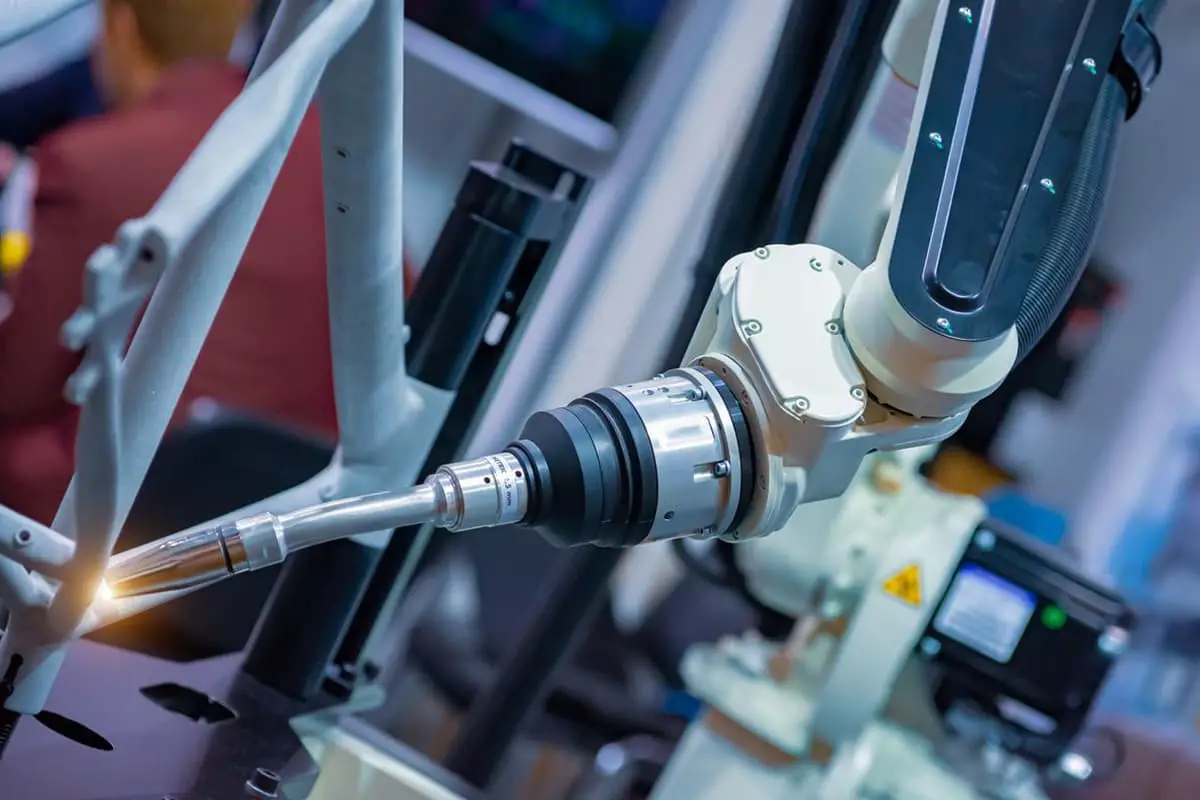
Imagine welding with precision, speed, and minimal heat distortion—welcome to the world of laser wire filling welding. This advanced technique surpasses traditional methods, offering solutions to challenges like weld cracking and thick material fusion. By incorporating additional welding wire, it ensures robust joints and improved weld quality. In this article, you’ll uncover the fundamental principles, benefits, and diverse applications of laser wire filling welding, setting the stage for innovations in industries from automotive to aerospace. Get ready to enhance your understanding and explore the future of welding technology.
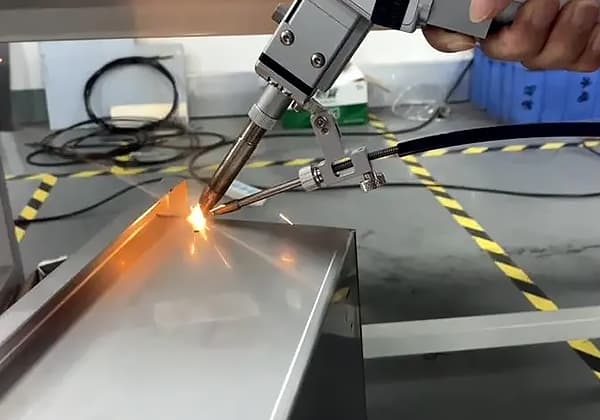

Compared to traditional welding methods, laser welding has significant advantages, including low heat input, fast welding speed, small heat affected zone, and minimal thermal distortion.
