What defines a good fillet weld? This article delves into the criteria for qualifying fillet welds, discussing the necessary dimensions, acceptable characteristics, and common issues like inadequate throat depth and poor fusion. Readers will gain insights into industry standards and learn how to ensure weld quality for their projects.
When designing a weld, several factors must be taken into consideration such as the weldability of the base metal, the matching of welding materials and the base metal, welding efficiency, the welding method, the size of the weld bead, welding deformation, and buckling of the joint plate.
Related reading: The Ultimate Guide to Welding
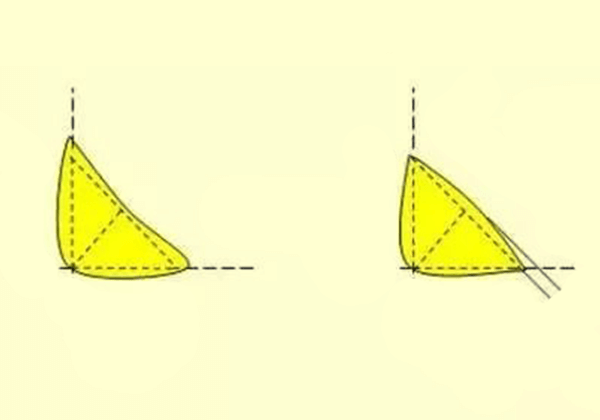
Let’s consider fillet weld beads as an example.
As per the American Welding Society Steel Structure Welding Code (AWSD1.1), fillet weld beads are classified into three categories, which are ideal weld bead, acceptable weld bead width, and unacceptable weld bead.
Inadequate throat depth of fillet weld bead, excessive convex surface, welding corrosion, overlap, insufficient leg length, and poor fusion are considered incorrect weld bead dimensions.
The minimum size of the fillet weld bead is also specified in the Steel Structure Welding Regulations of the American Welding Association and China’s Technical Code for Design of Steel Structures of Steel Buildings. Table 4 illustrates the minimum size of fillet weld bead.
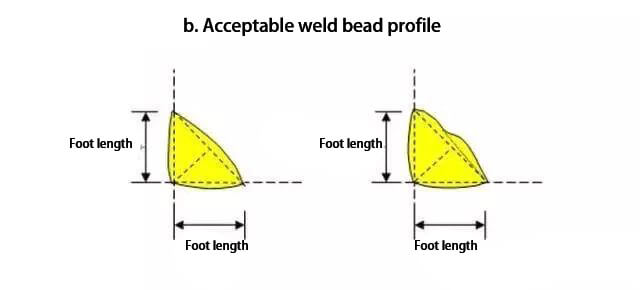

The minimum leg length of fillet welding is determined by the thicker plate of the two parts of the joint, but it should not be greater than the thickness of the thinner plate.
If the minimum leg length is exceeded, sufficient preheating should be provided to ensure the welding quality.
Related reading: Welding Quality of Welded Joints
If stress calculations dictate, the size of the welding can exceed the thickness of the thin plate in the joint.
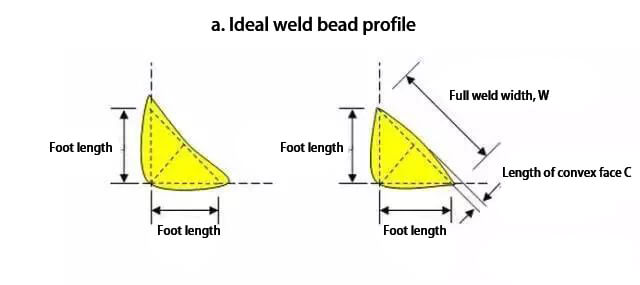
Table 3 lists the minimum leg length of fillet welding for different plate thicknesses, while Table 4 demonstrates the correlation between the full pass width of fillet welding and the maximum length of the convex face.
Table 3 Minimum angle length of fillet weld bead
| Thickness of thicker plate at joint, t (mm) | Minimum leg length of fillet weld (mm) |
| t≤6 | 3 |
| 6<t≤12 | 5 |
| 12<t≤19 | 6 |
| 19<t≤38 | 8 |
Table 4 Relation between the full pass width and the maximum convex length of fillet welding
| Full weld bead width, w | Maximum convex face length, c |
| w≤8mm | 1.6mm |
| 8mm<w≤25mm | 3mm |
| 25mm<w | 5mm |