Why is laser cutting galvanized steel sheets so challenging yet crucial in modern manufacturing? This article explores the difficulties faced when laser cutting galvanized steel and examines the solutions involving various auxiliary gases—air, oxygen, and nitrogen. You’ll learn the pros and cons of each method, helping you make informed decisions for efficient and high-quality cutting processes. Dive in to discover how to optimize your laser cutting operations and enhance your manufacturing outcomes.

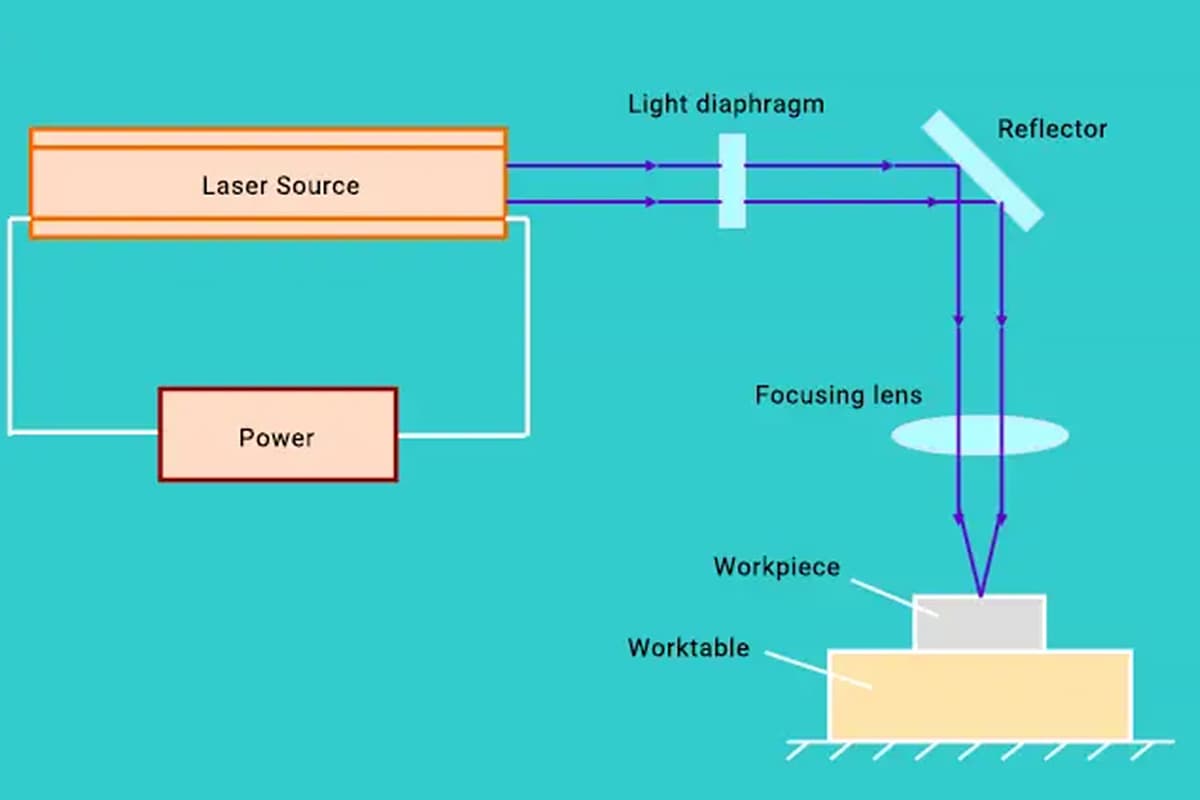
Nowadays, the use of laser cutting in sheet metal enterprises has become common.
