Imagine your car’s engine suddenly fails while you’re driving. What caused the failure? This article explores the four critical stages of fatigue fracture development, revealing how tiny cracks grow into catastrophic breaks. By understanding crack nucleation, microcrack propagation, macro crack growth, and final fracture, you’ll learn to predict and prevent material failures. Discover the hidden dangers lurking in seemingly solid materials and gain insights into ensuring the longevity of vital components.
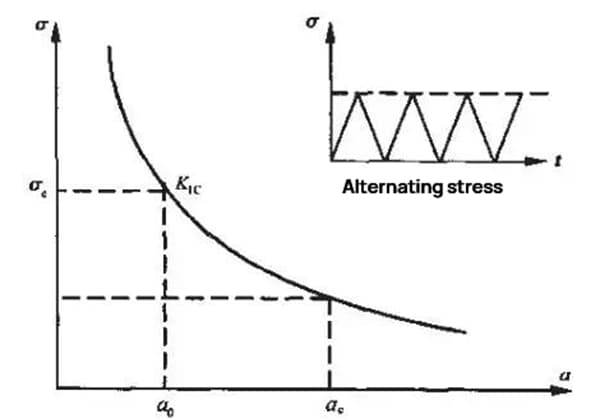
For a component with an initial crack of size a0, when subjected to static loads, as long as the working stress (σ) is less than the critical stress (σc), the component will function safely and reliably under the static stress level. Brittle failure will only occur when σ=σc or K1=K1c.
However, if the component experiences alternating stress with a value of σ<σc, the initial crack a0 will gradually increase in size under the influence of the alternating stress. When it reaches the critical size of a=ac, the component will become unstable and be damaged.
The process of the initial crack size a0 growing to the critical size ac is referred to as subcritical growth of fatigue crack or the residual life stage of macro crack a0, as depicted in Figure 1.

Fig. 1
The total fatigue life (N) of a material consists of two stages: the initiation life (Ni) and the propagation life (Np) from crack growth to fracture.
The process of fatigue fracture is complex and influenced by many factors, but it can generally be divided into four stages based on the development of cracks:
N = Ni + Np
When a component is subjected to alternating loads and has no cracks or defects, even if the nominal stress is below the yield limit of the material, the surface of the component can still experience slipping in localized areas due to uneven material.
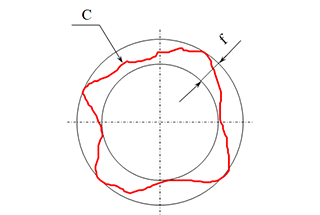
This is because the surface of the component is in a state of plane stress, making it susceptible to slipping without any plastic deformation. Over time, repeated cyclic slipping processes result in the formation of metal extrusion and extrusion slip bands, creating the nucleus for microcracks.
Once the crack nucleus is formed, the microcrack propagates along the 45° slip surface under the influence of the main stress.
At this stage, the crack depth into the surface is very shallow, only about ten microns, and there are many cracks along the slip band, as depicted in Figure 2.
This is the initial stage of crack growth.
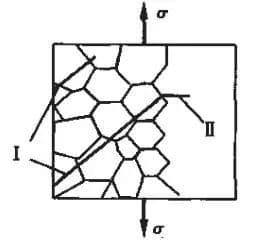
This stage marks the transition from micro cracks to macro cracks.
The rate of crack growth increases, and the growth direction is perpendicular to the tensile stress, with a single crack growing.
It is generally accepted that the crack length within the range of 0.01mm to ac represents the macro crack growth stage, also known as the second stage of crack growth.
Once the crack size reaches the critical size ac, instability propagation will occur and fracture will happen quickly.
This is a typical fatigue fracture process for components with smooth surfaces and no initial cracks.
For high-strength materials, due to their high yield strength, high sensitivity to notches, and the presence of internal inclusions and hard particles, cracks often form directly at macro stress concentration points and first crack along inclusions and the matrix interface, starting the stable macro crack growth stage rather than the inclined micro crack growth stage.
The macro crack growth stage is the most significant stage for analyzing fatigue from the perspective of fracture mechanics.