Imagine a tool that cuts through metal with the precision of a surgeon’s scalpel. Laser cutting technology promises exactly this, offering high-quality cuts, incredible speed, and versatility across a range of materials. But what are the trade-offs? In this article, we’ll explore the benefits and limitations of laser cutting, helping you understand how this advanced method can revolutionize manufacturing processes. Get ready to discover if laser cutting is the right solution for your needs!
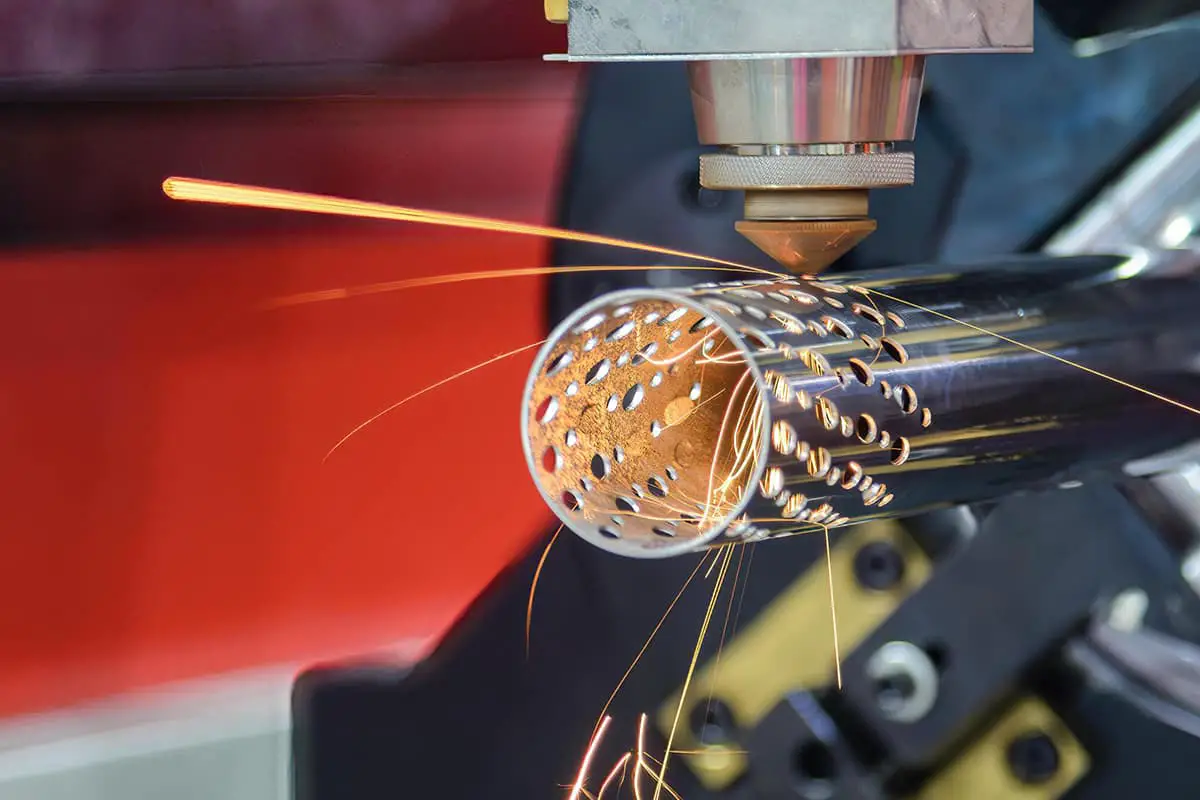
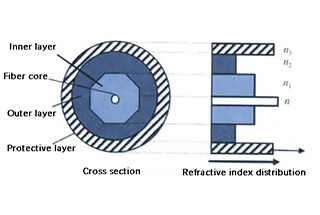
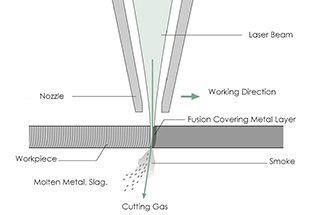
Laser cutting involves using a focused laser beam to quickly melt, vaporize, or reach the ignition point of the material being worked on. The melted or vaporized material is then removed by an auxiliary airflow to complete the cutting process.
