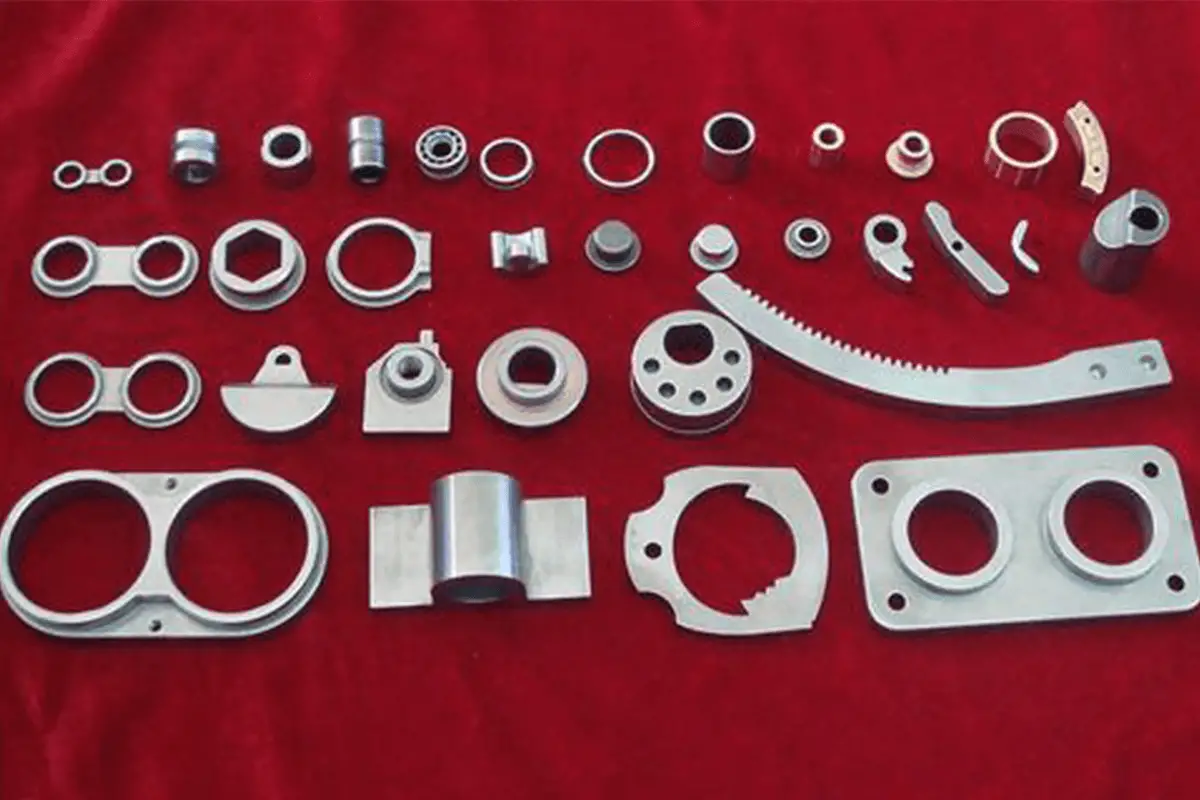
Imagine transforming raw metal powder into complex, high-performance parts without the need for traditional melting processes. This is powder metallurgy—a versatile manufacturing technique that combines powders to create materials with unique properties and intricate shapes. From automotive gears to aerospace components, powder metallurgy offers precision and efficiency. Dive into this article to uncover how powder metallurgy works, its advantages, and its wide-ranging applications across various industries.


Powder metallurgy is a manufacturing process that involves using metal powder, or a mixture of metal powder and non-metal powder, as a raw material. The powder is then formed and sintered to produce a range of metal materials, composite materials, and various types of articles.
Powder metallurgy shares similarities with ceramics production and belongs to the powder sintering technology family. As a result, a series of new powder metallurgy technologies can also be used to create ceramic materials.
The advantages of powder metallurgy technology have made it a critical tool in solving new material problems and playing a decisive role in the development of new materials.
Powder metallurgy involves creating powder and manufacturing products. Powder metallurgy is primarily a metallurgical process, as the name suggests.
The products created using powder metallurgy often extend beyond the realm of materials and metallurgy, encompassing multiple fields, such as materials and metallurgy, machinery and mechanics.
Modern metal powder 3D printing, in particular, combines various technologies such as mechanical engineering, CAD, reverse engineering, layered manufacturing, numerical control, material science, and laser technology. This integration has made powder metallurgy product technology a comprehensive and modern technology that spans across several disciplines.
Powder metallurgy offers a distinct chemical composition as well as mechanical and physical properties that are not attainable through traditional fusion casting methods.
Powder metallurgy techniques enable the direct production of porous, semi-dense, or fully dense materials and articles. This includes oil-containing bearings, gears, cams, guides, tools, and other items, which require less cutting during the manufacturing process.
(1) Powder metallurgy technology can minimize the segregation of alloy components and eliminate coarse and uneven cast structure.
The production of high-performance materials such as rare earth permanent magnets, rare earth hydrogen storage materials, rare earth luminescent materials, rare earth catalysts, high-temperature superconductors, and new metal materials like Al-Li alloy, heat-resistant Al alloy, superalloy, powder corrosion-resistant stainless steel, powder high-speed steel, and high-temperature structural materials such as intermetallic compounds, is crucial.
