Ever wondered how lasers can cut through metal like a hot knife through butter? This article dives into the fascinating world of laser cutting, focusing on the crucial role of focus position. Discover how adjusting this key factor can change everything, from the precision of cuts to the quality of the final product. Get ready to learn the secrets behind achieving perfect cuts every time!

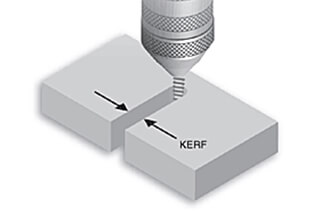
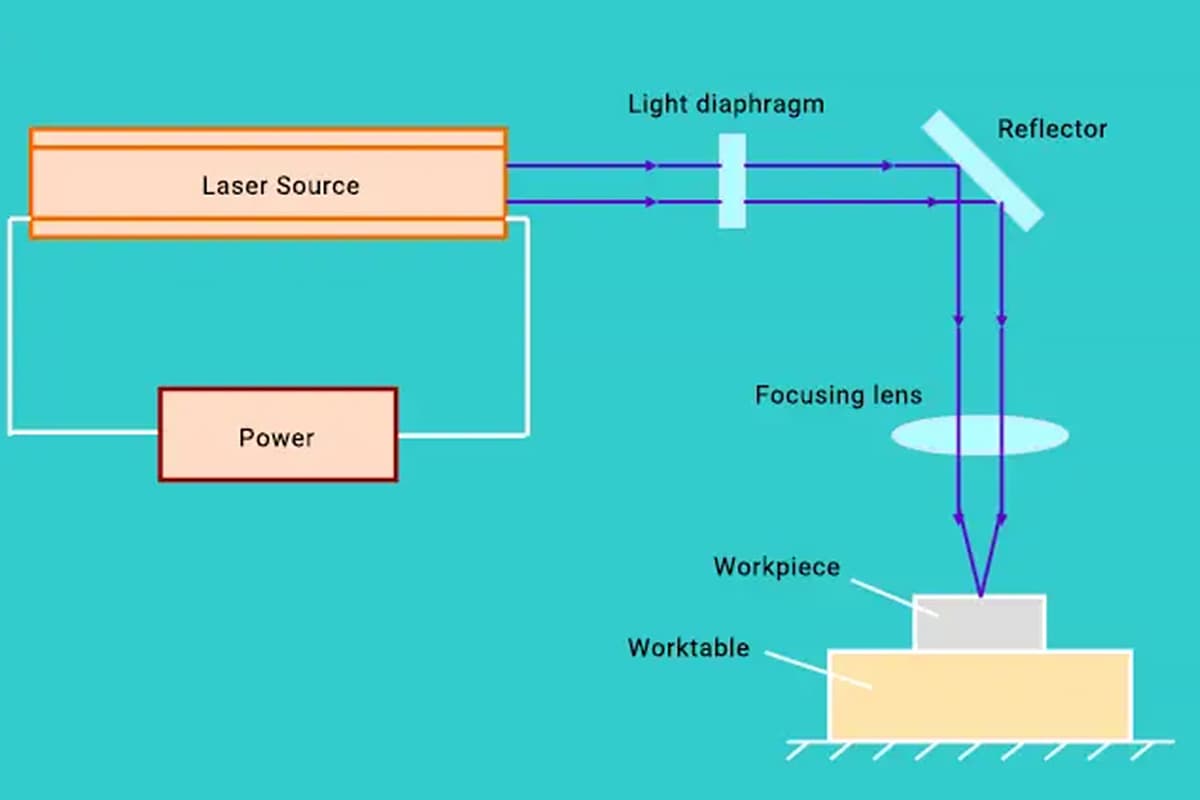
Laser cutting is an important application of lasers, in which the laser beam is focused on the material surface using a focusing lens to melt the material.
Simultaneously, the melted material is blown away by compressed gas coaxial with the laser beam. The laser beam and the material are moved relative to each other along a certain track, thus forming a specific shape of the cut.

The laser cutting process is accomplished through the cooperation of the motion mechanism, control system, laser source, and laser head. Therefore, factors that influence the cutting effect mainly originate from these four parts.
The main factors that affect the cutting effect include beam energy distribution, laser power, focus diameter, focus position, cutting speed, nozzle diameter, and so on.
