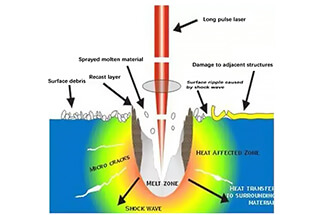
What makes one laser better than another for specific tasks? Whether cutting through metal or precisely marking components, the choice of laser can drastically impact efficiency and quality. This article compares CO2, Nd:YAG, semiconductor, disk, and fiber lasers, highlighting their unique properties and applications. You’ll learn which laser excels in different industries and discover the key factors to consider when selecting the right laser for your needs. Dive in to understand how to leverage these powerful tools for optimal performance.

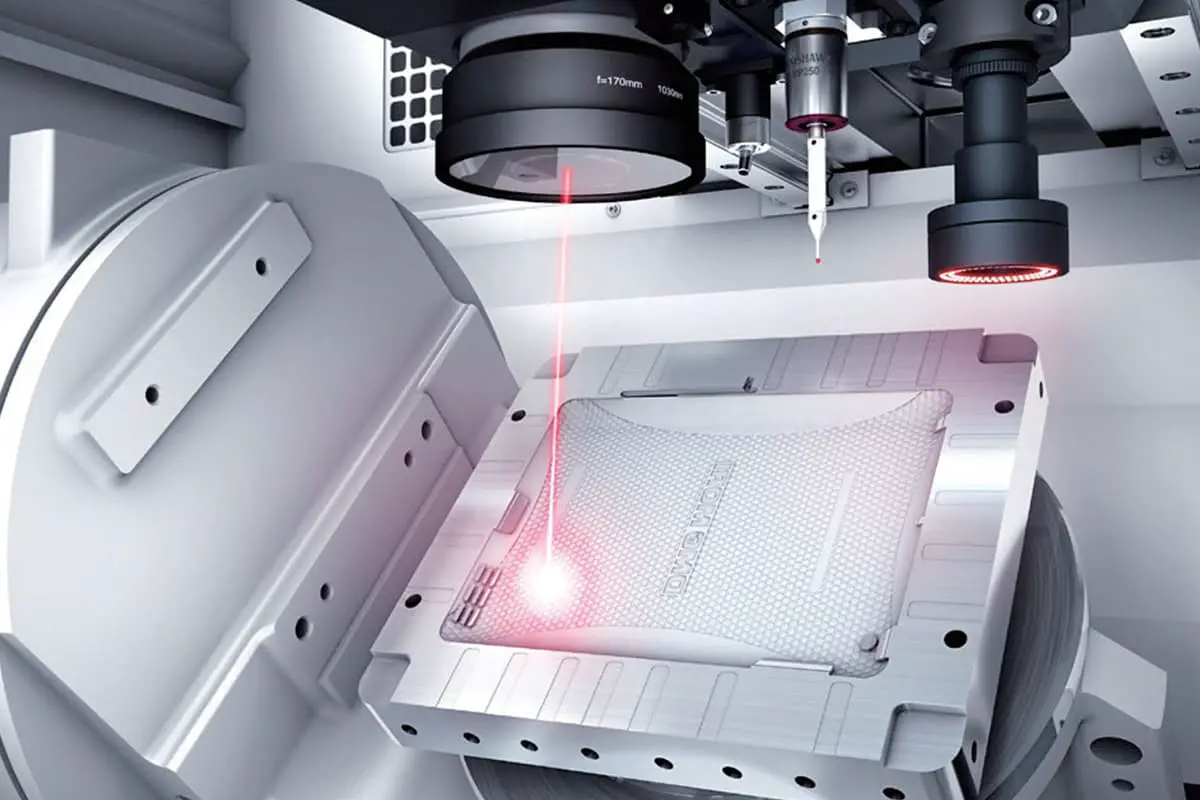
Lasers are an essential component in modern laser processing systems.
With the advancement of laser processing technology, lasers themselves are also evolving, leading to the emergence of new types.
Initially, the main types of lasers used for processing were high-power CO2 gas lasers and lamp-pumped solid-state YAG lasers.
The focus of development has shifted from increasing laser power to improving beam quality, once the power requirements have been met.
The development of semiconductor lasers, fiber lasers, and disk lasers has brought about significant progress in fields such as laser material processing, medical treatment, aerospace, and automobile manufacturing.
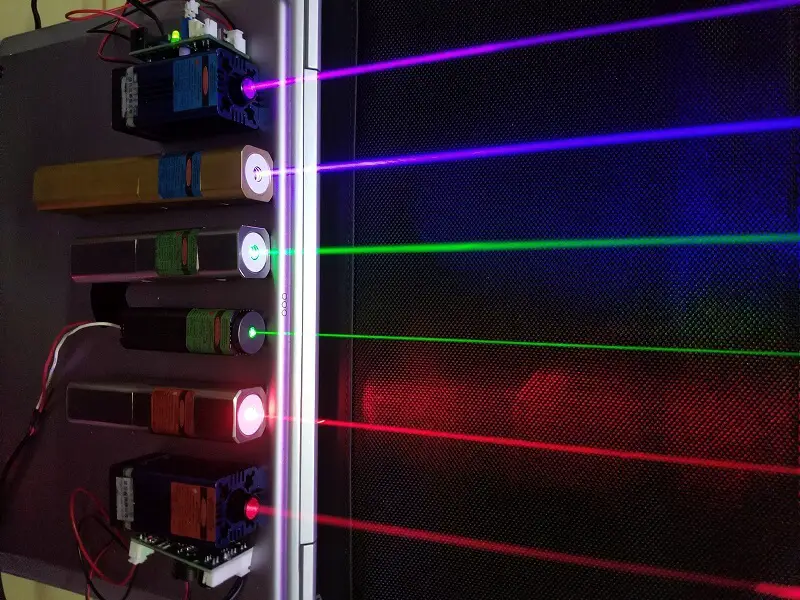

The five most prevalent lasers in the market are CO2 lasers, Nd:YAG lasers, semiconductor lasers, disk lasers, and fiber lasers. Can you provide information on their characteristics and application scope?