(2) A variety of high-performance non-equilibrium materials, including amorphous, microcrystalline, quasicrystal, nanocrystalline, and supersaturated solid solutions, can be prepared.
These materials have excellent electrical, magnetic, optical and mechanical properties.
(3) Powder metallurgy allows for easy realization of various types of recombination and enables each component material to fully exhibit its respective characteristics. This process technology is ideal for producing high-performance metal-based and ceramic composite materials at a low cost.
(4) With powder metallurgy, it becomes possible to produce materials and products with special structures and performances that are unattainable through ordinary smelting methods. Examples of such materials include new porous biological materials, porous separation membrane materials, high-performance structural ceramic abrasives, and functional ceramic materials.
(5) Powder metallurgy makes near-net formation and automated mass production achievable, thus effectively reducing production resources and energy consumption.
(6) By utilizing powder metallurgy, it becomes possible to make full use of raw materials such as ore, tailings, steelmaking sludge, rolling steel scales, and recycling waste metal. It is a new technology that enables effective material regeneration and comprehensive utilization.
Powder metallurgy technology is also used to create common machining tools and hardware grinding tools.
From a materials production standpoint, the powder metallurgy method can generate structural, functional, and composite materials with unique properties.
(1) Powder metallurgy can create materials with special characteristics that are unattainable through conventional melting methods:
1) It enables control over the porosity of the products;
2) It leverages the combined effect of metals with other metals and non-metals to produce materials with a variety of specific properties;
3) It can manufacture various composite materials;
(2) Certain materials produced via powder metallurgy demonstrate superior performance compared to those made by standard melting methods:
1) The properties of high alloy powder metallurgy materials exceed those produced by casting methods;
2) The production of refractory metal materials and products generally relies on powder metallurgy;
When looking at the manufacture of mechanical parts, powder metallurgy represents a novel process of minimal or non-cutting, significantly reducing the amount of machining required, conserving metal materials, and increasing labor productivity.
In summary, powder metallurgy is both a technology capable of producing materials with unique properties and a process for manufacturing cost-effective, high-quality mechanical parts.
(1) Powder production. This process includes the creation and mixing of the powder. To enhance the moldability and plasticity of the powder, plasticizers such as gasoline, rubber, or paraffin are often added.
(2) Press forming. The powder is pressed into the required shape under a pressure of 500-600 MPa.
(3) Sintering. This step is carried out in a high-temperature furnace or vacuum furnace under a protective atmosphere. Sintering is not like melting of metals; at least one element remains solid during the process. During sintering, the powder particles undergo a series of physicochemical processes like diffusion, recrystallization, welding, combining, and dissolution, transforming into metallurgical products with a certain porosity.
(4) Post-processing. In general, sintered parts can be used directly. However, for components requiring high precision and possessing high hardness and wear resistance, post-sintering treatments are necessary. This includes precision pressing, rolling, extrusion, quenching, surface hardening, oil impregnation, and infiltration.
Modern Powder Metallurgy Process:
The first is overcoming the difficulties encountered in the casting process of refractory metals such as tungsten and molybdenum.
The second is the successful production of porous oil-impregnated bearings using powder metallurgy methods in the 1930s.
The third is the development towards more advanced new materials and processes.
Powder metallurgy is an emerging field, yet it also has ancient roots. Archaeological evidence suggests that as far back as 3000 BC, Egyptians used a type of bellows to reduce iron oxide to sponge iron with carbon. This was then forged into a dense block at high temperatures and hammered into iron objects. In the 3rd century, Indian blacksmiths used this method to create the “Delhi Pillar”, weighing 6.5 tons.
In the early 19th century, the processes of cold pressing and sintering platinum powder to make dense platinum, which was then processed into platinum products, appeared in Russia and England. The use of this powder metallurgy process ceased after the smelting of platinum was introduced in the 1850s, but it laid a solid foundation for modern powder metallurgy.
Powder metallurgy did not see rapid development until the advent of W. D. Coolidge’s tungsten filament for light bulbs in 1909.