See also:
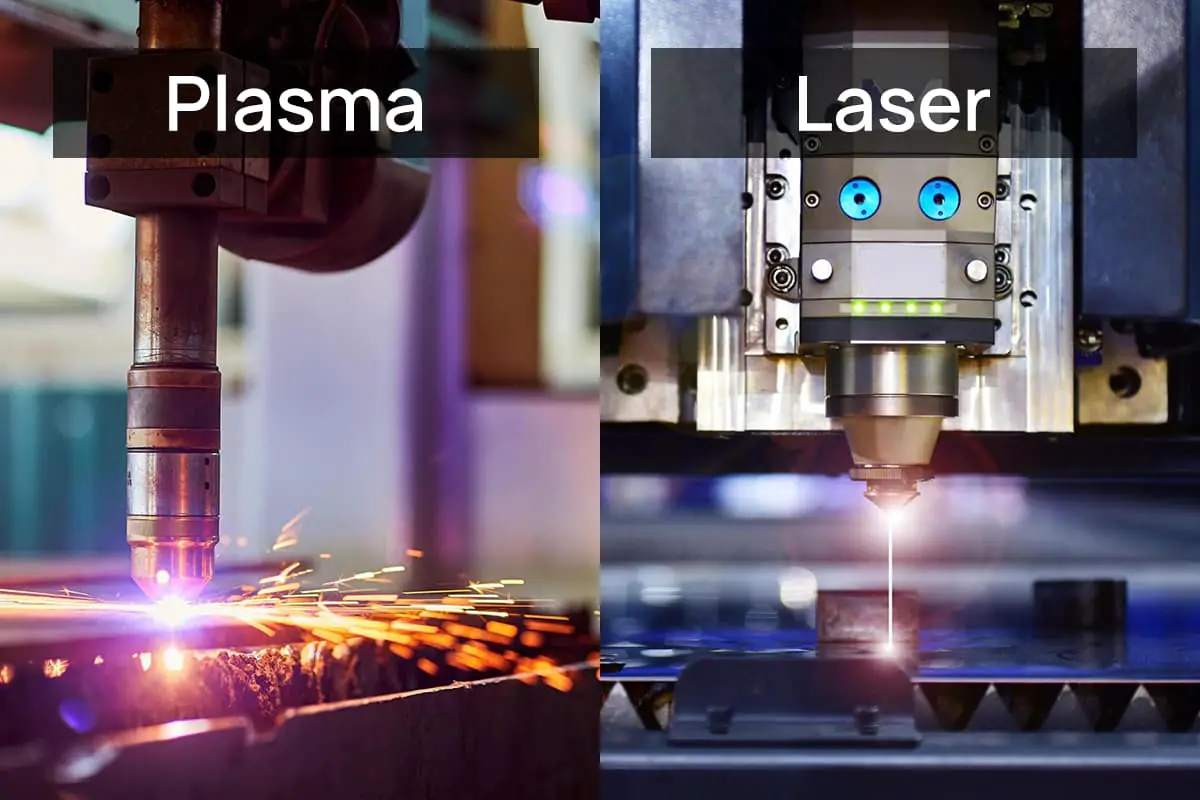
The laser beam can be focused into a very small spot, resulting in a concentrated heat source and high radiation intensity. This is what sets laser cutting apart from traditional cutting methods like oxyacetylene flame cutting and plasma cutting.
With its high-quality cuts, fast cutting speed, flexibility, and ability to work with a wide range of materials, laser cutting aligns with the trend of upgrading and transforming the manufacturing industry.
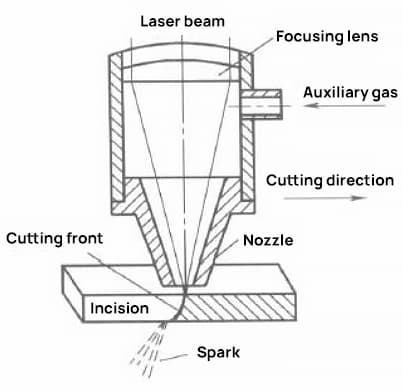
Laser cutting principle
| Process Type | Description |
| Fusion Cutting | The process involves directing the incoming laser beam onto the metal sheet. When the laser power reaches a certain critical value, it causes the localized area to melt, achieving the desired cutting effect. |
| Vaporization Cutting | This method uses a high-power density laser beam to heat the material, avoiding the burrs and slag formed by melting due to heat conduction. Some of the material vaporizes into steam and disappears, leaving the processed material edges looking rather aesthetic. |
| Oxidation Cutting | The oxygen sprayed from the nozzle is ignited by the laser beam, causing an intense chemical reaction that generates heat processing. For brittle materials prone to heat damage, the laser beam is used for fast, controlled cutting, creating a significant thermal gradient and mechanical deformation in the area, leading to the formation of cracks in the material. This process is also known as controlled fracturing cutting. |
See also:
| Advantages | Specific Features |
| Superior Cutting Quality | Laser cutting, characterized by a small laser spot and high energy density, achieves high-speed cutting and thus, excellent cutting quality. |
| High Cutting Efficiency | Due to the transmission characteristics of lasers, laser cutting machines typically come equipped with one or more CNC workbenches. The entire cutting process can be fully computer-controlled. By simply changing the CNC program, you can easily cut parts of different shapes. This setup permits both two-dimensional and three-dimensional cutting. |
| Fast Cutting Speed | With its high energy density and non-contact nature, laser cutting can rapidly melt, vaporize, ablate, or ignite the material being cut, resulting in a fast cutting speed. |
| Non-contact Cutting | During laser cutting, the cutting torch does not touch the workpiece, eliminating tool wear. When processing parts of different shapes, there’s no need to replace “tools”. You only need to adjust the output parameters of the laser. Laser cutting produces low noise, minimal vibration, and no pollution. |
| Versatility in Cutting Material | Compared to traditional cutting technologies like oxyacetylene cutting and plasma cutting, laser cutting can handle a wider variety of materials. This includes metals, non-metals, metal-based and non-metal-based composite materials, leather, wood, and fibers. |
| Cutting method: | Brief introduction | Comparison with laser cutting |
| Thermal cutting | Such as oxygen- combustible gas (such as acetylene) cutting and plasma cutting | Wide cut, large heat affected area, obvious workpiece thermal deformation, non-metallic cutting is not allowed. |
| Machining | Mechanical stamping, shearing, sawing and other processing methods | It will cause blade deformation, burr and wear, wide incision, low material utilization rate, great threat to operator safety, and serious noise and dust pollution. |
| Electric machining | Generally, there are two methods, EDM and electrochemical machining, which use electric corrosion and dissolution effect. They are mostly used for fine machining of hard materials with good notch roughness. | The cutting speed is several orders of magnitude slower than laser cutting. |
| Water cutting | When water is pressurized to 2700 ~ 5500kg / cm2, many materials can be cut through the high-pressure water flow formed by the small-diameter sapphire nozzle. | Many consumables, high operating costs, complex processes and low accuracy. |