Ever wondered why your laser-cut metal pieces aren’t as precise as they used to be? This article uncovers the secrets behind laser cutting kerf, exploring how factors like beam quality, material thickness, and cutting speed impact your results. Learn how to maintain top-notch performance and achieve perfect cuts every time!
As a common piece of equipment for sheet metal processing, a laser cutting machine plays a vital role.
Efficient and high-precision cutting are deeply ingrained in people’s minds.
However, after long-term use, the equipment’s performance may decline, and even the cutting plate may have large kerfs, which can affect cutting quality.
This issue needs to be resolved promptly. Let’s take a closer look below.
The cutting performance of an optical fiber laser cutting machine decreases due to machine wear and tear after long-term use, as well as due to insufficient maintenance during machine operation.

Different plates require different cutting methods, have different requirements, and use different equipment.
Moreover, the kerfs produced by cutting materials of different thicknesses also vary.
For example, a 10mm plate generally has the following characteristics when cut:
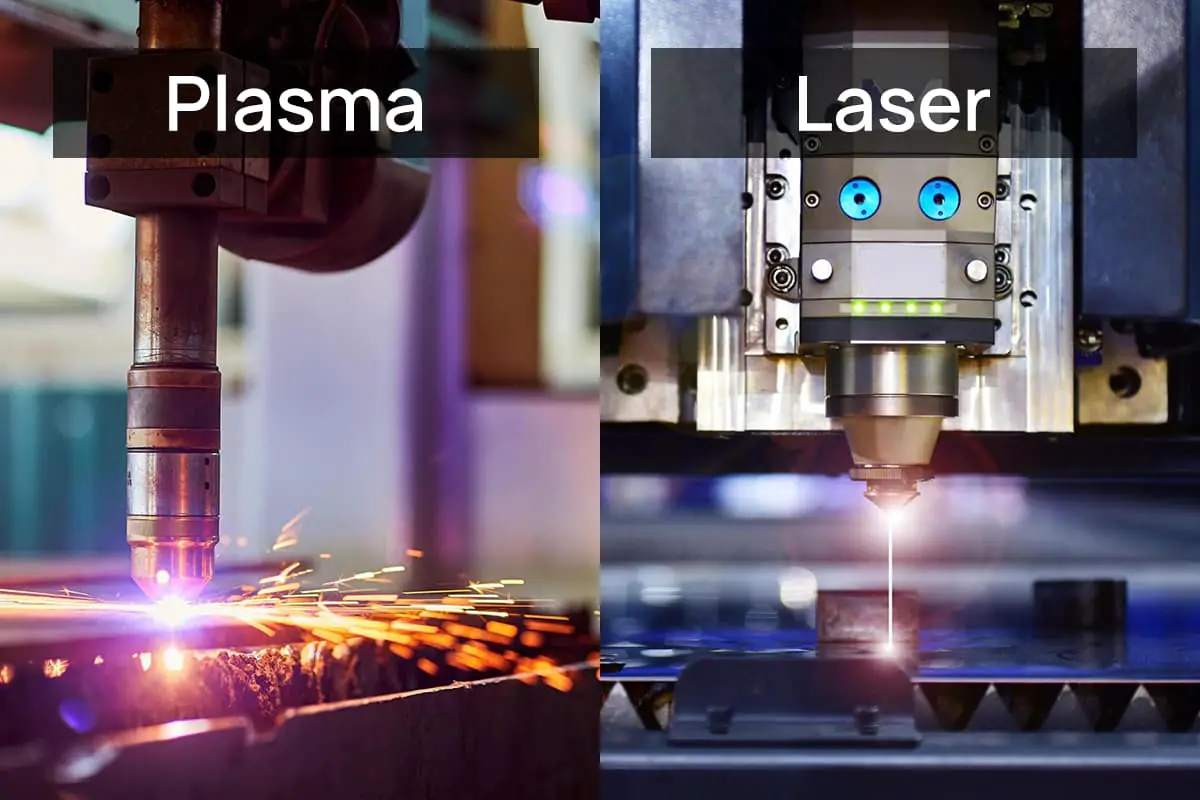
(1) Cutting with a metal laser cutting machine produces a cutting accuracy of ± 0.025mm, and a kerf width of 0.2 ~ 1mm.