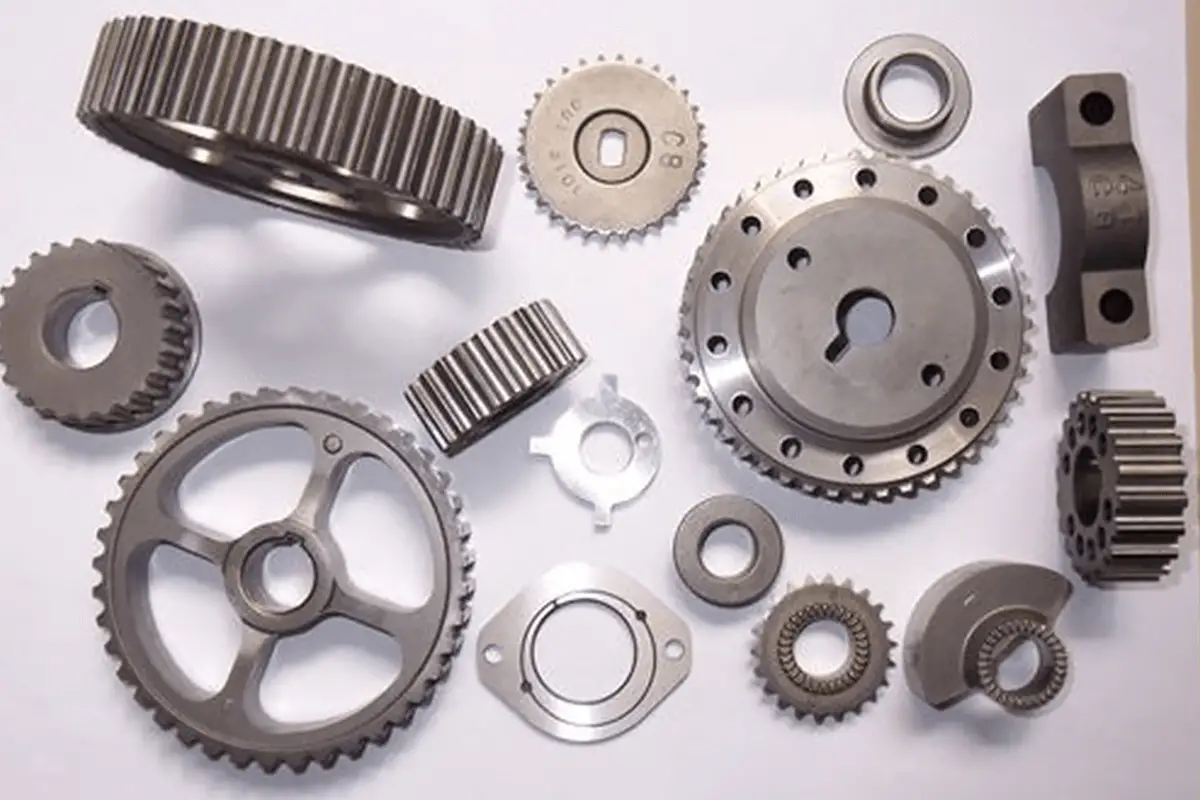

It plays a substantial role in energy conservation, material efficiency, performance enhancement, labor productivity improvement, and environmental protection. As a preparatory technique for special and high-performance materials, it promotes the growth of the defense industry and technological sectors. The advent of this technology could trigger a revolutionary transformation in traditional material processes, imparting a richer and profound essence to material science and metallurgy.
Enterprises related to powder metallurgy are primarily utilized in spare parts production and research for the automotive industry, equipment manufacturing, metal industry, aerospace, military industry, instrumentation, hardware tools, electronic appliances, and other fields. They also engage in the production of related raw materials, accessories, various types of powder-making equipment, and sintering equipment manufacturing.
Their products include bearings, gears, carbide tools, molds, friction products, and more.
In the military industry, heavy-duty weapons and equipment such as armor-piercing projectiles, torpedoes, aircraft, and tank brakes require the use of powder metallurgy in their production.
(1) Applications: (automobile, motorcycle, textile machinery, industrial sewing machines, power tools, hardware tools, engineering machinery, etc.) various powder metallurgy (iron-copper-based) parts.
High-performance structural materials, metal ceramics, superconducting materials, amorphous materials, nanomaterials, composite materials, porous materials
Powder metallurgy has a wide range of applications in addressing material-related issues. In terms of material composition, there are iron-based powder metallurgy, non-ferrous metal powder metallurgy, and rare metal powder metallurgy.
In terms of material properties, there are both porous and dense materials; both hard and soft materials; both heavy alloys and light foam materials; both magnetic materials and other functional materials.
In terms of material types, there are both metallic materials and composite materials. Broadly speaking, composite materials include metal and metal composites, metal and non-metal composites, metal-ceramic composites, dispersion-strengthened composites, and fiber-reinforced composites.
Due to its technical and economic advantages, powder metallurgy is increasingly used in the national economy. It can be said that there is no industrial sector that does not use powder metallurgy materials and products.
(2) Classification:
The iron powder and iron-based powder metallurgy industries are unable to meet the demands of our national economic development. We lack a specialized manufacturing sector for powder metallurgy equipment, and suffer from a lack of unified national planning.
The fragmentation is severe, investment intensity is low, and there is yet to be an organic integration of research, development, and industrial production. Additionally, improvements in the industrial structure and technical level of the tooling industry, including cutting tools, are still needed.
These include: geometric properties of the powder (particle size, specific surface area, pore size, and shape, etc.); the chemical properties of the powder (chemical composition, purity, oxygen content, and acid-insoluble substances, etc.); the mechanical characteristics of the powder (bulk density, flowability, moldability, compressibility, angle of repose, and shear angle, etc.); the physical properties and surface characteristics of the powder (true density, luster, shock absorption, surface activity, potential, and magnetism, etc.). The properties of the powder largely determine the performance of powder metallurgy products.
The most basic geometric properties are the particle size and shape of the powder.
(1) Particle size
It affects the processing and molding of the powder, shrinkage during sintering, and the final performance of the product. The performance of certain powder metallurgy products is almost directly related to particle size.
The powder used in production practices ranges in size from hundreds of nanometers to hundreds of micrometers. The smaller the particle size, the greater the activity, and the surface is more likely to oxidize and absorb water.
When the size is reduced to a certain extent, quantum effects begin to play a role, and its physical properties undergo significant changes, such as ferromagnetic powder becoming superparamagnetic powder, and the melting point decreasing with particle size reduction.
(2) The shape of the powder particles depends on the method of powder production.