Among these factors, the focus position is the most influential. Changing the focus position is equivalent to changing the beam diameter incident on the surface of the plate and the incident angle inside the plate. This can affect the formation of the cut, the reflection of the beam inside the cut, and subsequently, the width of the cut.
The width of the cut can affect almost all cutting effects, such as the roughness of the cutting surface and the adhesion state of the slag at the bottom.
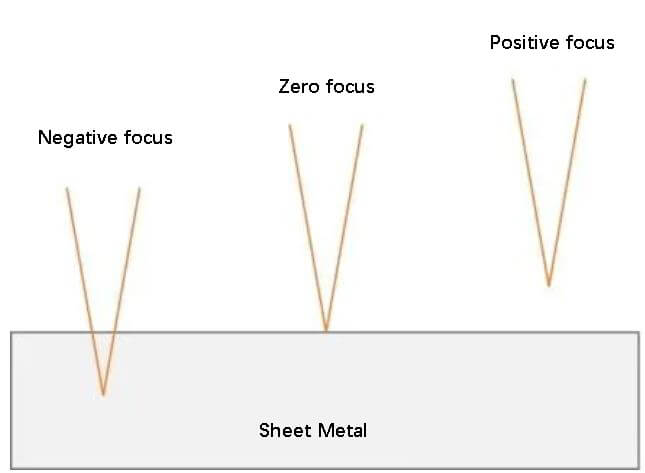
The focus position (Z) refers to the distance between the focus and the upper surface of the material to be cut.
Typically, the focus on the plate surface is referred to as zero focus, while the focus located above the plate is called positive focus, and the focus located below it is called negative focus.
A schematic diagram is presented below:
The following figure shows the variation relationship between the focus position (Z) and the width (W) of the upper part of the cutting seam of the processing material.
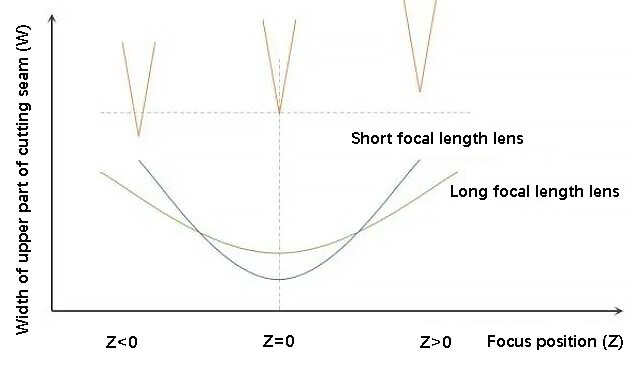
When the focus is on the plate surface, the width of the cut is the narrowest.
As the focus position changes, whether it is a positive or negative defocus, the width of the cut will widen.
The degree to which the width of the cut widens varies depending on the focal length of the cutting head lens and the focal depth. In general, the shorter the focal length and the smaller the focal depth, the greater the variation in the width of the cut with the focal position.
Before cutting any material, it is necessary to adjust the distance between the focus and the material.
Typically, the choice of the focus position will differ depending on the type of material being cut, so it is crucial to select it appropriately.
When the focus is positioned above the cutting material, the light beam will spread out and diffuse in the cutting seam after reaching the material surface. This will cause the lower part of the cut to be larger than the upper part.
This type of focus is suitable for oxidative cutting, such as oxygen cutting of carbon steel, as it allows oxygen to reach the bottom of the workpiece and participate in a sufficient oxidation reaction. Additionally, the larger cut at the bottom also helps to remove slag.
For oxygen cutting of carbon steel, a larger positive defocus within a certain range will result in a larger spot size on the material surface, as well as a brighter and smoother cutting surface. However, beyond a certain range, the energy of the lower part may not be sufficient, which can result in impervious cutting or slag hanging at the bottom.
2KW laser – positive focus cutting 15mm carbon steel with oxygen
Negative focus cutting involves positioning the focus inside the plate, thereby ensuring that the lower part of the cut has sufficient energy density.
The cut is wider at the top and narrower at the bottom, with the upper part experiencing a larger cutting amplitude, which improves the fluidity of the melt. However, the lower part has a smaller cut width and requires a greater airflow.
Negative defocus is typically used when cutting with air or nitrogen.