In recent years, laser welding has been widely used in high-tech industries such as automotive, shipbuilding, nuclear power, and aerospace, and with the decreasing cost of complete set equipment, its application in daily hardware products and other related fields is rapidly increasing.
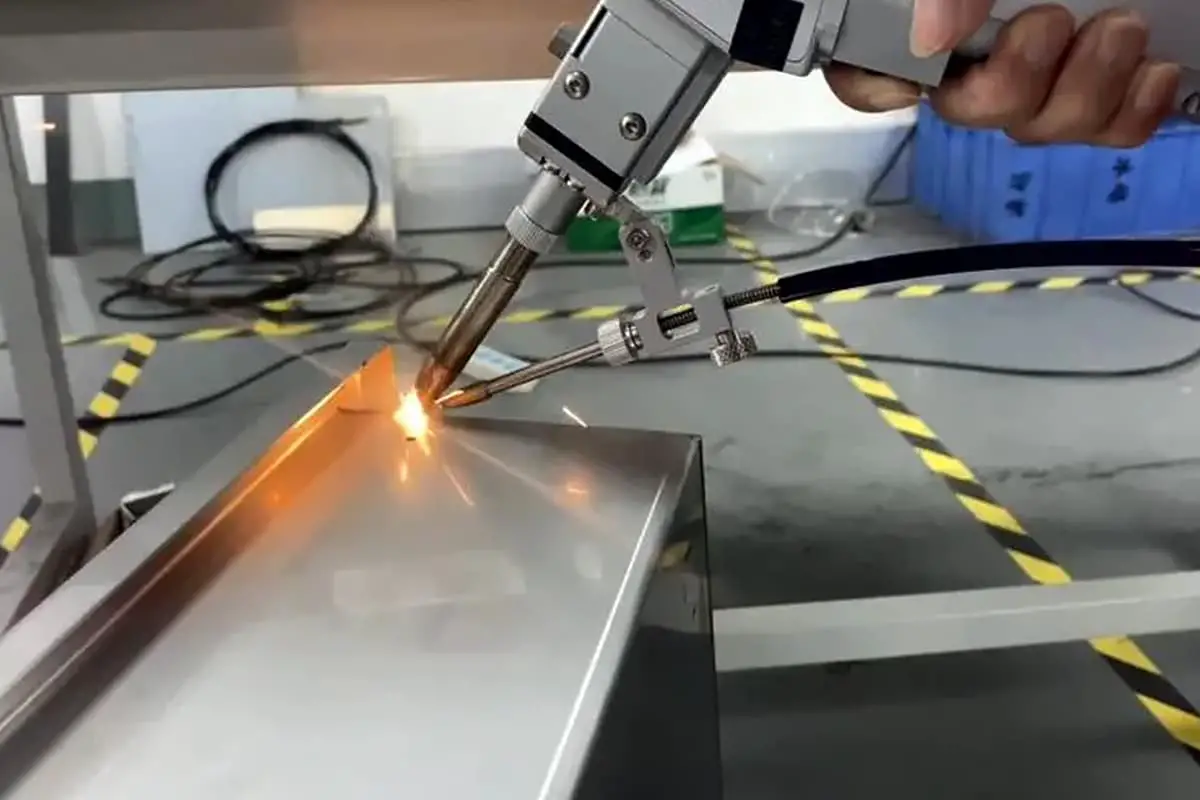

However, single laser welding also has some shortcomings and cannot fully meet the increasingly diverse demands.
Firstly, strict assembly clearance is required for single laser welding of the weld joint, usually less than 0.2mm, otherwise good connection may be difficult to achieve.
Secondly, single laser welding is prone to cause weld cracking when welding materials with high sensitivity to weld cracks, and cannot adjust the composition of the weld to control the generation of cracks.
Thirdly, when welding thick plates using single laser welding, an ultra-high power laser is required, and its melting ability completely depends on the upper limit of laser power, which cannot fully guarantee the quality of the weld.
In order to meet the demands of development in various industries, the methods of laser welding have also been improved and developed, such as the laser wire filling welding method that this article discusses.
