Have you ever wondered why your laser cutting machine fails to cut through metal cleanly? This article explores the common causes behind this issue and offers practical solutions to enhance your machine’s performance. Learn how to maintain your equipment for precise and efficient metal cutting.
.jpg)
Metal laser cutting machines are a crucial tool in the mechanical metal processing and manufacturing industry and are commonly used to replace traditional cutting equipment. However, improper operation or lack of maintenance can lead to various problems with this precision equipment.
One common issue during the cutting process is the phenomenon of not cutting through.
To address this issue, it’s important to understand the causes and find suitable solutions.
In the following, I will introduce the causes and solutions for the problem of not cutting through with laser.
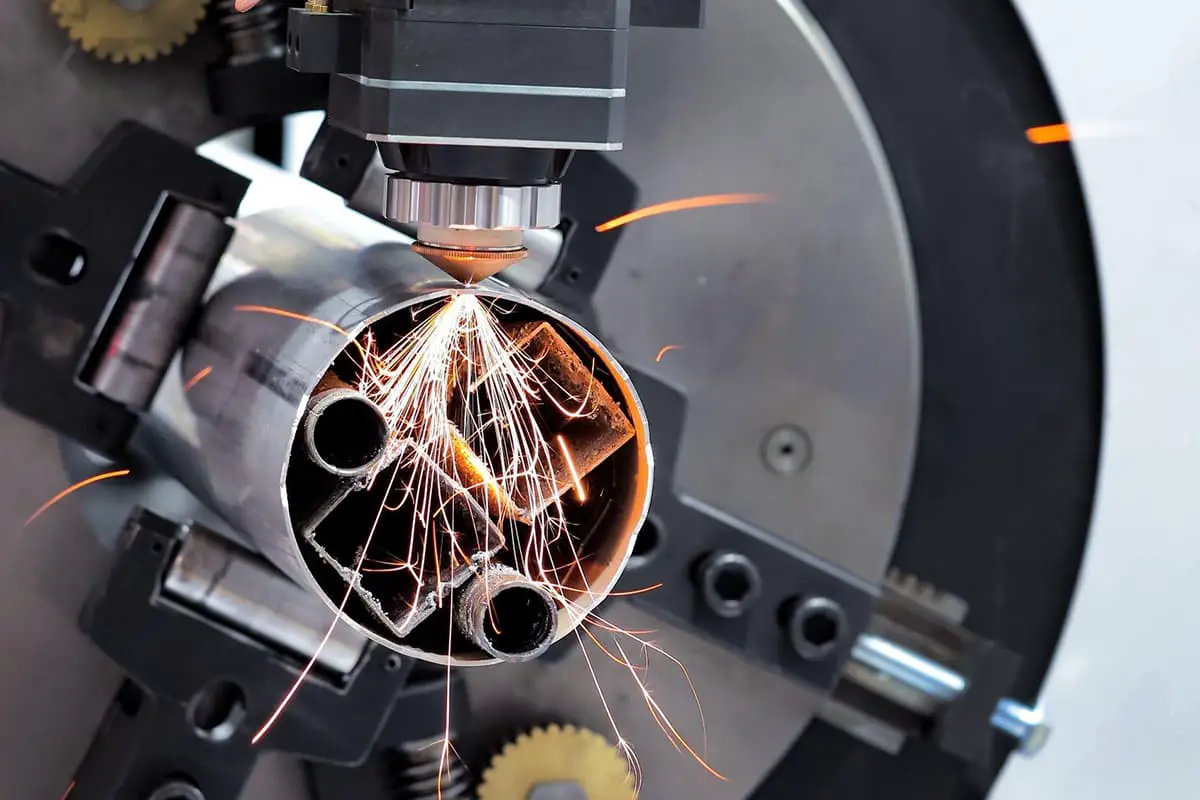

Laser cutting is a complex process and can often result in rough incisions or incomplete cuts. There are various reasons why this can occur, including a reduced laser power or aging lamp tube, which leads to insufficient laser beam energy.
Other reasons can include cutting at too fast a speed, damage to the focusing lens, poor focusing, incorrect light path, and unstable voltage.
Other factors that can cause rough incisions or incomplete cuts include the material itself, insufficient auxiliary gas pressure, dirty cooling system water, and poor heat dissipation.
It is important to take the issue of incomplete laser cuts seriously and work to identify and address the root causes in order to improve production efficiency and ensure high-quality laser cutting.

The following is a list of six reasons for a laser cutting failure.

To address the issue of declining laser power and low current, it is recommended to replace the laser tube and use a larger voltage regulator to increase the laser current output and enhance the output power.
In order to avoid incomplete cuts, it is important to reduce the cutting speed appropriately and keep the optical elements such as the mirrors and focus lenses clean and free from contamination. This may involve timely cleaning or replacement of the lenses.
If there is an issue with the light path, readjust it and adjust the focal length until the laser beam creates a circular spot on the paper.
For cutting materials such as copper and aluminum, which have a high reflection rate, it may be beneficial to polish the surface or apply light-absorbing material in advance.
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the foreign materials from the nozzle and increasing the pressure of the auxiliary gas, as well as replacing the distilled water in the cooling system in a timely manner, can also help improve the cutting quality and reduce the risk of incomplete cuts.
These measures can effectively solve the problem of the sample not cutting through, and we hope they help you. If you encounter issues that cannot be resolved on your own, it is important to promptly inform your supplier so that professional after-sales personnel can perform further investigation, examination, and maintenance.
Use a vacuum cleaner to remove dust and dirt from the machine once a week and make sure to keep all electrical cabinets closed to prevent dust buildup.
Regularly check the tension of the steel belt on the fiber laser cutting machine. Loose belts can cause operational problems and even pose a safety risk. Although it may seem like a small detail, it is still important to keep the belt tight.
Inspect the straightness of the laser cutting machine’s track and the machine’s verticality every six months and perform timely maintenance and debugging if any issues arise. Neglecting these checks can result in poor cutting quality and increased error, which affects the overall cutting quality.
The double focal length laser cutting head is a vulnerable component that may become damaged over time with prolonged use.
Regularly clean the guide rails of the optical fiber laser cutting machine to remove any dust or debris and ensure normal operation. Wipe down the rack frequently and add lubricating oil to keep it free of debris. Clean and lubricate the guide rail and motor regularly to improve the machine’s movement and cutting accuracy, ultimately leading to improved cut product quality.