For instance, powder produced by electrolysis is dendritic in shape; iron powder produced by reduction has a sponge-like shape; and powder made by gas atomization is predominantly spherical.
Furthermore, some powders have an ovoid, disc-like, needle-like, or onion head-like shape.
The shape of the powder particles influences the flowability and bulk density of the powder, and due to mechanical interlocking between particles, irregular powders also have a high compact strength, especially dendritic powders which have the highest compact strength. However, for porous materials, spherical powders are preferred.
The mechanical properties of the powder, or the processability of the powder, are important technical parameters in the powder metallurgy molding process. The bulk density of the powder is the basis for volume measurement during compression; the flowability of the powder determines the filling speed of the powder in the die and the production capacity of the press; the compressibility of the powder determines the difficulty of the pressing process and the level of pressure applied; and the formability of the powder determines the strength of the compact.
The chemical properties mainly depend on the chemical purity of the raw materials and the method of powder production. A higher oxygen content can reduce the pressing performance, compact strength, and mechanical properties of sintered products, so most technical conditions in powder metallurgy stipulate this.
For example, the allowable oxygen content of the powder is between 0.2% and 1.5%, which is equivalent to an oxide content of 1% to 10%.
(1) Granularity and Distribution
The smallest independent entity in a powder is a single particle. Actual powders usually consist of aggregated particles, also known as secondary particles. The percentage of different sizes within the actual powder particles constitutes the granularity distribution.
(2) Particle Shape
This refers to the geometric appearance of the powder particles. Common shapes include spherical, cylindrical, needle-like, plate-like, and flake-like, which can be determined through microscopic observation.
(3) Specific Surface Area
This is the total surface area per unit mass of the powder, which can be measured empirically. The size of the specific surface area influences the powder’s surface energy, surface adsorption, and agglomeration among other surface properties.
Powder’s Process Performance
The process performance of powder includes flowability, filling characteristics, compressibility, and formability.
(1) Filling Characteristics
This refers to the degree of looseness or compactness of the powder when it is freely piled without external conditions, commonly represented by bulk density or stacking density. The filling characteristics of the powder are related to the size, shape, and surface properties of the particles.
(2) Flowability
This refers to the ability of the powder to flow, often represented by the time required for 50 grams of powder to flow out of a standard funnel. The flowability is affected by particle adhesion.
(3) Compressibility
This represents the powder’s ability to be compressed during the pressing process, represented by the compact density achieved under a specified unit pressure, measured under specified lubrication conditions in a standard mold.
Factors affecting the compressibility of the powder include the plasticity or microhardness of the particles; plastic metal powders have better compressibility than hard, brittle materials. The shape and structure of the particles also affect the compressibility of the powder.

To meet various requirements for powders, there are diverse methods of production, transforming metals, alloys, or metal compounds from solid, liquid, or gaseous states into powder form. The various methods of powder preparation, along with typical examples of the powders produced, are detailed in the table.
Methods of powder preparation in the solid state include:
1. Extracting metal and alloy powders from solid metals and alloys through mechanical pulverization and electrochemical corrosion;
2. Deriving metal and alloy powders from solid metal oxides and salts via the reduction method; and preparing metal compound powders from metal and non-metal powders, as well as metal oxides and non-metal powders, through the reduction-combination method.
Methods of powder preparation in the liquid state include:
1. atomization of liquid metals and alloys to produce metal and alloy powders;
2. displacement and reduction of metal salt solutions to produce metal, alloy, and coated powders using displacement methods and solution hydrogen reduction methods; precipitation of metal powders from molten salts using the molten salt precipitation method; derivation of metal compound powders from auxiliary metal baths via the metal bath method;
3. electrolysis of metal salt solutions to produce metal and alloy powders using aqueous electrolysis; production of metal and metal compound powders through electrolysis of molten metal salts using the molten salt electrolysis method.
Methods for preparing powders in gaseous state include:
1) vapor condensation method for generating metal powders from metal vapors;
2) thermal decomposition of gaseous metal carbonyls for generating metals, alloys, and coated powders;
3) gas-phase hydrogen reduction method for preparing metals, alloy powders, and metal/alloy coatings from gaseous metal halides;
4) chemical vapor deposition method for generating metal compound powders and coatings from gaseous metal halides.
However, in essence, the existing powder preparation methods can be broadly categorized into two main types: mechanical and physicochemical methods. The mechanical method involves mechanically pulverizing the raw materials without significant changes in their chemical composition.
The physicochemical method leverages chemical or physical effects to alter the chemical composition or aggregation state of the raw materials to obtain powders. There are various powder production methods.
On an industrial scale, the most widely used methods are reduction, atomization, and electrolysis. The methods of vapor deposition and liquid precipitation are also important for special applications.
1. Twin-Fluid Atomization Powder Characteristics:
The powder produced by water atomization usually has an irregular shape with a high surface oxygen content. The powder created by gas atomization typically has a spherical shape, and if an inert gas is used for atomization, the oxygen content is relatively low.
2. Mechanical Pulverization
This method is generally suitable for preparing powders of brittle materials. The particle shape is irregular and the size is uneven.
3. Carbon Reduction
11. Mechanical pulverization methods are primarily utilized for crushing brittle metals and alloys, while techniques like vortex grinding and cold air stream grinding are used for malleable metals and alloys.
