Press brake operators play a crucial role in shaping the world around us, but their work is not without risks. In this article, we’ll explore essential safety tips from industry experts to help keep these skilled professionals out of harm’s way while they craft the components that make our lives better.
Because operators have to work very close to press brakes and hold the sheet metal firmly with their hands, their safety is continuously at risk.
Hence it is important to minimise an operator’s exposure to injury as much as possible.
Modern press brakes are equipped with safety systems with fixed photoelectric guards and laser protection systems to prevent operators’ fingers from being crushed between the sheet metal and the punch tip.
For this reason, press brake safety devices must always be active.
However, operators must pay particular attention during working phases when safety devices do not stop the press brake automatically in the event of danger.
During press brake set-up, the machine must always be locked to ensure that accidental pressure on the foot pedal does not activate the upper beam which should be in the dead-center position.
During working phases, operators must support and handle the sheet metal properly; they must also avoid actions that are dangerous or that could impede the normal movement of the sheet metal.
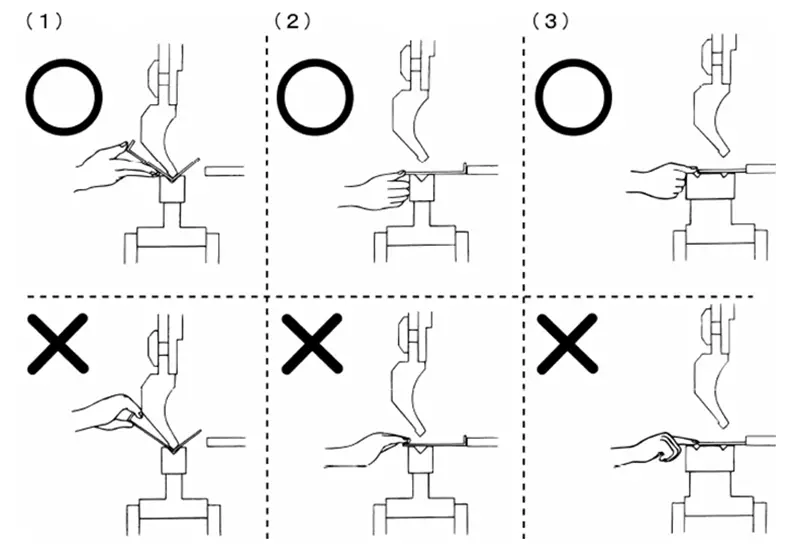
Operators should pay particular attention to ensuring that they do not hold the sheet in such a way as to risk crushing their fingers between the
sheet metal and the punch tip.
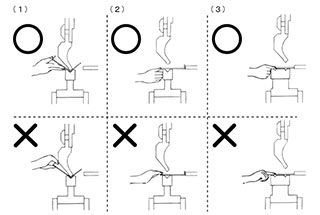
The correct way to hold workpieces:
Start
Open the power switch → Hold up the pedal switch to start pump → Turn on the boot key → L-axis reset → D-axis reset → Commissioning
Install Punch & Die
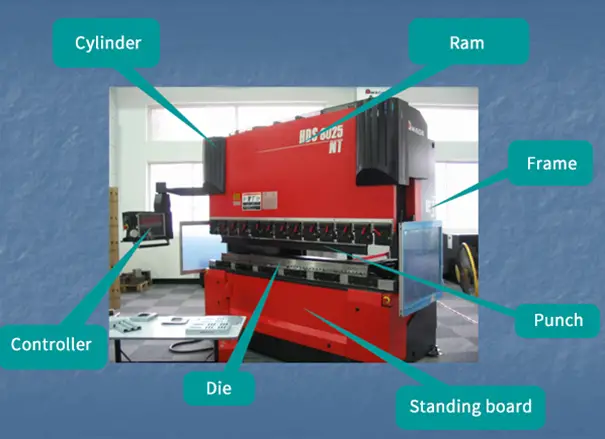
First, install the punch and then the die. To align them, loosen the two screws under the guide rail.
Raise the height of the punch first and then slowly step on the pedal to check if the mold is concentric. Always check the pressure gauge to ensure that the pressure does not exceed the range.
Pickup & placement of the workpiece
Do not place your hands between the folded workpiece and the die to avoid pinching your fingers. When aligning the mold, keep your hands and any part of your body away from the space between the upper and lower mold.
When bending large pieces, be aware of the rebound of the workpiece as it may cause injury to your face.
If the press brake is being operated by two or more people, one of the operators should have control over the pedal switch and operate it carefully.
Strictly adhere to the safety regulations for machine tool workers and wear the required protective gear.
Before starting the press brake, thoroughly inspect the motor, switch, wires, and grounding to ensure they are functioning properly and securely. Make sure that the control parts of the equipment and buttons are in the correct positions.
Check the alignment and stability of the upper and lower dies, and ensure that the positioning devices meet the fabrication requirements.
If the upper slide plate and position axes are not in the origin state, reset the program.
If you hear an abnormal sound or experience a breakdown within 1-2 minutes of starting the press brake or after the upper slide plate has completed 2-3 movements, stop the press brake immediately. Only restart the press brake operation once everything has been confirmed to be working normally.
During the operation of the press brake, only one person should be in control. This requires close cooperation between the operator and the feed suppression personnel to ensure that the bending signal is given only after all personnel are in a safe position.