Laser wire filling welding is developed based on single laser welding and has obvious advantages over it:
① It significantly reduces the assembly requirements of the workpiece, because the addition of welding wire in the welding process will greatly increase the molten metal of the weld pool, bridge larger gaps between the welds, and make the weld more full.
② The organization and performance of the weld area can be controlled. The composition of the welding wire is different from that of the base material of the weld joint. After the welding wire is melted into the weld pool, the quality, composition, and ratio of the weld pool can be adjusted to control the solidification process and the formation of microstructures.
③ The input of line energy is small, and the heat affected zone and thermal deformation are small, which is very beneficial for welding workpieces with strict requirements for deformation.
④ It can achieve welding of thick materials with small laser power. By adding welding wire in the welding process, it can realize multi-pass welding, and the molten metal of the weld pool will increase significantly. This can be used to handle the opening and breaking of the weld joint, thereby reducing the actual laser welding thickness of the weldment, and achieving multi-pass laser wire filling welding of thick plate materials.

Laser wire filling welding is shown in Figure 1, which is different from laser brazing with wire feeding shown in Figure 2.
The basic elements of the two welding methods are the same, consisting of a laser beam, welding wire, and workpiece to be welded.
The addition of protective gas depends on the actual needs.
The main equipment involved includes wire feeder, welding machine, filler wire feeding torch, welding head, and high-power laser.

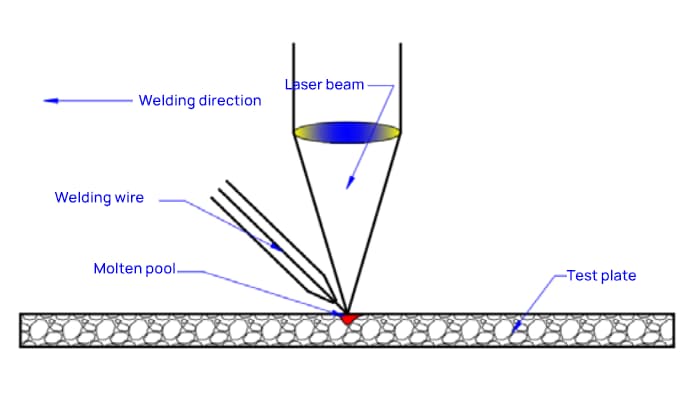
Although the two welding methods have almost no difference in external form, they have significant differences in essence. For laser wire filling welding, high-power fiber laser is generally used.
Not only does the laser need to melt the welding wire, but it also needs to melt the base material and form a small hole effect unique to laser deep penetration welding on the base material, forming a deeper weld pool.
The composition and ratio of elements in the mixing pool formed by the full mixing of the welding wire components and the base metal are significantly different from those of the welding wire and the base metal.
Therefore, suitable welding wire can be chosen according to the performance defects of the base material itself and added to the welding process in order to achieve aimed improvement on the microcosmic level of welding seam’s crack resistance, fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
In addition, laser wire filling welding can be piled up with multiple passes welding because the deep penetration welding with small hole effect can be achieved, which enables sufficient fusion of the upper and lower two welding passes and can avoid serious defects of incomplete fusion, thus having the ability to weld thick joints.
For laser brazing with wire feeding, high-power semiconductor laser is generally used. Almost all of the laser energy acts on the welding wire, and only a very small amount of laser melts a small amount of metal on the surface of the welded joint. The weld pool is almost formed by the melted welding wire.
Therefore, the performance of the weld mainly depends on the element composition and ratio of the welding wire, as well as the spreading and combination of the melted welding wire at the weld joint. The main purpose of laser brazing with wire feeding is to achieve a certain connection strength and sealing performance of the weld joint.
Moreover, laser brazing with wire feeding cannot be piled up with multiple passes, and its upper and lower two welding passes cannot achieve sufficient and effective fusion. The mechanical performance of the joint is very poor.

With the development of laser wire filling welding technology and the improvement of the upper limit of laser power, the application range of laser wire filling welding is becoming wider and wider, mainly in the following aspects:
Generally, because aluminum alloy has a high reflectivity and high thermal conductivity to laser, the laser power required for laser welding aluminum alloy is relatively high, which can cause serious evaporation and burning of low boiling point elements (such as Mg, Zn, etc.) in aluminum alloy, as well as low surface tension of the weld pool, affecting the solidification characteristics of the weld.