The shape of powder particles depends on the method of powder production. For instance, electrochemical processes produce dendritic particles; reduction methods yield sponge-like iron particles; and gas atomization typically results in spherical powder.
Additionally, some powders may adopt ovoid, discoid, acicular, or onion-like shapes.
The shape of the powder particles impacts the powder flowability and loose packing density.
Due to mechanical interlocking between particles, irregular powders also have greater compacting strength, especially dendritic powders which demonstrate the highest compacting strength.
However, for porous materials, spherical powders are optimal.
According to the type of powder material: Powder Metallurgy Molding Methods and Ceramic Molding Methods;
According to the characteristics of the billet: Dry Billet Molding, Plastic Billet Molding, Slurry Molding;
According to the continuity of the molding: Continuous Molding, Non-continuous Molding;
According to the necessity of a mold: Molded Molding, Mold-less Molding.
Plastic blanks contain more various types of molding agents than dry blanks, generally not exceeding 20% to 30%.
The blank is in a semi-solidified state, possesses certain rheological properties, and exhibits excellent plasticity. It can maintain its shape after molding or after cooling (refer to page 15 in the book).
Molded blanks possess certain strength due to the interlocking of particles and the shape-retaining effects caused by other factors.
They can withstand their own weight and appropriate forces exerted during subsequent processing stages, preventing damage before completion of sintering.
For refractory powders like ceramic powder, with very poor plastic deformation capability, a large elastic deformation occurs under high pressure.
When the pressure is removed, the particles rebound, the compressed gas restores, leading to brittle fracture. Therefore, the molding pressure should not be too high.
The greater the molding pressure, the larger the elastic aftereffect generally is; the finer the powder particles and the more complex their shape, the higher the elastic aftereffect value of the compact; the elastic aftereffect value of the compact decreases with the increase of the compact porosity; when a surface-active lubricant is added to the powder, the powder particle surface is activated due to adsorption, making particle deformation easier and transitioning from elastic deformation to plastic deformation, thus significantly reducing the elastic aftereffect value; non-surface-active lubricants almost have no effect on the elastic aftereffect value; the material and structure of the mold also significantly affect the elastic aftereffect.
The distribution of pressure during compression is related to the method used.
Unidirectional Compression: Due to friction from the mold walls, the compressive force experienced from top to bottom at the edge of the compaction decreases continuously, consequently reducing its density.
The particles at the bottom edge of the compaction receive the least pressure, and therefore have the lowest density.
Bidirectional Compression: High pressure at the top and bottom, lower pressure in the middle. Although this method doesn’t reduce friction during molding, the effective distance of pressure gradient transmission is halved.
Hence, the reduction in compressive force due to friction is only half of what it is during unidirectional compression.
Isostatic Compression: The pressure received from all directions is uniform and consistent.
(Powder compaction within a mold exerts two types of compressive forces on the powder: one part is used to overcome the internal friction of the powder and causes it to displace and deform; the other part of the force is used to overcome the external friction between the powder and the mold wall.
The total pressure of compression is the sum of these two forces. As the powder tries to flow in all directions under compression, it exerts a lateral pressure on the mold wall.)
The main causes of pressure drop are the internal friction among the powder particles and the external friction between the powder and the die wall.
The presence of external friction causes a continuous loss of pressure as the compressive force on the compact surface is transmitted downward along the axis.
Lengthwise: The strip blank density gradually increases from the starting end, remains constant during the stable stage, and gradually reduces from the stable stage to the unstable ending stage.
Cause: At the rolling start stage, due to the increasing bite and compaction of the powder, elastic deformation occurs. The bitten powder generates a wedging force, widening the roll gap to allow more powder to be bitten into the deformation zone.
When the powder’s wedging force and the mill’s elastic deformation resistance balance, the compaction zone forms, and rolling enters the stable stage. The sign of reaching the stable stage is consistent density along the length.
In the unstable ending stage, the powder in the feed hopper has dropped to a certain height, the amount of powder bitten into deformation decreases, the rolling load also falls, the rolling elastic deformation reduces, and the rolling gap restores to its initial size. Therefore, the density gradually decreases along the length.
Thickness: The density is higher at the center and lower at the edges, showing a symmetric distribution around the center.
Cause: In the powder layer in contact with the rolling surface, the primary stress is tensile due to friction, while the powder layer at the center is under multidirectional compressive stress. The deformation of the powder on the strip blank surface is somewhat inhibited, even causing uneven stretching.
Therefore, the compression degree of the central powder layer is relatively greater. Under certain conditions, this difference in stress states can cause lamination along the strip thickness.
Width: The density is higher at the center and lower at the edges.
Cause: During rolling, the powder at the center and edges moves at different speeds towards the deformation zone along the width. This unevenness in powder flow ultimately leads to an uneven density distribution across the width.
While the powder at the edges should have a higher density after rolling due to faster flow, the friction between the powder and the baffle and the inevitable loss of powder at the edges generally result in a low-density zone of a certain width at the edges.
(1). Influence of Powder Flowability on Billet Performance
The flowability of the powder directly affects the density and its uniformity of billet, affecting the bite angle during rolling. The thickness and average density of the billet decrease as the powder flowability worsens.