(2) Cutting with a plasma cutting machine produces a cutting accuracy of ± 0.3mm, and a kerf width of 0.5 ~ 1.2mm.
(3) Cutting manually with acetylene produces a cutting accuracy of ± 1mm, and a kerf width of 1.0 ~ 1.5mm.
For materials with a thickness of less than 3.0mm, kerfs are generally within 0.3 ~ 0.5mm.
The thicker the material, the wider the cutting kerf, which is also related to the cutting nozzle and method used.
Laser cutting machines have been in development for many years and have gradually become the mainstream processing equipment for metal processing.
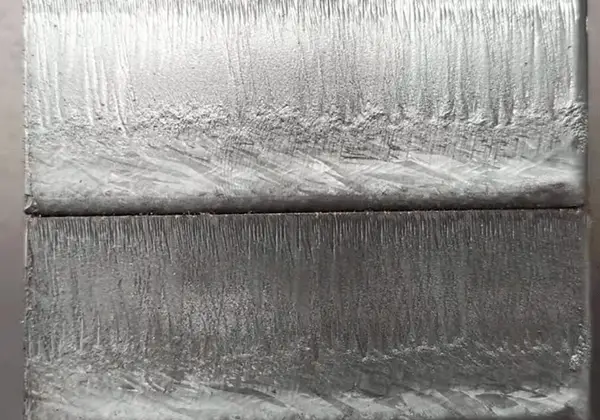
However, there are always some issues with cutting, such as producing a cutting kerf that is too wide.
So, what are the factors that affect the kerf width of a laser cutting machine?
There are four main factors:

The laser beam generated by a laser is not emitted vertically, but at a scattering angle.
Therefore, when using a laser cutting machine to cut a workpiece, a certain taper will be formed. Thus, the quality of the laser beam is also critical for cutting.
Generally, the focus should not be adjusted arbitrarily after adjustment. It should only be adjusted when there are noticeable issues in the cutting effect.

The actual cutting effect varies depending on the material being cut.
In laser cutting, a smaller spot from the laser beam produces a better cutting effect.
In addition to the quality of the laser beam affecting the spot, the workpiece material also affects the size of the spot.
For example, copper is highly reflective, which makes it challenging to form light spots. Therefore, the requirements of a copper laser cutting machine are higher compared to ordinary metals.
Under the same material and power cutting conditions, the thicker the material, the more likely it is to have burrs and unevenness on the cross-section.
To achieve the exact same section as the sheet material, the laser’s power needs to be increased.
The reason why the laser cutting machine is widely accepted is due to its fast cutting speed.
When other conditions remain constant, the cutting speed of a laser cutting machine must be appropriately adjusted to achieve the best cutting effect.
If the speed is too slow, the kerf’s roughness may be very large. If the speed is too fast, the kerf’s roughness may be reduced.
However, if the speed is too fast, it may not be able to penetrate the material, so it is essential to control the speed and not blindly pursue high-speed cutting.
When the laser power and auxiliary gas pressure are constant, the laser cutting speed maintains a nonlinear inverse relationship with the kerf width.
As the cutting speed increases, the kerf width decreases. As the cutting speed decreases, the kerf width will increase.
There is a parabolic relationship between cutting speed and the surface roughness of the cutting section.
As the cutting speed decreases, the surface roughness of the section increases, and as the cutting speed increases, the surface roughness improves.
When the optimal cutting speed is reached, the surface roughness of the cutting section is minimized.
If the cutting speed increases to a certain value, the plate cannot be cut through.
The most significant factor that affects the processing quality and capacity of a laser cutting machine is the focus position, and its specific relationship with processing is as follows.
The focus position is defined as the position after the laser beam is focused relative to the surface of the processed material.