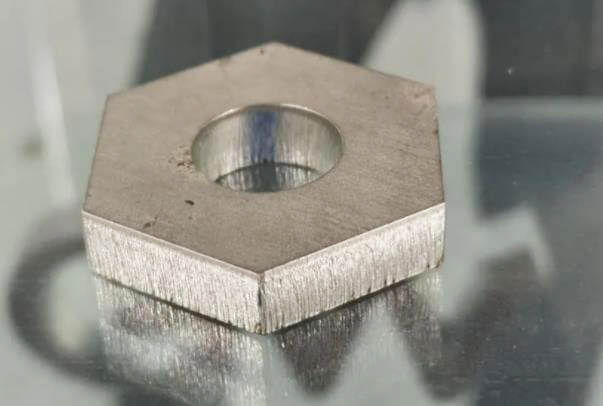

6kW laser – negative focus cutting 10mm stainless steel with nitrogen
During zero focus cutting, the smallest spot size can be obtained on the plate surface. This results in a relatively narrow melting range and a smaller cut, making it suitable for high-precision cutting of thin materials.

2KW laser – zero focus cutting 1mm brass with nitrogen
Cutting characteristics and application scope of different focus positions
|
Focus position | Cutting characteristics |
Scope of application |
 Positive focus | The slit at the bottom of the plate is larger than that at the top, which helps the bottom participate in full oxidation reaction and slag discharge. | Oxygen cutting of carbon steel |
 Negative focus | The focus is inside the plate, and the cutting seam of the upper part of the plate is larger, which ensures that the lower part has sufficient energy density. | Nitrogen/air cutting of stainless steel, carbon steel, galvanized steel, aluminum and copper |
 Zero focus | The slit is the narrowest and the machining precision is high | Sheet/foil cutting
Precision cutting |
In recent years, the power range of fiber lasers has been increasing annually, and laser cutting applications have changed from kilowatts to 10,000 watts.
Our laser factory has been continuously exploring the application of high-power lasers and has developed a unique HBF (high brightness flat mode) laser output. This output ensures excellent cutting quality for thick plates while also accounting for the need for efficient thin plate cutting.
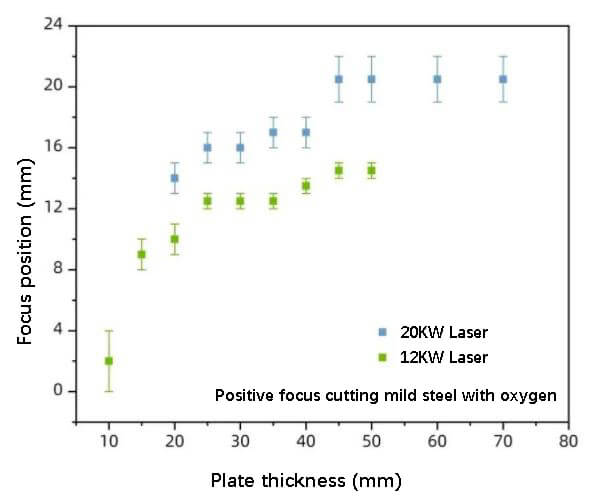
Positive focus on cutting mild steel with oxygen
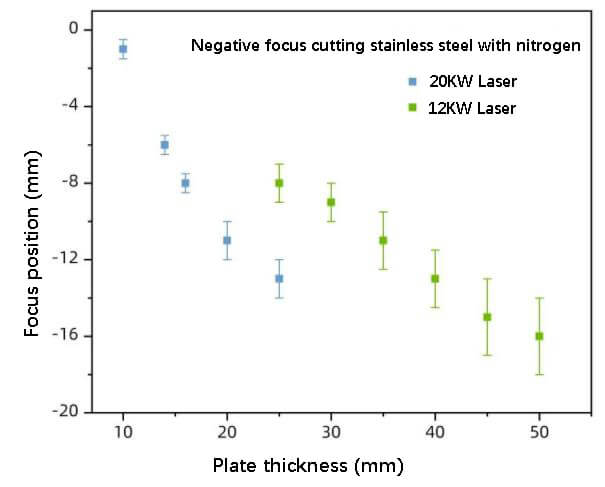
Negative focus on cutting stainless steel with oxygen
In actual cutting applications, it is necessary to select the appropriate focus position according to specific cutting requirements.