These reasons can lead to many problems in laser welding aluminum alloy, such as poor mechanical properties of the weld joint, poor weld formation, and serious pores and cracks.
However, laser wire filling welding of aluminum alloy can significantly improve these problems:
① Laser wire filling welding can improve the depression on the surface of the weld and effectively improve the weld formation, and the welding process has a small amount of spatter.
② The addition of welding wire can not only affect the crystal orientation of columnar crystals in the weld, weaken the crystal interfacial generated by the relative growth of columnar crystals at the center of the weld, improve the weld formation but also increase the material’s absorption rate of laser, increase the melting width, and slightly reduce the microhardness.
Furthermore, under optimized process parameters, the tensile strength and elongation of the joint can be significantly improved.
③ Proper welding process parameters can obtain weld joint without significant internal defects, the microhardness of more than HV60, and no significant softening in the HAZ area of the weld joint. The fracture in the tensile test occurs in the parent material area.
In some harsh working environments or for cost reasons, it is often necessary for a workpiece to simultaneously possess multiple special properties, such as corrosion resistance, high specific strength, heat resistance, wear resistance, high conductivity, good heat dissipation, etc.
However, most metal materials cannot possess multiple prominent special properties at the same time.
Moreover, metals with special properties are often scarce and expensive, and cannot be used in large quantities.
Therefore, if multiple materials with special properties can be effectively connected, it may meet the usage demands.
The physical and chemical properties of dissimilar metal materials generally differ significantly, and inevitable intermetallic compounds will be formed during the welding process.
The influence of intermetallic compounds on the weld joint performance is significant, and brittle intermetallic compounds can easily cause weld cracking.
Therefore, direct single-laser welding of dissimilar metal joints is very difficult, and its process stability is difficult to control, and process reproducibility is difficult.
Many scholars and experts have found that using laser wire filling welding for welding dissimilar metals is relatively effective.
Properly selected filler wire can have a certain inhibitory effect on the formation of intermetallic compounds, which can greatly improve the mechanical properties of the welding joint:
① Laser wire filling welding of Mg/Cu lap joint can obtain a good-shaped dissimilar metal joint with certain strength under appropriate process parameters, and its maximum shear strength can reach 164.2 MPa, which is 64% of the strength of the magnesium alloy base material.
② Research on the welding of Al/Ti lap joint and butt joint shows that using a rectangular beam, the welding process is stable, the formation is beautiful, the process parameter range is wide, the weld quality is high, and its maximum tensile strength reaches 94% of the strength of the aluminum alloy base material.
For workpieces with load-bearing purposes, if the weld joint collapses, it will reduce its effective thickness and lower its mechanical properties.
If the weld joint has a biting edge, it will cause stress concentration at the edge of the weld joint, which will also reduce the mechanical properties.
For workpieces with appearance requirements, the collapse or biting edge of the weld joint will produce serious visual effects, which is unacceptable. In order to make the weld joint full and smooth, laser wire filling welding is a very good method.
The addition of welding wire to the weld pool can effectively increase the volume of the weld pool, thereby ensuring a full and smooth weld joint without biting edges.
For workpieces with large joint gaps (usually ≥0.3mm), single laser welding is difficult to achieve effective connection, and the joint gaps can only be filled by filling additional materials.
Therefore, laser wire filling welding is a very effective solution.
Narrow gap laser wire filling welding can be used to achieve effective welding of medium-thick plates using medium and small power laser welders.
By adding welding wire, the composition and microstructure of the weld metal can be changed, which can improve the comprehensive performance of the welding joint.
At the same time, it can also improve the adaptability and fault tolerance of single laser welding to the groove gap, and the heat-affected zone of the weld is narrow with lower post-welding joint stresses.
Therefore, it has great engineering application value, and many experts and scholars have conducted relevant research in recent years:
① Narrow gap laser wire feeding multi-pass welding method was used to weld 40mm thick Q345D ship steel plate, and the results showed that appropriate welding process parameters could obtain a well-formed welding joint without defects such as porosity and lack of fusion.
The impact toughness at the center of the weld joint was good, and the tensile strength of the weld was higher than that of the base material.
② Narrow gap laser wire feeding multi-pass welding method was used to weld 50mm thick rotor steel, and the results showed that appropriate welding process parameters could obtain a well-formed welding joint without defects such as lack of fusion on the sidewall.
The impact toughness of the joint was slightly reduced, but its tensile strength was higher than that of the base material.