The focus position affects nearly all processing parameters, such as the width, slope, roughness of the cutting surface, adhesion state of slag, and cutting speed.
This is because changing the focus position causes a change in the beam diameter on the surface of the processed material and the incident angle into the processing material.
Consequently, it affects the kerf’s formation state and the multiple reflections of the beam in the kerf, which affects the flow state of auxiliary gas and molten metal in the kerf.
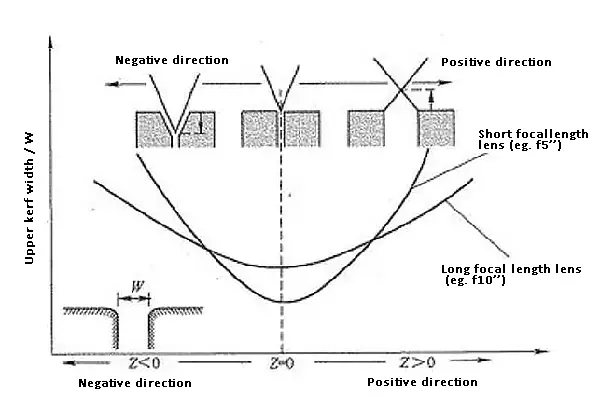
The figure shows the relationship between the focus position Z of a laser cutting machine and the kerf width W of the processed material surface.
The focus state on the processed material surface is set to Z = 0 “zero,” the focus position is represented by “+” when moving upward, “-” when moving downward, and the movement amount is in mm.
When the focus is at the focus position Z = 0, the upper kerf width W is the minimum.
Whether the focus position moves up or down, the upper kerf width W becomes wider.
This tendency is the same when processing lenses with different focal lengths.
The smaller the beam diameter at the focus position and the shorter the focal depth of the lens, the greater the variation of the upper kerf width with the focus position’s change.
| Focus position | Features | Application |
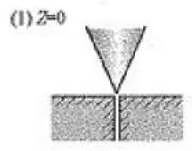 | The kerf is the narrowest and can be processed with high precision | Processing requiring slope reduction; Processing with high requirements for surface roughness; High speed cutting; Reduce the processing of heat affected zone; Micro machining |
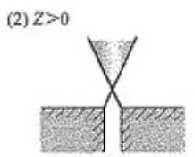
| Widening below the kerf, can improve the flow of gas and the fluidity of melt | CW and high frequency pulse processing of thick plate; Acrylic plate processing; Tool die processing; Ceramic tile processing |
 | Widening above the kerf, can improve the flow of gas and the fluidity of melt | Air cutting of aluminum; Nitrogen cutting of aluminum; Air cutting of stainless steel; Nitrogen cutting of stainless steel; Air cutting of galvanized steel sheet |
The figure above shows the best focus position of the metal laser cutting machine when processing various processing materials.
(1) The minimum beam diameter Z = 0 can be obtained at the material surface.
At this point, the maximum energy density can be obtained on the processed material surface, and the melting range is relatively narrow, which determines the processing characteristics.
(2) The focus position is on the “+” side (Z > 0).
At this point, the irradiation range of the laser beam on the processed material surface becomes wider, and the beam in the kerf has a diffusion angle, which increases the kerf width.
(3) The focus position is on the “-” side (Z < 0).
At this point, the range of the laser beam irradiated on the processed material surface becomes wider.
The closer the focus position is to the plate thickness direction, the higher the melting capacity, and then a reverse slope occurs.
Usually, during laser cutting machine processing, there are instances where a large cutting kerf occurs. This situation results in low cutting accuracy, which does not meet our requirements.
What is the reason for this situation? Is there a way to solve it?
After continuous observation and analysis, the technical engineer has devised three solutions:
The optical fiber focal length adjustment can be in manual or automatic form.
Manual focusing is prone to be forgotten by technicians, especially after lens replacement or cleaning; thus, the focal length should be readjusted.
Check if the lens is damaged or dirty since this can cause laser scattering and beam thickening. Replacing or cleaning the lens is the only solution.