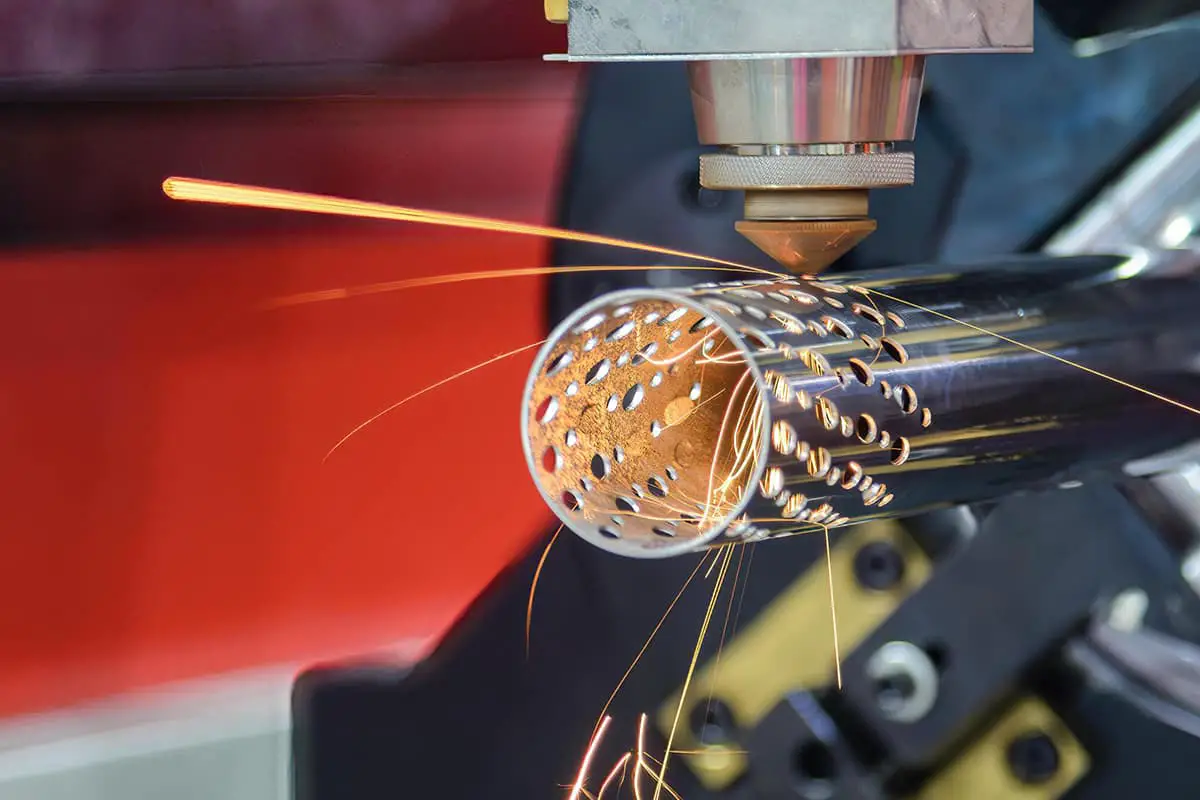
One of the advantages of laser cutting is that it is a non-contact processing method, which means it does not damage the surface of the plate and there are no burrs on the cut sections. This method can significantly reduce the need for subsequent processing.
However, laser cutting also faces various practical challenges that can be difficult to overcome. This article will focus on the cutting difficulties and solutions of galvanized steel plates, which are widely used in daily processing.
As we know, the purpose of galvanized steel plates is to protect the carbon steel inside by coating the surface with a layer of zinc that prevents rusting over time. Although these plates are slightly more expensive than ordinary carbon steel plates, they are cost-effective in terms of the overall cost of the product as they do not require additional processes like rust prevention spraying.
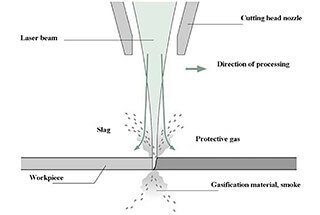
However, the situation changes after laser processing. When it comes to the choice of auxiliary gas, there are generally three cutting processes for galvanized steel plates: air cutting, oxygen cutting, and nitrogen cutting.
Let’s take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of these three cutting processes:
The advantage of air cutting is its low cost of processing. It only requires the cost of electricity for the laser and the air compressor, eliminating the need for expensive auxiliary gas. However, its cutting efficiency for thin plates can be comparable to nitrogen cutting, making it an economical and efficient method.
Despite its cost benefits, air cutting also has clear disadvantages. Firstly, it produces bottom burrs on the cut sections, requiring secondary deburring processes that are not conducive to the production cycle. Secondly, the air cut sections are prone to blackening, affecting the quality of the final product.
As a result, many enterprises avoid air cutting when processing galvanized steel plates, as it does not fully showcase the advantages of laser processing, such as reducing the need for subsequent processing.
Oxygen cutting is the most traditional and conventional cutting method. Its advantage lies in its low cost of gas and the convenience of factory management, as it does not require frequent switching of auxiliary gases when processing sheet metal primarily made of carbon steel.
However, the drawback of oxygen cutting is that it leaves an oxide skin on the surface of the cut section. If this product with an oxide skin is welded directly, the oxide skin will eventually peel off over time, contributing to the ease of soldering in galvanized sheets.
Nitrogen is utilized for high-speed processing. Unlike oxygen which supports combustion, nitrogen plays a protective role in the cutting process, preventing the formation of oxide skin on the cut section. This advantage has made nitrogen a popular choice for cutting galvanized steel plates among many enterprises.
However, nitrogen cutting also has its disadvantages. The unprotected cut section is susceptible to rusting, requiring additional rust prevention measures like spraying. This negates the benefits of the galvanized layer, making the higher cost of the galvanized sheet not fully justified.