(2). Influence of Powder Bulk Density on Billet Performance
With a smaller bulk density, the powder has a more complex shape, a larger specific surface, a smaller particle diameter, and better rolling properties. It can be rolled into a billet with higher strength. The bulk density of the powder has a significant impact on the performance of the rolled billet. As the bulk density of the powder increases, the density and thickness of the obtained billet also increase. The density and thickness of the rolled billet are directly proportional to the bulk density of the powder. This is because, under the same bite thickness, the powder with a larger bulk density will increase the amount of powder bitten in proportion during rolling, naturally increasing the thickness and density of the billet.
For a billet of a given density, its thickness will increase with the increase in roll diameter; the density of the billet rolled by a large roll is higher than that rolled by a small roll.
Assuming the compression coefficient value is the same and given the bite angle and the density of the rolled billet, it can be concluded that the powder bite cross-section is directly proportional to the thickness of the billet.
3. Influence of Feeding Method
If other rolling conditions remain the same, only changing the feed amount will affect the thickness or density of the rolled billet. If the billet thickness remains unchanged and the feed amount is reduced, the density of the rolled billet will inevitably decrease, and vice versa.
The powder in front of the deformation zone of rolling is pre-compressed due to the pressure exerted by the material column or forced feed, resulting in an increase in the bulk density of the powder.
The powder body in the deformation zone is pre-compressed, increasing its relative density and causing the lateral pressure coefficient value to increase, resulting in an increase in the bite angle; the powder body in the deformation zone is subjected to pressure, causing the extension coefficient value to decrease, which in turn increases the relative density of the rolled billet.
4. The Impact of Rolling Speed
Under the conditions of fixed feed speed and roll gap, increasing the rolling speed reduces the density and thickness of the rolled strip. This is because the rolling speed directly affects the friction coefficient value, which decreases as the speed increases.
5. The Influence of Rolling Atmosphere
Using a low-viscosity gas (like hydrogen) as the rolling atmosphere is beneficial for improving the density and thickness of the strip. When all other conditions remain constant, the density and thickness of the strip rolled in hydrogen can increase by up to 70% compared to those rolled in air.
Using a method to reduce air pressure or filling the powder with low-viscosity gas for rolling, especially for fine-grain powders, can achieve uniformly dense strips. To obtain a strip of certain thickness and density, you can reduce the pressure of the rolling atmosphere.
6. The Impact of Roll Gap Size
As the roll gap distance decreases, the thickness of the strip decreases, the compression ratio increases, and the density of the strip subsequently increases.
7. The Effect of Roll Surface Processing Degree
The thickness of the strip rolled by the sandblasted roll is twice as large as that of the highly polished roll. This can be explained by the increase in the friction coefficient between the powder body and the roll surface, as well as the enlargement of the bite angle.
The size of the extrusion force is related to the compression ratio; a larger compression ratio requires a larger extrusion force.
The larger the cone angle, the greater the extrusion resistance, requiring a larger extrusion force. If the sizing belt is long, the additional internal stress increases, and the billet is prone to longitudinal cracks.
On the other hand, if the sizing belt is too short, the extruded billet is prone to elastic expansion, resulting in transverse cracks.
Slurry molding methods are divided into basic and accelerated types. Basic slurry molding consists of hollow and solid slurry molding; accelerated slurry molding includes vacuum, pressure, and centrifugal slurry molding.
The most critical process in injection molding is the degreasing stage. Degreasing involves eliminating organic substances within the molded body through heating and other physical methods, resulting in a minimal amount of sintering.
It is the most challenging and significant factor in injection molding and constitutes the longest step in the process.
Powder injection molding is a new process that combines powder metallurgy technology with plastic injection molding. The process involves uniformly mixing the powder with thermoplastic material (such as polystyrene) to create a fluid substance with good flow properties under specific temperature conditions.
This fluid substance is then injected into a mold under certain temperature and pressure conditions on an injection molding machine. This process can produce complexly shaped blanks. The obtained blanks, after solvent treatment or special binder removal in a thermal decomposition oven, are then sintered.
Pressing Molding:
Definition: Pressing molding refers to the process where powdered material is shaped into a specific form (pressed blank) by unidirectional pressing in a steel mold.
Rolling Molding:
Definition: Rolling molding is when metal powder continuously fed by a feeding device into the gap between two rolling cylinders moving in opposite directions on the same plane, gets compacted into a continuous billet under the pressure of the cylinders.
Process: Feeding, rolling molding, sintering.
Features: Suitable for producing strips or sheets with relatively simple cross-section shapes, belonging to a continuous molding process. Capable of producing strips and sheets with precise composition. The process is simple, low-cost, energy-saving, with high yield and low equipment investment.
Extrusion Molding:
Definition: Extrusion molding is a type of plastic forming method, where a plastic powder or billet is placed in an extruder, and under the effect of external force, it is extruded through a die mouth into a billet of a specific shape. In this molding method, the die mouth serves as the molding mold, and by changing the die mouth, billets of different shapes can be extruded.
Process: Mixing of powder material and plasticizer, top pressure, extrusion, extruded billet.
Features: Suitable for tubular and consistent cross-section products, commonly used in the manufacture of rods, tubes, and plate products. Capable of extruding complex-shaped products.