Check the quality of the laser spot.
If there are two points or the light spot is not round, the laser tube’s support point may require adjustment.
This reason is often neglected, but it still demands attention.
Large laser cutting seams are not a significant issue, but the equipment must undergo maintenance after production and processing for a certain period.
In fact, some minor irregularities may occur during use, which necessitates proper maintenance to ensure efficient and long-term laser cutting machine operation, and create the maximum value for users.
The factors that affect the quality of laser cutting kerf are very complex.
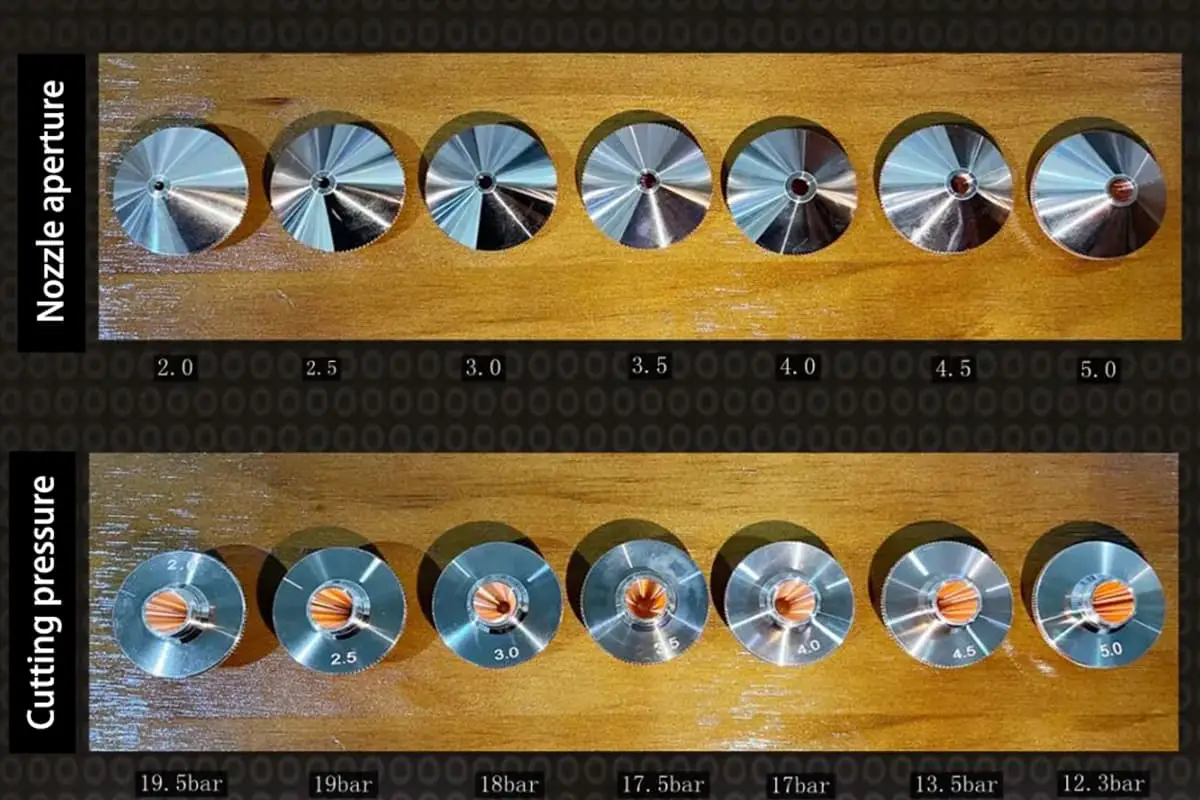
From the above content, we know that besides the processing material itself, many other factors determine the kerf width, including beam characteristics, laser power, cutting speed, nozzle type (aperture), and nozzle height, focus position, auxiliary gas type, and pressure, among others.
See also:
Here are some tips for ensuring the cutting quality when using a laser cutting machine:
Note: observe every day and maintain the lens once a week.