the output voltage of the welding machine can be adjusted according to the table below:
| Welding current Cable length | 100A | 200A | 300A | 400A | 500A |
| 10m | About 1V | About 1.5V | About 1V | About 1.5V | About 2V |
| 15m | About 1V | About 2.5V | About 2V | About 2.5V | About 3V |
| 20m | About 1.5V | About 3V | About 2.5V | About 3V | About 4V |
| 25m | About 2V | About 4V | About 3V | About 4V | About 5V |

Choose the appropriate welding current based on the plate thickness and welding conditions, and then calculate the welding voltage using the following formula:
< 300A: welding voltage=(0.05 × Welding current+14 ± 2) V
> 300A: welding voltage=(0.05 × Welding current+14 ± 3) V
Example 1: If the welding current is 200A, the welding voltage is calculated as follows:
Welding voltage=(0.05 × 200+14 ± 2)
=(10+14 ± 2) V
=(24 ± 2) V
Example 2: If the welding current 400A is selected, the welding voltage is calculated as follows:
Welding voltage=(0.05 × 400+14 ± 3)
=(20+14 ± 3) V
=(34 ± 3) V

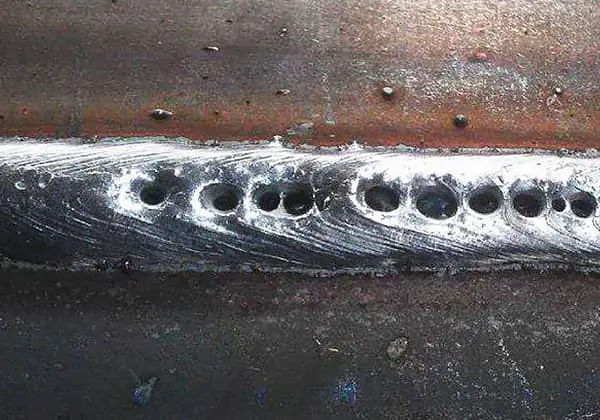
When the voltage is too high, the arc length increases, leading to larger spatter particles that can easily produce pores. Additionally, the weld bead becomes wider, while the solution depth and surplus height become smaller. This can also result in a “patter! patter!” sound.
Conversely, when the voltage is too low, the spatter increases as the welding wire is inserted into the base metal. Furthermore, the weld bead narrows, and both the solution depth and surplus height increase. This can lead to a “bang! bang! bang!” sound.