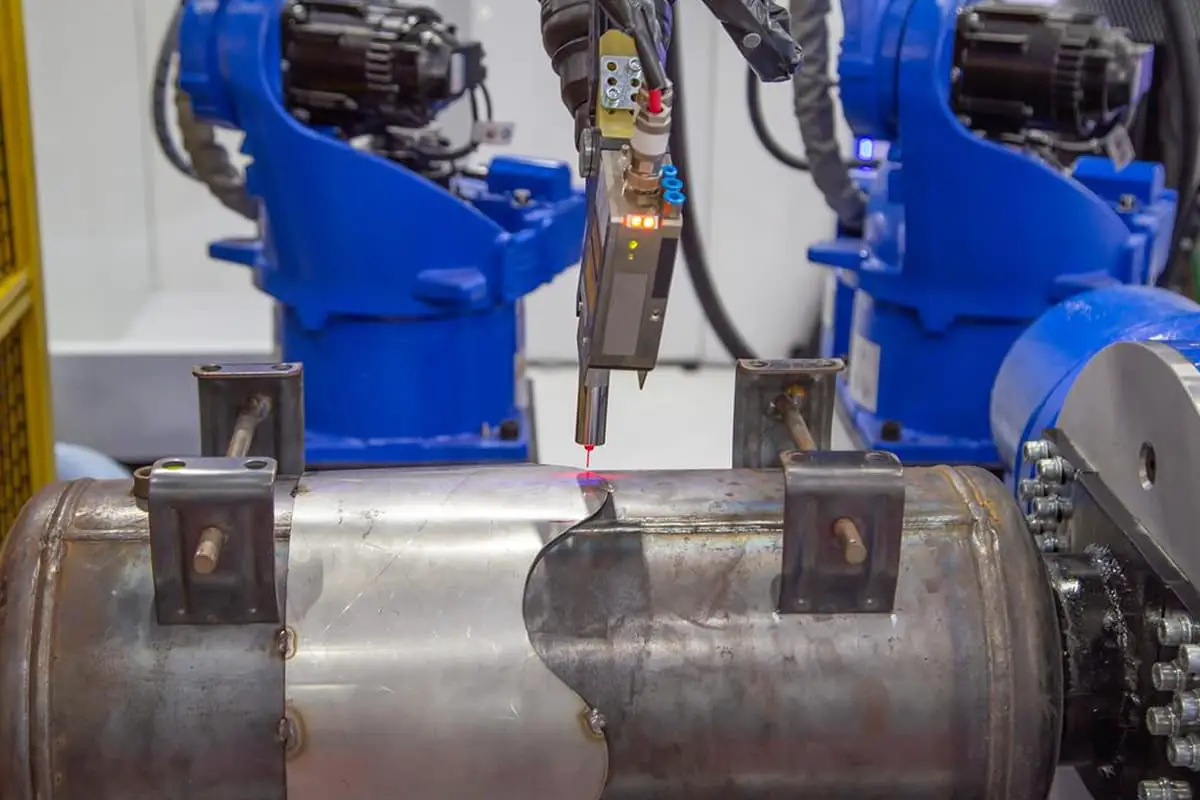
Ever wondered how laser welding transforms metalwork? This article unveils the secrets of laser welding, focusing on the crucial parameters that ensure precision and strength. From adjusting laser power to mastering swing width, you’ll uncover the essential techniques that make laser welding a game-changer in the industry. Get ready to enhance your understanding and skills!

① Adjust the swing width of the galvanometer to match the width of the plate being welded.
② The laser power required is directly proportional to the thickness of the plate. The thicker the plate, the higher the laser power needed, and vice versa.
③ The parameters for thin plates less than 1.0mm are different. The duty cycle parameters of the laser must be adjusted based on the thickness of the thin plate. These parameters mainly impact the penetration strength of the thin plate.
④ The linetype is suitable for most welding types, including diagonal and butt welding.
⑤ The range of frequency for the welding gun is 4-20Hz, and the power used for different plates can be adjusted as needed.
⑥ The swing width of the galvanometer for internal angle welding should not be too large. The smaller the swing width, the higher the energy and the deeper the penetration.
| Metals | Welding Material & Method | Laser parameters | Welding gun parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power (W) | Frequency (Hz) | Duty cycle | Frequency (Hz) | Width (mm) | ||
| S.S | 0.5mm S.S Internal fillet welding | ~300W | 3000-5000 | 60%-80% | 12—22 | 1.2—1.8 |
| 0.5mm S.S External fillet welding | ~300W | 3000-5000 | 60%-80% | 12—22 | 1.2—1.8 | |
| 0.5mm S.S Diagonal welding | ~300W | 3000-5000 | 60%-80% | 12—22 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 0.5mm S.S Fillet welding | ~300W | 3000-5000 | 60%-80% | 12—22 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 1mm S.S Internal fillet welding | ~450W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.2—1.8 | |
| 1mm S.S External fillet welding | ~450W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.2—1.8 | |
| 1mm S.S Diagonal welding | ~450W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 1mm S.S Fillet welding | ~450W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 2mm S.S Internal fillet welding | ~700W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.2—1.8 | |
| 2mm S.S External fillet welding | ~700W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.2—1.8 | |
| 2mm S.S Diagonal welding | ~700W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 2mm S.S Fillet welding | ~700W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 4MM S.S Internal fillet welding | ~1300W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 4MM S.S Diagonal welding | ~1300W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| Al. | 1MM Al. Internal fillet welding | ~700W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 4—12 | 0.8—1.8 |
| 1MM Al. Diagonal welding | ~700W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 4—12 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 1MM Al. Fillet welding | ~700W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 4—12 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 2MM Al. Internal fillet welding | ~1200W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 4—12 | 1.2—1.8 | |
| 2MM Al. External fillet welding | ~1200W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 4—12 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 2MM Al. Diagonal welding | ~1200W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 4—12 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| MS. | 1MM M.S Internal fillet welding | ~450W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.2—2 |
| 1MM M.S External fillet welding | ~450W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 1MM M.S Diagonal welding | ~450W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 4—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 1MM M.S Fillet welding | ~450W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 2MM M.S Internal fillet welding | ~700W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.2—2 | |
| 2MM M.S External fillet welding | ~700W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 2MM M.S Fillet welding | ~700W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 4MM M.S Internal fillet welding | ~1200W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.2—2 | |
| 4MM M.S External fillet welding | ~1200W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 4MM M.S Fillet welding | ~1200W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
Special note:
Please note that the above parameters are only guidelines. The actual adjustments to the parameters should be based on factors such as laser power, material, welding method, and width. Generally speaking, the thinner the plate, the lower the laser power required, and vice versa.