③ A study of narrow gap laser wire filling welding of 20mm thick 5083 aluminum alloy showed that with appropriate welding process parameters, welding joints with fewer defects such as porosity and lack of fusion could be obtained.

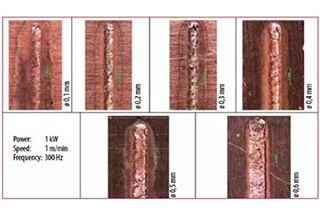
Improvement of Weld Seam Forming
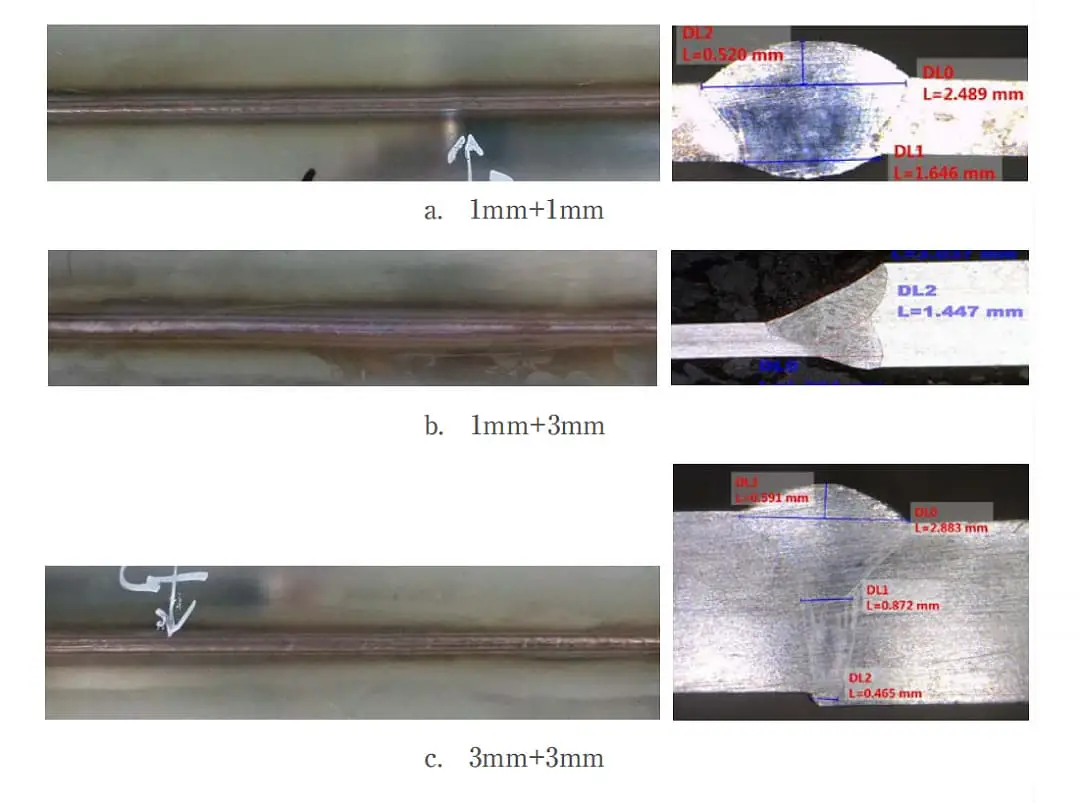
Requirements: Welding of 1mm and 3mm stainless steel with no pores in the weld seam and good forming.
Equipment: 4000W laser (fiber core diameter 200μm), wire feeder, welding head.
Process Parameters: As shown in Table 1.
Table 1
| Thickness of Joint (mm) | Laser Power (W) | Welding Speed (mm/s) | Wire Feeding Speed (m/min) | Defocus Amount (mm) |
| 1mm+1mm | 2500 | 35 | 1.2 | +5 |
| 3mm+3mm | 1000 | 25 | 1.0 | +5 |
| 1mm+3mm | 3100 | 35 | 1.5 | +5 |
Results: Good forming with no pores in the weld seam, as shown in Figure 3.
Narrow Gap Laser Filling Multi-pass Welding
Requirements: Welding of 18mm thick Q345 shipbuilding steel plate with few pores in the weld seam, no lack of fusion, joint tensile strength higher than base metal, and good forming of the weld seam.
Equipment: 6000W laser (fiber core diameter 400μm), wire feeder, welding head.