Application:
The wavelength of a CO2 laser is 10.6 micrometers, and it has low absorption when it comes to metal materials.
It is typically used for cutting non-metallic materials and welding metal materials.
Its applications are widespread and include welding in aviation, electronic instruments, machinery, and the automobile industry.
Application:
Nd:YAG lasers have a high absorption coefficient for metal, making them suitable for cutting, welding, and marking applications.
Thanks to their high energy, high peak power, compact design, durability, and reliable performance, they are widely used across industries such as defense, medical treatment, scientific research, and more.
Application: due to the high uniformity of laser beam and poor penetration, the semiconductor laser is not suitable for metal cutting, but its spot characteristics are suitable for metal surface treatment, such as cladding, hardening, 3D printing, etc.
It can be widely used in aerospace, medical, automotive fields.
Application: disc laser is a spatial optical path coupling structure, so the beam quality is very high
The laser is appropriate for laser material applications such as cutting metal, welding, marking, cladding, hardening, and 3D printing.
It is widely used in the automobile manufacturing, aerospace, precision machinery, and 3C electronics industries.
Application: due to high electro-optic conversion efficiency, good metal absorption coefficient and high beam quality, fiber laser can be used for metal cutting, welding, marking, metal surface treatment applications.
Laser technology is extensively utilized in industries such as aerospace, automobile manufacturing, 3C electronics, and the medical field.
However, to determine the most suitable laser product, it is necessary to consider the performance and application of each type of laser.
Below is a table that provides the characteristics and applications of the five mentioned types of lasers.
| Laser type | Nd:YAG Laser | CO2 Laser | Fiber Laser | Semiconductor Laser | Disk Laser |
| Laser wavelength (μm) | 1.0-1.1 | 10.6 | 1. 0-1.1 | 0.9-1.0 | 1.0-1.1 |
| Photoelectric conversion efficiency | 3%-5% | 10% | 35%-40% | 70%-80% | 30% |
| Output power (kw) | 1-3 | 1-20 | 0.5-20 | 0.5-10 | 1-20 |
| Beam quality | 15 | 6 | <2.5 | 10 | <2.5 |
| Focusing performance | The beam divergence angle is large, it is difficult to obtain a single mode, the focused spot is large and the power density is low | The beam divergence angle is small, the base film is easy to obtain, the focused spot is small, and the power density is high | Small beam divergence angle, small spot after focusing, good single-mode and multi-mode beam quality, high peak power and high power density | The beam divergence angle is large, the focused spot is large, and the spot uniformity is good | The beam divergence angle is small, the focused spot is small, and the power density is high |
| Cutting characteristics | Poor, low cutting capacity | Generally, it is not suitable for cutting metal materials. When cutting non-metal materials, the cutting thickness is large and the cutting speed is fast | It is generally suitable for cutting metal materials with fast cutting speed, and can adapt to the cutting of plates with different thickness, high efficiency and large cutting thickness | Due to the uniform spot and poor beam penetration, it is not suitable for cutting application and metal surface treatment | It is generally suitable for cutting metal materials, with fast cutting speed, and can adapt to the cutting of plates with different thickness |
| Welding characteristics | It is suitable for spot welding, three-dimensional laser welding and welding of high reflection materials | It is suitable for laser brazing and high reflection material welding | It is suitable for spot welding, brazing, laser compound welding, laser scanning welding and high reflection material welding | It is suitable for brazing, compound welding, laser cladding welding, gold room surface treatment and high reflection material welding | It is suitable for laser spot welding, brazing, compound welding, laser scanning welding and high reflection material welding |
| Type of processing material | Copper, aluminum | Non Machinable high inversion material | High inversion material | High inversion material | High inversion material |
| Metal absorptivity | 35% | 12% | 35% | 35% | 35% |
| Volume | Small | Maximum | Compact and compact | Small | Small |
| Maintenance cycle | 300 hours | 1000-2000 hours | No maintenance required | No maintenance required | No maintenance required |
| Relative operating cost | High | High | Low | commonly | high |
| Processing portability | Good flexibility and adaptability | Inconvenient to move | Good flexibility and flexibility | Good flexibility and adaptability | Good flexibility, strong adaptability, but sensitive to earthquake |
| Technology | used | used | newest | new | new |
| Service life | >300 hours | >2000 hours | >100000 hours | >15000 hours | >100000 hours |
Semiconductor lasers have clear technical advantages compared to traditional CO2 lasers and solid-state YAG lasers, such as their small size, lightweight, high efficiency, low energy consumption, long lifespan, and high metal absorption.
With the continued advancements in semiconductor laser technology, other solid-state lasers based on semiconductors, such as fiber lasers, direct-output fiber semiconductor lasers, and disk lasers, are also growing rapidly.
Fiber lasers, particularly rare earth-doped fiber lasers, have experienced rapid growth and are widely used in fields such as optical fiber communication, sensing, and laser material processing.