The linetype parameter for laser head control is typically suitable for diagonal and male fillet welding, while the O-type is suitable for most welding applications.
① Adjust the swing width of the galvanometer to match the width of the plate being welded.
② The laser power required is directly proportional to the thickness of the plate. The thicker the plate, the higher the laser power needed, and vice versa.
③ The parameters for thin plates less than 1.0mm are different and must be adjusted based on the thickness of the thin plate. These parameters primarily affect the penetration strength of the thin plate.
④ The linetype is suitable for most welding types, including diagonal and butt welding.
⑤ The range of frequency for the welding gun is 4-20Hz, and the power used for different plates can be adjusted as needed.
⑥ The O-type is suitable for all welding applications. The double motor swing in O-type welding mode ensures that the material is melted thoroughly, resulting in a more stable weld compared to linear welding. Higher laser power is required for this mode.
| Metals | Welding Material & Method | Laser parameters | Welding gun parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power (W) | Frequency (Hz) | Duty cycle | Frequency (Hz) | Width (mm) | ||
| S.S | 0.5mm S.S Internal fillet welding | ~350W | 3000-5000 | 60%-80% | 12—22 | 0.8—1.8 |
| 0.5mm S.S External fillet welding | ~350W | 3000-5000 | 60%-80% | 12—22 | 0.8—1.8 | |
| 0.5mm S.S Diagonal welding | ~350W | 3000-5000 | 60%-80% | 12—22 | 1.4—2.8 | |
| 0.5mm S.S Fillet welding | ~350W | 3000-5000 | 60%-80% | 12—22 | 1.4—2.8 | |
| 1mm S.S Internal fillet welding | ~500W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 0.8—1.8 | |
| 1mm S.S External fillet welding | ~500W | 3000-5000 | 200% | 8—16 | 0.8—1.8 | |
| 1mm S.S Diagonal welding | ~500W | 3000-5000 | 300% | 8—16 | 1.4—2.8 | |
| 1mm S.S Fillet welding | ~500W | 3000-5000 | 400% | 8—16 | 1.4—2.8 | |
| 2mm S.S Internal fillet welding | ~750W | 3000-5000 | 500% | 8—16 | 0.8—1.8 | |
| 2mm S.S External fillet welding | ~750W | 3000-5000 | 600% | 8—16 | 0.8—1.8 | |
| 2mm S.S Diagonal welding | ~750W | 3000-5000 | 700% | 8—16 | 1.4—2.8 | |
| 2mm S.S Fillet welding | ~750W | 3000-5000 | 800% | 8—16 | 1.4—2.8 | |
| 4MM S.S Internal fillet welding | ~1350W | 3000-5000 | 900% | 8—16 | 1.4—2.8 | |
| 4MM S.S Fillet welding | ~1350W | 3000-5000 | 1000% | 8—16 | 1.4—2.8 | |
| Alu. | 1MM Al. Internal fillet welding | ~750W | 3000-5000 | 1100% | 4—12 | 0.8—1.8 |
| 1MM Al. Diagonal welding | ~750W | 3000-5000 | 1200% | 4—12 | 1.4—2.8 | |
| 1MM Al. Fillet welding | ~750W | 3000-5000 | 1300% | 4—12 | 1.4—2.8 | |
| 2MM Al. Internal fillet welding | ~1300W | 3000-5000 | 1400% | 4—12 | 0.8—1.8 | |
| 2MM Al. External fillet welding | ~1300W | 3000-5000 | 1500% | 4—12 | 1.4—2.8 | |
| 2MM Al. Diagonal welding | ~1300W | 3000-5000 | 1600% | 4—12 | 1.4—2.8 | |
| M.S | 1MM M.S Internal fillet welding | ~500W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.2—2 |
| 1MM M.S External fillet welding | ~500W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 1MM M.S Diagonal welding | ~500W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 4—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 1MM M.S Fillet welding | ~500W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 2MM M.S Internal fillet welding | ~750W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.2—2 | |
| 2MM M.S External fillet welding | ~750W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 2MM M.S Fillet welding | ~750W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 4MM M.S Internal fillet welding | ~1250W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.2—2 | |
| 4MM M.S External fillet welding | ~1250W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
| 4MM M.S Fillet welding | ~1250W | 3000-5000 | 100% | 8—16 | 1.6—2.8 | |
Special note:
Please note that the above parameters are only suggestions. The actual adjustments to the parameters should be based on factors such as laser power, material, welding method, and width. Generally speaking, the thinner the plate, the lower the laser power required, and vice versa. The linetype parameter for laser head control is typically suitable for diagonal and male fillet welding, while the O-type is suitable for most welding applications.