Slip casting:
Definition: The prepared slurry is poured into a porous mold. Due to the water absorption (solution) of the porous mold, the slurry forms a uniform blank layer close to the mold wall, which thickens over time. When the required thickness is reached, the excess slurry is poured out. Finally, the blank layer continues to dewater and shrink, separating from the mold. The product, known as the green body, is then removed from the mold. (PPT)
Ceramic or metal powder is dispersed in a liquid medium to form a suspension with good fluidity. This suspension is poured into a mold cavity of a certain shape. The suspension solidifies through the mold’s water absorption action, producing a green body with a specific shape. (Textbook) Currently, all forming methods based on the fluidity of the blank are classified as slip casting.
Process:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Injection Molding:
Definition: After mixing powder and binder to create a feed suitable for injection molding, the feed is heated to enhance its flowability. Under certain pressure, the feed is injected into the mold cavity of the injection molding machine to form a blank. The cooled and solidified molded body is then debinded at a certain temperature, removing the binder in the blank and then sintered to obtain the product.
Process:

Features:
High adaptability, short cycles, high productivity, and easy automation control. Parts have a high degree of freedom in their geometric shapes, uniform density across all sections, and high dimensional precision. Suitable for manufacturing small parts (0.2g-200g) with complex geometries, precision, and special requirements. Product quality is stable and reliable, with a relative density of 95-98% achievable. Carburizing, quenching, and tempering treatments can be applied.
1. The influence of powder properties
Regardless of the type of powder, an increase in hardness always causes significant wear on the mold. For metal powders, purity also has a significant impact on the pressing process. The purer the powder, the easier it is to press, because the impurities in metal powders often exist on the surface of powder particles in an oxidized state, and metal oxides are ceramics, which are hard and have poor plasticity. The fluidity and bulk density of the powder have a significant impact on pressing performance. Good fluidity and high bulk density are beneficial for increasing the density of the compact. The fluidity of the powder is related to its particle size and shape. The finer the powder, the worse the fluidity, and the easier it is to form a bridging effect; spherical powder particles have good fluidity, they easily slide against each other during accumulation, and are not prone to bridging. The particle size ratio of the powder has a significant impact on its filling density in the mold. An appropriate particle size ratio is beneficial for increasing the density of the compact.
2. Influence of Process Parameters:
1. Effect of Pressing Speed: Impact forming is significantly more efficient than static pressing. For a compact achieving the same density, the strength of a dynamically pressed compact is noticeably higher than that of a statically pressed one. During the pressing process, an appropriate reduction in pressing speed facilitates gas expulsion from the compact, which is beneficial for enhancing its density.
2. Holding Time and Depressurization Speed: When pressing large, tall, and complex compacts, moderately extending the holding time aids in pressure transmission, making the density of different parts of the compact more uniform. Additionally, lengthening the holding time allows sufficient time for gas expulsion from the compact. This extension is advantageous for improving the strength of the compact and reducing its resistivity. During depressurization, controlling the depressurization speed can prevent particles that have undergone elastic deformation under pressure from rebounding rapidly, thereby causing layer cracking.
1. Influence of Powder Properties:
1. Impact of powder bulk density: Under specific rolling process conditions, powders with lower bulk density and good formability can produce porous tape with a high porosity and thin thickness. Conversely, powders with higher bulk density and good compactability can produce tape with higher density and greater thickness.
2. Influence of powder flowability: For powders with good flowability, a higher rolling speed should be selected. The thickness and density of the tape blank would be larger, leading to better integrity of the tape blank.
3. Influence of powder compactability and formability: Powders with good formability can mold into a complete tape blank with certain strength under lower rolling pressure. Powders with good compactability can produce tape blanks with better density after molding.
2. Influence of Process Parameters and Conditions:
1. Impact of Roller Diameter: Increasing the roller diameter can yield thicker, relatively higher-density strip billets; using smaller diameter rollers allows for the rolling of thinner porous strips.
2. Impact of Roller Gap: As the roller gap increases, the thickness of the strip billet increases. If the loose packing density remains constant, the density of the strip billet will decrease. When the roller gap increases to a certain size, the powder cannot be rolled into shape.
With the reduction of the roller gap, the thickness of the strip billet decreases, and its density increases accordingly, while the required rolling pressure also increases. When the roller gap is reduced to a certain extent, the degree of uneven deformation of the powder also increases.
When the rolling pressure increases to a limit value, the rolling process cannot proceed normally. For any specific metal powder and certain rolling process conditions, the thickness of the rolled strip billet has a maximum and a minimum value, and the roller gap also has a corresponding range. Beyond this range, the normal rolling process cannot be realized.
3. Impact of Roller Surface Condition: The density and thickness of the strip billet increase as the roughness of the roller surface increases. When the roughness increases to a certain size, the trend of increasing density and thickness of the strip billet slows down.
Powder sticking to the roll can cause an increase in the density and thickness of the strip billet along the length direction.
As the rolling process proceeds, the amount of powder sticking to the roller surface will gradually decrease, and the increase in the density and thickness of the strip billet will slow down and eventually stabilize.
4. Impact of Rolling Speed: Within the normal rolling speed range, increasing the rolling speed will cause the density and thickness of the strip billet to decrease. The higher the rolling speed, the more significant the decrease in thickness and density, and the worse the uniformity.
5. Impact of Feed Thickness: The greater the feed thickness, the greater the thickness and density of the strip billet. However, when the feed angle increases to a certain value, further increases in the feed angle will no longer increase the thickness and density.
6. Impact of strip blank width: As the width of the strip blank increases, the thickness of the resulting strip blank also increases, while its density decreases.