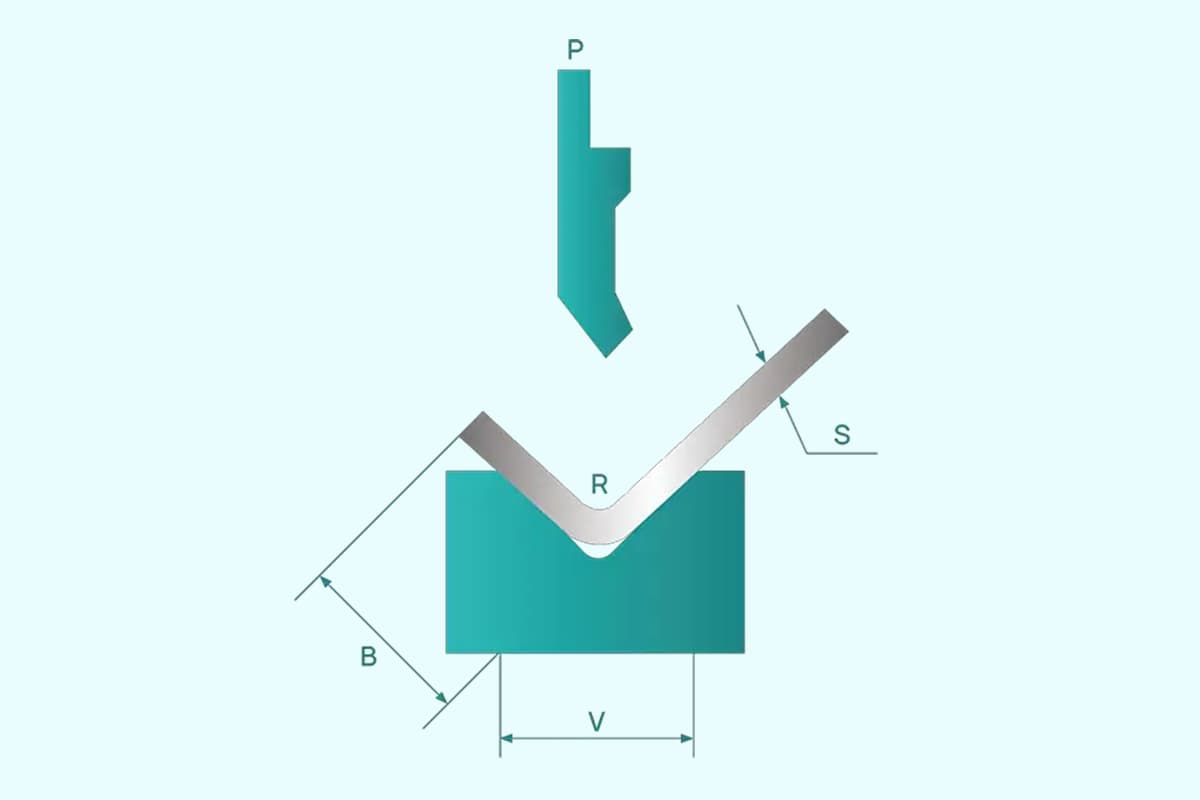
Adjust the slider stroke and select the upper and lower die and bending force based on the thickness and shape of the sheet to be bent. Choose the V-width of the lower die and check the bending force of the workpiece according to the press brake bending force chart on the right side of the machine. The bending force should not exceed the nominal force.
When adjusting the clearance between the upper and lower molds, the slider must be parked on the dead point. Clearance should be adjusted from large to small.
The initial clearance between the upper and lower molds should generally be 1mm larger than the plate thickness, with a gap greater than the plate thickness to avoid damage to the molds due to insufficient clearance.
When bending with two people, designate one person to step on the brakes and cut off the power when leaving the machine.
Do not make unilateral and single-point loads.
The sheet must be compacted to prevent warping and injury during bending.
Do not place gauges or other objects between the upper and lower molds.
Cut off the power and stop the press brake when adjusting the molds.
Ensure the correct selection of bending molds and proper fastening of the upper and lower dies to prevent injury during installation.
Do not allow material to touch the lower die when changing the opening of a variable die.
Choose the correct bending pressure, with eccentric loads being 1/2 less than the maximum pressure.
The length of the bending workpiece should not be less than 1/3 of the worktable length under maximum bending pressure.
Do not stand behind the press brake during operation.
Do not apply pressure to one end of the sheet material alone.
If the workpiece or mold is found to be misaligned during operation, stop the press brake and make corrections. Do not use manual correction during operation to prevent injury.
Do not bend ultra-thick iron sheets, quenched steel plates, advanced alloy steel, square steel, or material exceeding the performance of the press brake to prevent damage to the press brake.
Regularly check the alignment of the upper and lower molds and the indication of the pressure gauge.
If any abnormal situation occurs, stop the press brake immediately, investigate the cause, and notify the relevant personnel for prompt troubleshooting.
Before shutting down, place a wooden block under the cylinder at both ends of the lower die and drop the top slide onto the block.
After completion, exit the control system procedures, cut off the power, and clean the worksite.
Safety procedures must always be followed at all times, such as the use of personal protective equipment, in particular gloves and clothing suitable for sheet metal working.
At the same time, they must ensure that they position their hands correctly when supporting and subsequently processing the workpiece while avoiding unnatural actions that impede the normal movement of the sheet metal.