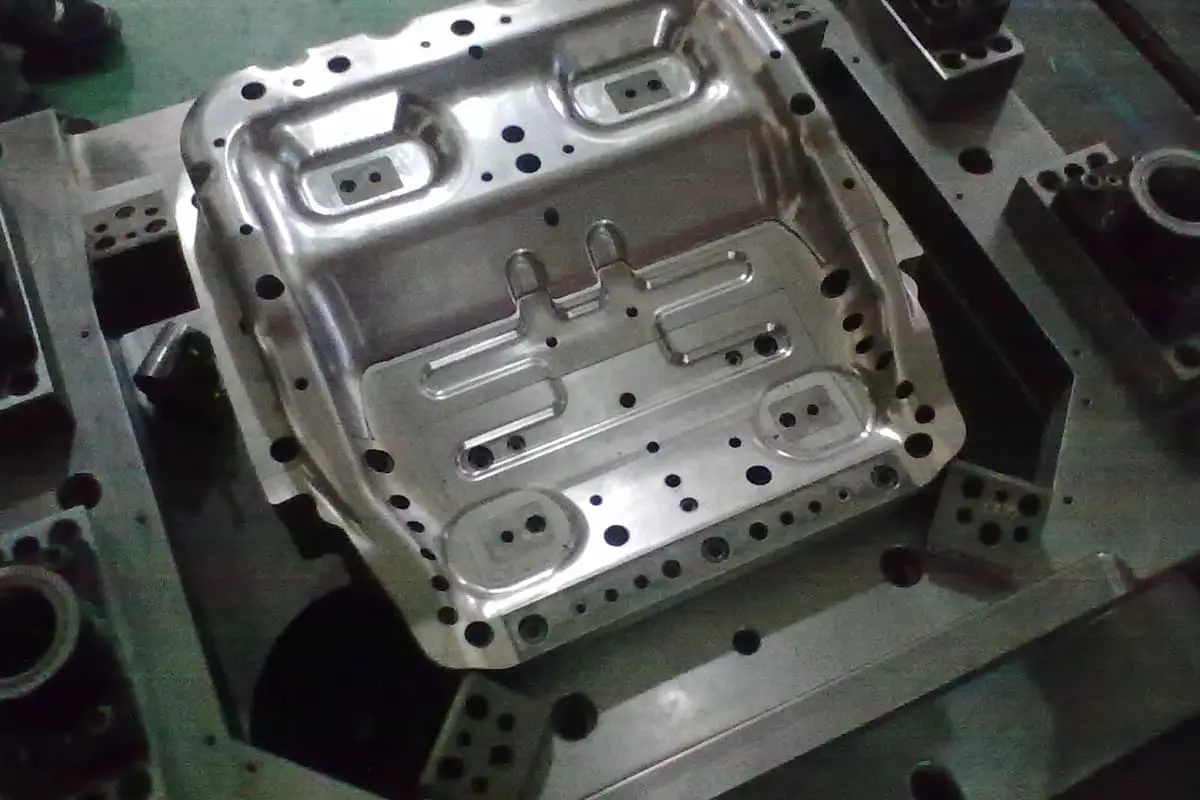
Ever wondered how the metal parts in your car or home appliances are made? Metal stamping, a process involving shaping metal sheets with dies, is key. This method offers high efficiency and precision, producing everything from tiny watch components to large car parts. However, it also comes with challenges like noise and high initial costs. In this article, you’ll explore the pros and cons of metal stamping and understand its role in various industries.
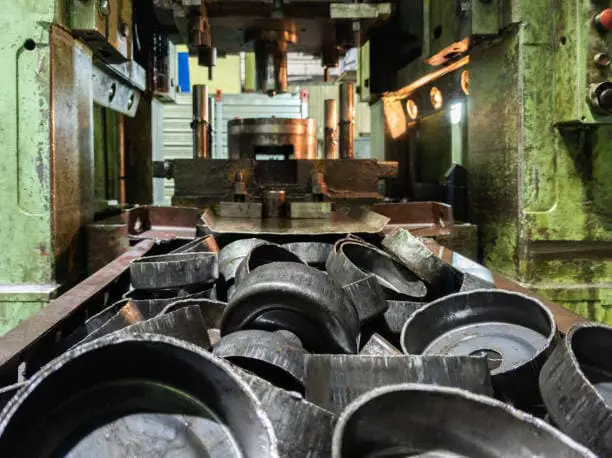


Metal stamping is a manufacturing process that forms a metal plate into a three-dimensional workpiece of desired size and shape using a single metal stamping die or a series of dies. The products produced through metal stamping are used in industries such as automobiles and household appliances, with automobile stamping parts being a crucial aspect of the metal stamping industry.
Metal stamping is an efficient method of forming sheet metal, with the metal stamping die being installed on a press and each press stroke creating a workpiece. The process is carried out by skilled metal stamping workers. Metal stamping dies are manufactured by either machine tools or specialized die factories, with some of these also producing the stamping parts.
See also:

Stamping production is dependent on molds and presses to carry out the processing process. It has several technical and economic advantages over other processing methods:
(1) The mold ensures the dimensional accuracy of stamped parts, leading to consistent quality and good interchangeability.
(2) Mold processing enables the production of parts with thin walls, light weight, high rigidity, good surface quality, and complex shapes that are difficult or impossible to manufacture through other methods.
(3) Stamping typically does not require heating the blank or cutting a large amount of metal, thus saving energy and conserving metal.
(4) Ordinary presses can produce dozens of pieces per minute, while high-speed presses can produce hundreds of thousands of pieces per minute, making it an efficient processing method.
Due to its outstanding characteristics, the stamping process is widely utilized across various industries in the national economy. For instance, industries such as aerospace, machinery, electronics, transportation, weapons, household appliances, and light industry all make use of stamping processing. Not only is it prevalent in industry, but individuals also encounter stamped products in their daily lives.
Stamping can be used to produce both small, precise parts found in clocks, watches, and instruments, as well as larger cover parts for automobiles and tractors. The materials that can be stamped include ferrous metals, non-ferrous metals, and some non-metallic materials.
Related reading: Ferrous vs Non-ferrous Metals
Stamping also has some drawbacks, mainly in the form of noise and vibration during the stamping process. These issues are not solely caused by the stamping process or die, but are primarily attributed to outdated traditional stamping equipment.

Compared to other mechanical and plastic processing methods, stamping processing offers several unique advantages in terms of technology and economy. The main benefits are as follows:
(1) The stamping process is efficient, easy to operate, and can be easily automated and mechanized. This is due to the use of stamping dies and equipment, with ordinary presses capable of producing dozens of strokes per minute and high-speed presses capable of producing hundreds or even thousands of strokes per minute. Additionally, each stamping stroke can result in a punch.
(2) The stamping process ensures dimensional accuracy and shape consistency through the use of a die, and typically does not compromise the surface quality of the stamped parts. Furthermore, the die has a long lifespan, leading to stable and consistent quality, good interchangeability, and “identical” characteristics.
(3) Stamping can process parts of a large size range and complex shape, such as small clocks and watches, automobile longitudinal beams, and covers. Additionally, the cold deformation hardening of materials during stamping leads to increased strength and stiffness.
(4) Stamping generates minimal waste, conserves materials, and does not require additional heating equipment, making it a material-saving and energy-efficient process with low costs for stamped parts.
The stamping process is becoming increasingly sophisticated, but it also has some drawbacks:
① The mechanical press is widely used in stamping processing, with fast operation speed and high manual strength.
② The dies used in stamping are complex, with a long manufacturing cycle and high cost.
③ Stamping processing requires specific molds, making it best suited for large-scale production and limiting it for single piece or small batch production.
④ The design of the stamping die emphasizes traditional theory and experience, requiring strong imagination and creativity, and imposing high requirements on the die designer and manufacturer.
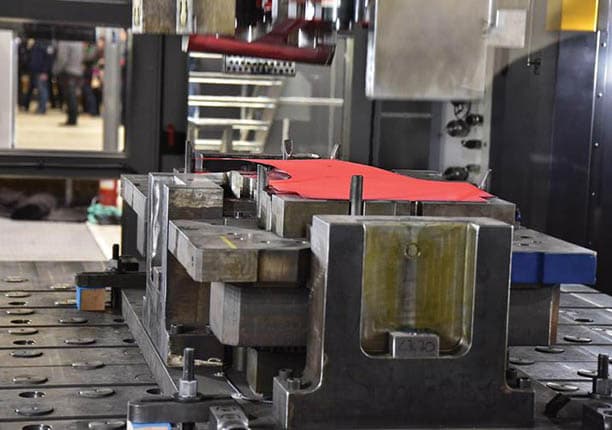

Metal stamping parts can be processed through two methods: cold stamping and hot stamping, depending on the temperature during the stamping process. The appropriate processing method is determined by factors such as the strength, plasticity, thickness, degree of deformation, and capacity of the equipment of the material, as well as the original heat treatment state and intended end use of the material.
Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of these two forming methods.
Cold stamping is a manufacturing process for metal workpieces at normal temperature. It has the benefits of not requiring heating, producing stamped parts with no oxide skin and good surface quality, and having low hardness.
The drawback is that hardening may occur and, in severe cases, the metal may lose its ability for further deformation. Cold stamping necessitates that the blank has a uniform thickness with minimal fluctuation, and that the surface is clean and free from spots and scratches.
Hot stamping is a stamping method that heats metal within a specific temperature range. Its benefits include the elimination of internal stress to prevent hardening, increased material plasticity, reduced deformation resistance, decreased equipment power consumption, and high hardness.
Its drawback is the presence of oxide skin, which requires acid washing or shot peening. The high hardness also increases the difficulty of subsequent processing, requiring laser technology for cutting and drilling.