7. Impact of rolling atmosphere: The atmosphere during rolling, the viscosity, and pressure of the gas phase can severely affect the performance of the powder-rolled strip blank. Increasing the rolling speed can amplify the effects of reverse airflow, hence, the density and thickness of the strip blank decrease as the rolling speed increases, and the uniformity of the strip blank’s performance also deteriorates. When the reverse speed increases to a certain extent, it may even prevent the production of continuous strip blanks.
Because changes in the rolling atmosphere and gas phase viscosity and pressure inevitably cause changes in the size of the reverse airflow, they have a significant impact on the performance of the strip blank.
Generally speaking, the larger the gas phase viscosity, the slower the flow speed of the powder into the bite deformation zone and the smaller the flow rate per unit time, the thinner the resulting strip blank.
Not only that, the density of the strip blank also decreases with the increase in gas phase viscosity. Experimental results show that during powder rolling in a vacuum, the amount of residual gas is very small, which greatly weakens the reverse airflow. Compared with rolling in air and other gases, strip blanks with higher density and greater thickness can be obtained.
I. Impact of Powder Properties:
Extrusion molding requires fine-grained powders, ideally spherical in shape. Plate-like particles, under the action of extrusion force, will orientate and align in a certain direction, creating anisotropy in the molded blank, which is detrimental to the performance of the product. When preparing powders for ceramic extrusion molding, those that have been ball milled for a long time yield the best quality.
II. Influence of Process Parameters:
1. Geometric Dimensions of the Extrusion Die:
The extrusion die determines the compression ratio and the shape and size of the product during the extrusion process. The compression ratio is the relative ratio of the cross-sectional area under pressure before the blank passes through the extrusion die to the cross-sectional area after passing through the die. A larger compression ratio requires a larger extrusion force.
The force exerted on the extrusion die is also closely related to the cone angle; the larger the cone angle, the greater the extrusion resistance and the greater the required extrusion force. The length of the sizing section is another important geometric dimension of the extrusion die.
A longer sizing section increases the additional internal stress, making the blank prone to longitudinal cracks; while a short sizing section leads to elastic expansion of the extruded blank, which can result in transverse cracks.
2. Pre-Treatment of the Blank:
In the extrusion molding of hard alloy and stainless steel powder porous materials, the metal powder and plasticizer are often mixed evenly before pre-pressing. The purpose of pre-pressing is to increase the contact area between the plasticizer and the powder particles, and to eliminate the gas entrapped in the powder, thus making the density of the blank more uniform, thereby improving the green density of the molded blank.
Before the extrusion molding of ceramic plastic materials, they must go through the aging and vacuum kneading processes. Aging allows for a more uniform distribution of moisture in the blank and improves the plasticity of the blank through the fermentation or decay of organic matter.
Vacuum kneading makes the distribution of plasticizers, organic matter, and moisture in the blank more uniform, and eliminates air in the blank, which benefits the green density of the molded blank, the uniformity of the components, and the performance of the product.
3. Extrusion Speed and Temperature:
If the extrusion speed is too fast, the flowability of the billet in the central part of the extrusion barrel is much ahead of that near the barrel wall, which can generate considerable shear stress, leading to the cracking of the billet.
The plasticizing effect of ceramic billets is not significantly related to temperature, so it’s generally extruded at room temperature. The most commonly used plasticizer for metal billets is paraffin, which exhibits optimal plasticity between 35-45°C.
Therefore, the temperature can’t be too low when extruding metal billets. However, excessively high temperatures may cause a sharp decrease in the strength and adhesion of paraffin, which is also unfavorable for molding.
Slurry Molding:
1. Powder Properties:
Reducing the particle size of the powder is beneficial for improving the suspension performance of particles and the stability of the slurry.
However, for ultrafine powder, although the suspension performance of particles is good, the large specific surface area of the powder results in higher viscosity and poorer fluidity under the same concentration conditions.
Ultrafine powder is prone to agglomeration, affecting the denseness of the billet. Therefore, special measures are needed to improve the billet performance. Besides the size of particles, their shape is also a key factor affecting slurry stability. Spherical particles are well dispersed in the medium, and the slurry has good fluidity.
During the slurry molding process, when a solidified billet layer forms, the layer created by spherical particles has good permeability, which is conducive to the absorption of water molecules in the slurry by the plaster mold.
Plate-like particles can attract each other through forces such as static electricity, forming a card-like structure, which results in thixotropy, affecting the stability and fluidity of the slurry.
Furthermore, the directional arrangement of plate-like particles in the billet layer results in poorer water filtration performance of the billet.
2. Solid Phase Content:
An increase in the solid phase content of the slurry will increase its viscosity.
On the other hand, a decrease in solid phase content will increase the water absorption of the plaster mold, not only reducing production efficiency but also reducing the density of the green billet, which may lead to deformation of the billet after drying.
Therefore, while meeting the requirements of slurry molding process performance, the slurry should maximize the solid phase content to achieve low viscosity and high solid phase content.
3. Effect of Gas:
When making the slurry for slurry molding, gas is often adsorbed on the surface of powder raw material particles, causing the slurry to contain bubbles. When such slurry is used for slurry molding, it can lead to the presence of pores in the molded body, affecting product quality. Therefore, it’s necessary to degas the slurry.