Process Parameters: Welding groove must be opened, and the groove dimensions are shown in Figure 4. Other welding process parameters are shown in Table 2.

Table 2
| Welding Sequence | Laser Power (W) | Welding Speed (mm/s) | Wire Feeding Speed (m/min) | Defocus Amount (mm) |
| 1 | 6000 | 20 | 4 | +4 |
| 2 | 5000 | 20 | 6 | +10 |
| 3 | 5000 | 20 | 6 | +10 |
| 4 | 5000 | 15 | 6 | +10 |
| 5 | 6000 | 15 | 6 | +10 |
Results: Good forming with no lack of fusion and minimal pores in the weld seam, as shown in Figure 5.
Moreover, after conducting a tensile test, the weld seam fractured in the base metal, indicating that the joint’s tensile strength was higher than that of the base metal.

Improvement of Weld Seam Forming and Quality
For laser filler wire welding of commonly used materials for butt joint, in order to improve the weld seam forming, it is generally recommended that the laser power and fiber core diameter, and the configuration of the welding head should ensure a focused spot diameter between 0.4mm to 0.6mm.
Moreover, the appropriate wire grade should be selected, and other welding parameters are shown in Table 3 and Table 4.
Table 3: Carbon Steel and Stainless Steel Materials
| Welding Sequence | Laser Power (W) | Welding Speed (mm/s) | Wire Feeding Speed (m/min) | Defocus Amount (mm) |
| 1mm | 1500~3000 | 25~40 | 1.0~2.0 | +3~+8 |
| 2mm | 2000~3500 | 25~35 | 1.0~2.0 | +3~+8 |
| 3mm | 3500~5000 | 20~35 | 1.5~2.5 | +3~+8 |
| 4mm | 4000~5500 | 20~35 | 2.0~3.0 | +3~+8 |
| 5mm | 5000~6500 | 20~35 | 3.0~4.0 | +3~+8 |
| 6mm | 6500~8000 | 20~35 | 4.0~5.0 | +3~+8 |
| >6mm | It is not recommended to use single-pass laser filler wire welding because the power requirement is too high and the deformation is significant. | |||
Table 4: Aluminum Alloy Materials
| Thickness of Joint (mm) | Laser Power (W) | Welding Speed (mm/s) | Wire Feeding Speed (m/min) | Defocus Amount (mm) |
| 1mm | 2000~3000 | 30~50 | 2.0~3.0 | 0~+3 |
| 2mm | 2000~4000 | 25~45 | 2.0~3.5 | 0~+3 |
| 3mm | 3000~5000 | 20~40 | 2.5~4.0 | 0~+3 |
| 4mm | 4000~6000 | 20~40 | 3.0~4.5 | 0~+3 |
| 5mm | 5000~7000 | 20~40 | 3.5~5.0 | 0~+3 |
| 6mm | 6000~8000 | 20~40 | 4.0~6.0 | 0~+3 |
| >6mm | It is not recommended to use single-pass laser filler wire welding because the power requirement is too high and the deformation is significant. | |||
Narrow Gap Laser Filling Multi-pass Welding
For the thick plate in the narrow gap laser filling multi-pass welding, it is generally recommended that the focused spot diameter should be between 0.6mm to 1.0mm, and the appropriate wire grade should be selected.
In addition, the groove dimensions of the joint must be designed reasonably, and the groove size cannot be too large, otherwise it will easily lead to lack of fusion inside the weld seam. The recommended groove dimensions are shown in Table 5.
The number of welding passes should be determined based on the maximum thickness of the joint. The first pass should be welded using the maximum welding capacity of the equipment, and each subsequent pass should have a depth of generally 3mm to 5mm.
As for the welding process parameters used for each welding pass, they should be determined based on the required welding depth and the current width of the welding pass.
The defocus amount should be moderately increased as the welding pass width increases to prevent lack of fusion in the sidewalls.
Table 5: Recommended Groove Shape and Dimensions
| Material Thickness (mm) | Groove Shape | Blunt Edge Height (mm) | Groove Bottom Width (mm) | Double-sided Groove Angle (°) |
| 10 | U | 4~6 | 2~3 | 5°~10° |
| 14 | U | 4~8 | 2~2.5 | 9°~5° |
| 18 | U | 4~10 | 1.5~2 | 8°~9° |
| 20 | U | 4~10 | 1.5~2 | 5°~7° |